- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 20th JANUARY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 20th JANUARY 2025

Chincholi Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
- The Forest Department has initiated efforts to persuade residents of Sheribikanahalli Tanda, a hamlet situated within the Chincholi Wildlife Sanctuary on the Karnataka-Telangana border, to relocate.
- The relocation aims to reduce human impact on the sanctuary and protect its biodiversity while ensuring the safety and welfare of the inhabitants.
- Authorities are engaging with the residents, highlighting the benefits of relocation, which include better living conditions and access to essential amenities outside the protected forest area.
About Chincholi Wildlife Sanctuary:
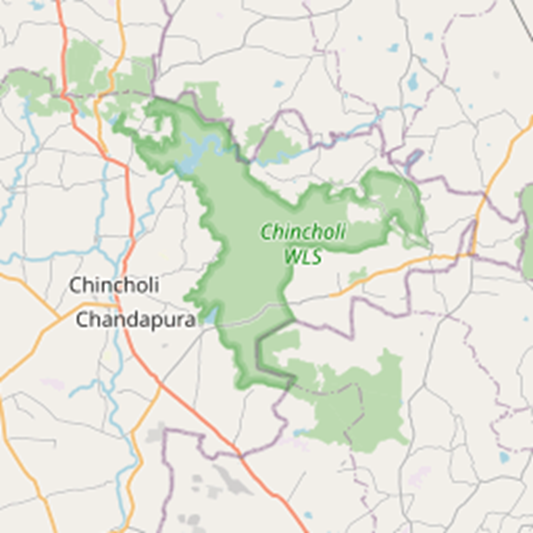
- Chincholi Wildlife Sanctuary, located in the Kalaburagi district of Karnataka, India, covers an area of approximately 134.88 square kilometres.
- As the first dryland wildlife sanctuary in South India, it is characterised by dry deciduous forests with significant plantations of Acacia and teak.
- The sanctuary boasts a rich diversity of flora, including valuable species such as sandalwood and red sanders, as well as various medicinal herbs and trees. This diverse vegetation supports a wide array of fauna.
- Notably, Chincholi Wildlife Sanctuary is home to all four Canidae species found in Karnataka: dholes, wolves, golden jackals, and Bengal foxes. Other significant wildlife includes the blackbuck, striped hyena, and various species of fruit bats.
- Avian diversity is also prominent, with over 35 species of birds recorded in the sanctuary. Some of the notable species include the blue pigeon, black-winged kite, blossom-headed parakeet, and black drongo. This rich birdlife adds to the ecological significance of the area.
- The ecological importance of Chincholi Wildlife Sanctuary lies in its unique dryland ecosystem, which is relatively rare in the region.
- By preserving this habitat, the sanctuary plays a crucial role in maintaining the biodiversity of the Hyderabad-Karnataka region.
- The presence of diverse flora and fauna, including several species of conservation concern, underscores the need for ongoing protection and sustainable management of this vital ecological area.
Gulf of Aden
Why in news?
The Defence Minister highlighted potential rising threats in the Gulf of Aden, Red Sea, and waters near East African nations, emphasizing the need for enhanced maritime security.
About Gulf of Aden:
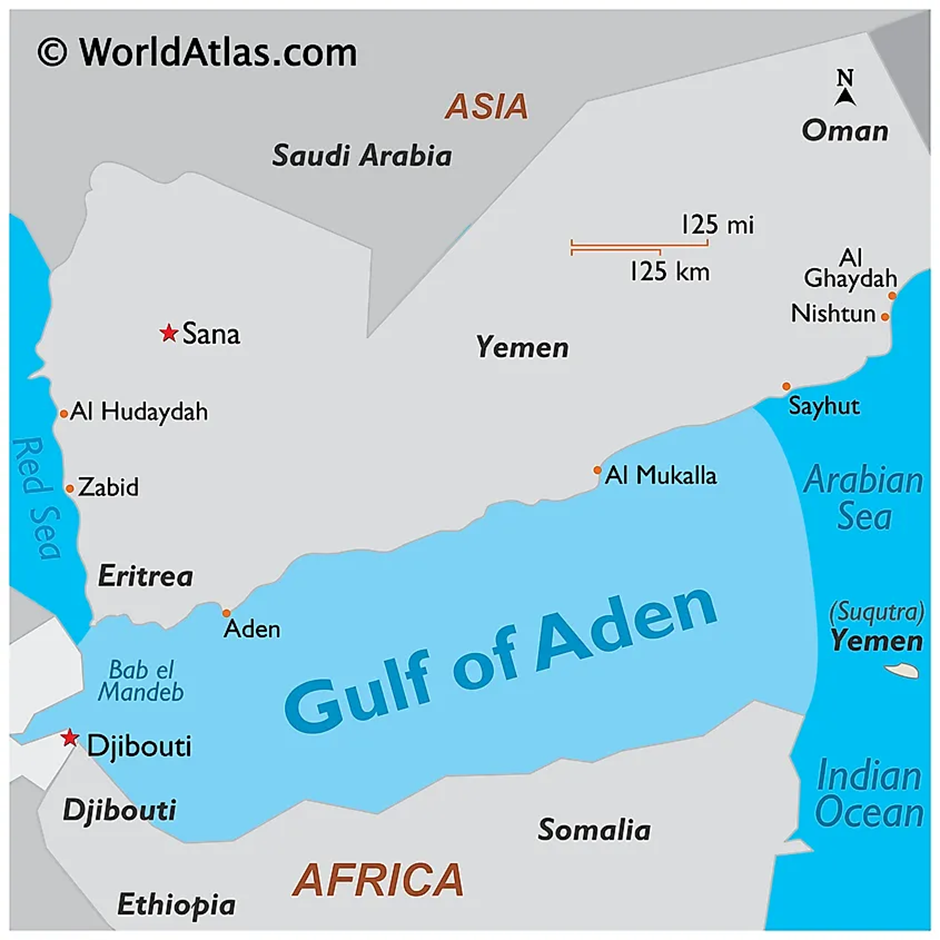
- The Gulf of Aden, located in the Arabian Sea, lies between Yemen to the north and Somalia and Djibouti to the south, connecting to the Red Sea via the Bab el-Mandeb Strait.
- This critical waterway serves as a link between the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea through the Suez Canal, making it one of the most important maritime routes globally.
- Strategic Importance:
- The strategic importance of the Gulf of Aden stems from its role as a conduit for a significant portion of the world’s energy supplies and trade.
- Around 12% of global oil passes through this region, making it a lifeline for energy-hungry nations. The route is also vital for commercial shipping, with goods from Asia reaching Europe and Africa via this path.
- Additionally, its location near the Middle East, a region with complex geopolitical dynamics, enhances its importance for global powers, as it provides access to critical resources and markets.
- The Gulf's strategic value has made it a focal point for international naval operations. Countries like the United States, China, and India maintain a naval presence in the region to secure shipping lanes and assert geopolitical influence. The area also serves as a vital zone for counter-piracy efforts and maritime security collaborations.
- Continued challenges:
- Despite its importance, the Gulf of Aden faces several challenges. Piracy, once rampant in the region, remains a latent threat, with attacks on merchant vessels occasionally reported.
- The instability in Yemen, characterised by civil conflict and a humanitarian crisis, has further complicated the security landscape.
- The proximity to Somalia, a nation with ongoing issues of lawlessness and terrorism, adds another layer of concern. Environmental challenges, including pollution from shipping and the threat of oil spills, also pose risks to marine ecosystems.
- In response to these challenges, coordinated international efforts have intensified. Naval task forces such as Combined Task Force 151 and independent deployments by nations aim to ensure the safety of maritime traffic. However, lasting stability requires addressing root causes, including regional conflicts and socio-economic issues. The Gulf of Aden remains a vital, yet contested, maritime corridor that demands sustained global attention.
Musi River
Why in news?
The Musi River Historic Buildings in Hyderabad have been included in the 2025 World Monuments Watch, recognizing their cultural significance. This listing highlights the need for their preservation amid growing urbanization and environmental challenges in the region.
About Musi River:
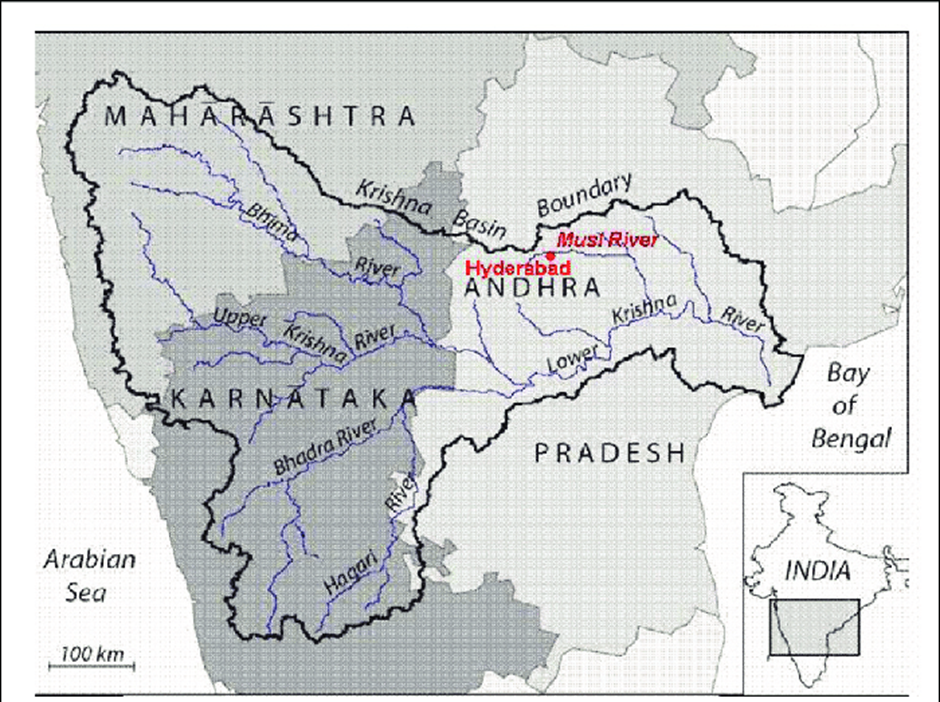
- The Musi River, also known as the Muchukunda River, originates in the Ananthagiri Hills near Vikarabad in the Indian state of Telangana.
- It traverses approximately 240 kilometers eastward, flowing through the city of Hyderabad, before merging with the Krishna River in Nalgonda district.
- The river's primary tributaries include the Esi and Korti streams, which contribute to its flow, especially during the monsoon season.
- Historically, it was the city's lifeline, providing water and supporting livelihoods. The riverbanks are home to several historic structures, such as the High Court, Osmania General Hospital, and the City College, reflecting the architectural heritage of the region.
- The river also played a pivotal role in the city's layout and development during the reign of the Qutb Shahi and Asaf Jahi dynasties. However, rapid urbanization has led to pollution and encroachments, diminishing its prominence in contemporary times.
About World Monuments Watch:
- The World Monuments Watch is a biennial program initiated by the World Monuments Fund (WMF) in 1996.
- It aims to identify and raise awareness about cultural heritage sites worldwide that face threats from factors like neglect, conflict, natural disasters, or urbanization.
- Every two years, the Watch announces a list of 25 sites, selected from nominations by individuals and community-based organizations globally.
- This selection brings international attention to these sites, fostering support for their preservation through advocacy, capacity building, and collaboration with local communities.
- The 2025 Watch, for instance, includes diverse sites spanning multiple countries and, notably, extends to the Moon, highlighting the need for a cooperative framework to protect extra-terrestrial heritage sites.
Gir National Park
Why in news?
- The Gir National Park, home to the endangered Asiatic Lion, faces challenges balancing conservation with developmental demands.
- Plans for a solar energy park near the sanctuary have sparked concerns over habitat disruption and wildlife movement.
- Conservationists fear that such projects could undermine decades of efforts to protect the lion population.
About Gir National Park:
- Gir National Park, also known as Sasan Gir, is situated in Gujarat, approximately 60 kilometres south-southwest of Junagadh.
- Encompassing an area of about 1,295 square kilometres, it represents the largest tract of natural forests in the Saurashtra region.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The park's diverse ecosystem comprises a mix of deciduous forests, grasslands, and scrublands. Dominant tree species include teak, sal (Shorea robusta), and dhak (Butea frondosa), contributing to a rich and varied habitat.
- Gir is globally renowned as the last natural habitat of the Asiatic lion (Panthera leo persica). Beyond lions, the park supports a variety of wildlife, including leopards, deer, antelopes, and numerous bird species, reflecting its ecological significance.
- Community Engagement in Conservation:
- Local communities, notably the Maldharis—a pastoral group residing within the forest—play a pivotal role in conservation efforts.
- Their traditional knowledge and coexistence with wildlife have been integral to preserving the park's biodiversity.
- Collaborative initiatives between the Forest Department and these communities have fostered a sense of ownership and reduced human-wildlife conflicts, contributing to the park's conservation success.
- Balancing Conservation and Development:
- Gir National Park faces the complex challenge of balancing ecological conservation with developmental aspirations.
- Proposals for infrastructure projects, such as roads and railways, pose potential threats to wildlife habitats and corridors.
- Additionally, the establishment of renewable energy projects, like solar parks, near the sanctuary raises concerns about habitat fragmentation and disturbance to wildlife.
- Conservationists emphasise the need for careful planning and environmental impact assessments to ensure that development does not compromise the ecological integrity of the park.
- Engaging local communities in decision-making processes and promoting sustainable development practices are crucial steps toward achieving a harmonious balance between conservation and development objectives.
Morocco
Why in news?
- Morocco, set to co-host the 2030 FIFA World Cup with Spain and Portugal, has announced plans to kill or euthanize up to three million stray dogs to improve its cities' appeal for the event.
- This decision has sparked widespread criticism from animal welfare groups and activists globally.
About Morocco:
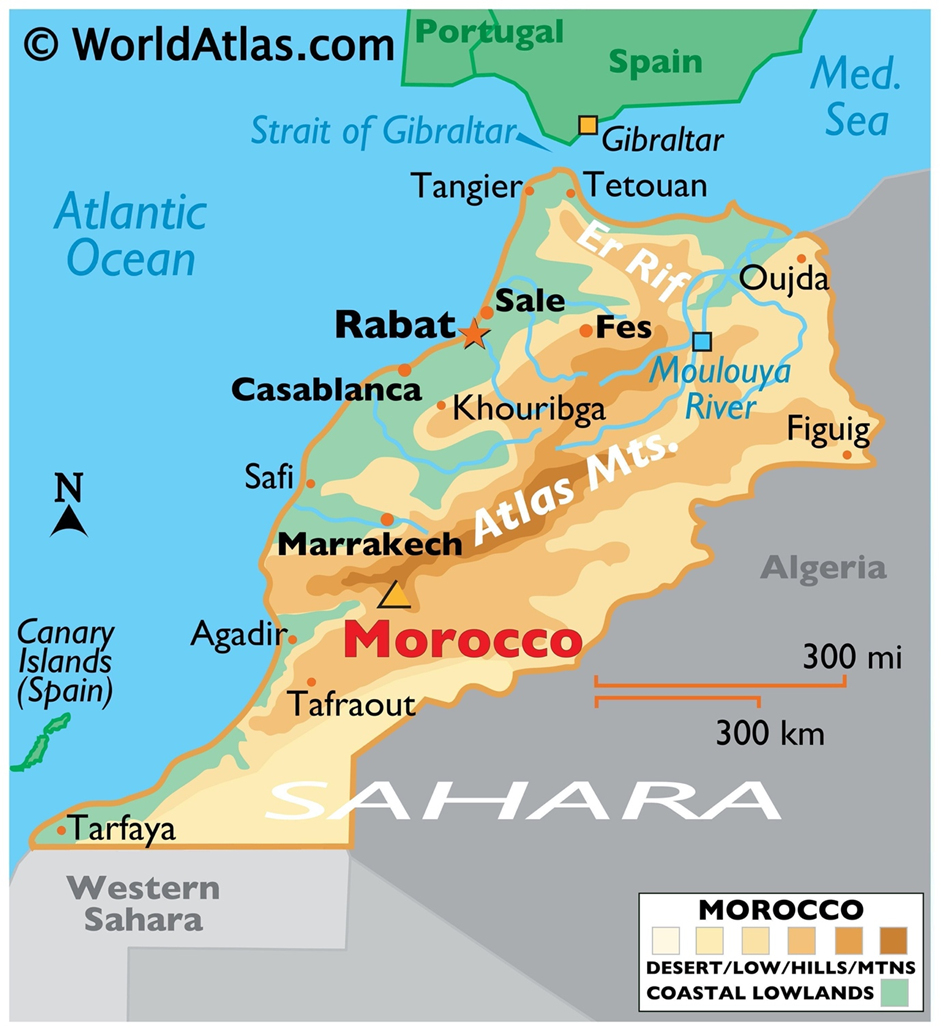
- Location and Geography:
- Morocco, located in North Africa, is bordered by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea to the west and north, Algeria to the east, and Western Sahara to the south.
- Its diverse geography includes coastal plains, mountain ranges like the Atlas and Rif, and the vast Sahara Desert.
- This strategic location places Morocco at the crossroads of Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, influencing its climate and ecosystems.
- Potential natural resources:
- Morocco is richly endowed with natural resources that significantly contribute to its economy. The country holds approximately two-thirds of the world's phosphate reserves, making it a key player in the global fertiliser industry.
- In addition to phosphates, Morocco is rich in various minerals, including iron ore, manganese, lead, zinc, and barite, which are mined for both domestic use and export.
- The nation's extensive Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts also provide abundant marine resources, supporting a robust fishing industry.
- Agriculture thrives in the fertile plains and valleys of Morocco, where crops such as cereals, citrus fruits, and olives are cultivated. These natural resources play a crucial role in sustaining Morocco's economy and positioning it as an important global player in several sectors.
- Stray Dog Issues:
- Morocco faces challenges with a significant stray dog population, estimated at around three million. These animals often live in dire conditions, scavenging for food and suffering from injuries and diseases.
- The overpopulation of stray dogs poses public health risks, including the spread of diseases such as rabies and other infectious illnesses.
- In response, Moroccan authorities have initiated measures to address the issue. Reports indicate that authorities have resorted to inhumane methods, including poisoning with highly toxic substances like strychnine and shooting dogs in public spaces.
- These actions have drawn significant international condemnation from animal rights groups, including Jane Goodall, who have called for immediate intervention and the adoption of more humane population control methods.
|
Q. Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2019)
Answer: Option A |
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |



