- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 1st MAY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 1st MAY 2025

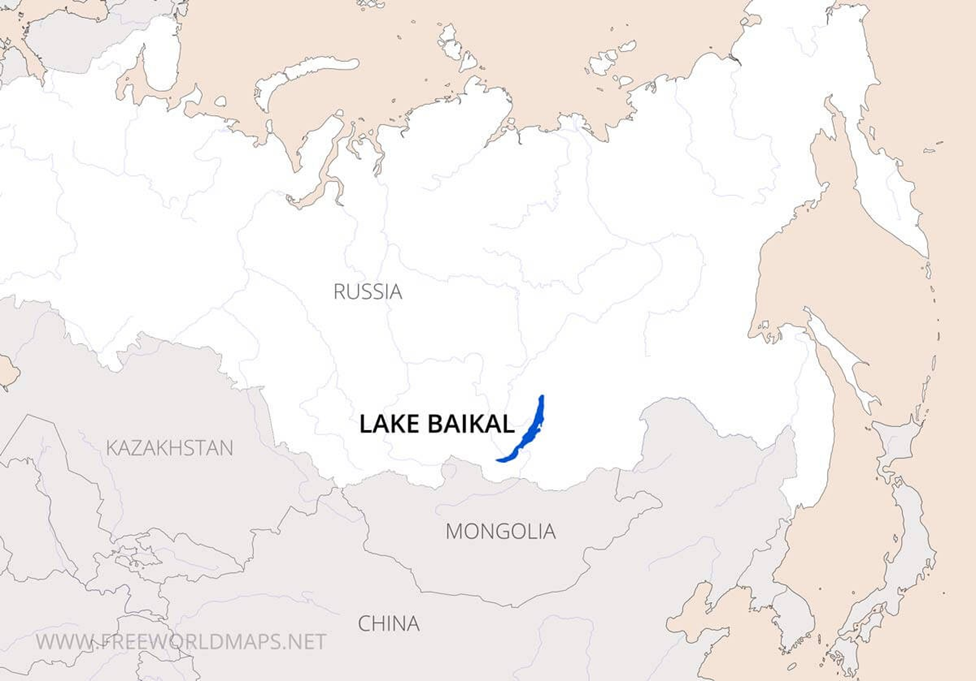
Lake Baikal
Why in news?
a. A robot exploring Lake Baikal discovered mysterious underwater structures or anomalies, sparking scientific curiosity about their origin and significance.
About Lake Baikal:
- Location and Origin:
- Lake Baikal, located in southern Siberia, Russia, is the world’s deepest and
oldest freshwater lake.
-
- It stretches approximately 636 km in length and 79 km in width, covering about
31,722 sq. km.
-
- The lake was formed due to a continental rift system that began developing nearly 25 to 30 million years ago.
-
- This active geological rift continues to widen, contributing to Baikal’s dynamic landscape.
- Ecological Significance:
- Often called the "Galapagos of Russia", Lake Baikal is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and an ecological treasure trove.
- Due to its isolation and ancient origins, the lake harbours over 1,500–1,800 unique animal species, many of which are endemic.
- The most iconic is the Baikal seal (Nerpa), the only freshwater seal species in the world.
- The lake also supports more than 320 bird species and numerous plant species, offering an incredibly diverse ecosystem.
- Its crystal-clear waters, with visibility up to 40 metres, enhance both its pristine beauty and scientific significance.
- Recent discoveries:
- A robotic dive near Lake Baikal’s northwest shore revealed mud volcanoes and deep geological activity, including hundreds of craters.
- These features lie near the Severobaikalsk fault, raising concerns about possible
future seismic activity in the region.
-
- Microbial life—especially extremophiles—was discovered in the mud, thriving under high pressure and low temperatures.
- This breakthrough offers insights into life in extreme environments, aiding
astrobiological studies on moons like Europa or Enceladus.
-
- Lake Baikal remains a natural laboratory, revealing complex ties between
geology, biology, and potential clues about life beyond Earth.
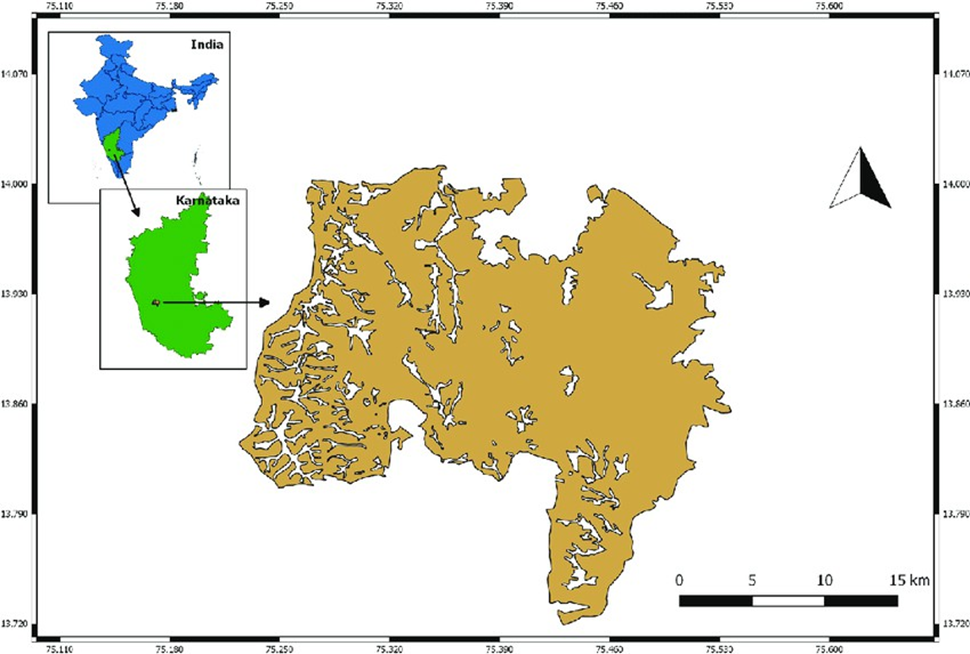
Shettihalli Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
a. Environmentalists urge the minister to redraw Shettihalli Sanctuary boundaries to prevent habitat loss and protect biodiversity from development threats.
About Shettihalli Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Location:
- Shettihalli Wildlife Sanctuary, located in the Shimoga district of Karnataka, India, was declared a wildlife sanctuary on 23 November 1974.
- It spans an area of approximately 395.6 sq. km and is divided into three zones: the core zone, buffer zone, and tourism zone.
- The sanctuary is situated about 30 km from Teerthahalli, with Mangalore International Airport being the nearest airport and Shimoga Railway Station the closest railhead.
- The iconic Jog Falls, one of India’s tallest waterfalls, lies close to the sanctuary, enhancing its geographical significance.
- Flora and Fauna:
- Shettihalli Wildlife Sanctuary is home to a rich variety of flora and fauna, making it a vital ecological hotspot in Karnataka.
- The sanctuary shelters rare species such as the white-backed vulture, Indian nightjar, and white-bellied dingo.
- Larger mammals, including tigers, leopards, elephants, sloth bears, and
langurs, inhabit its dense forest zones.
-
- It also supports a diverse range of reptiles, including the king cobra and python, reflecting its vibrant biodiversity.
-
- This biologically rich landscape not only contributes to wildlife conservation but also plays a crucial role in ecotourism and environmental education in the region.
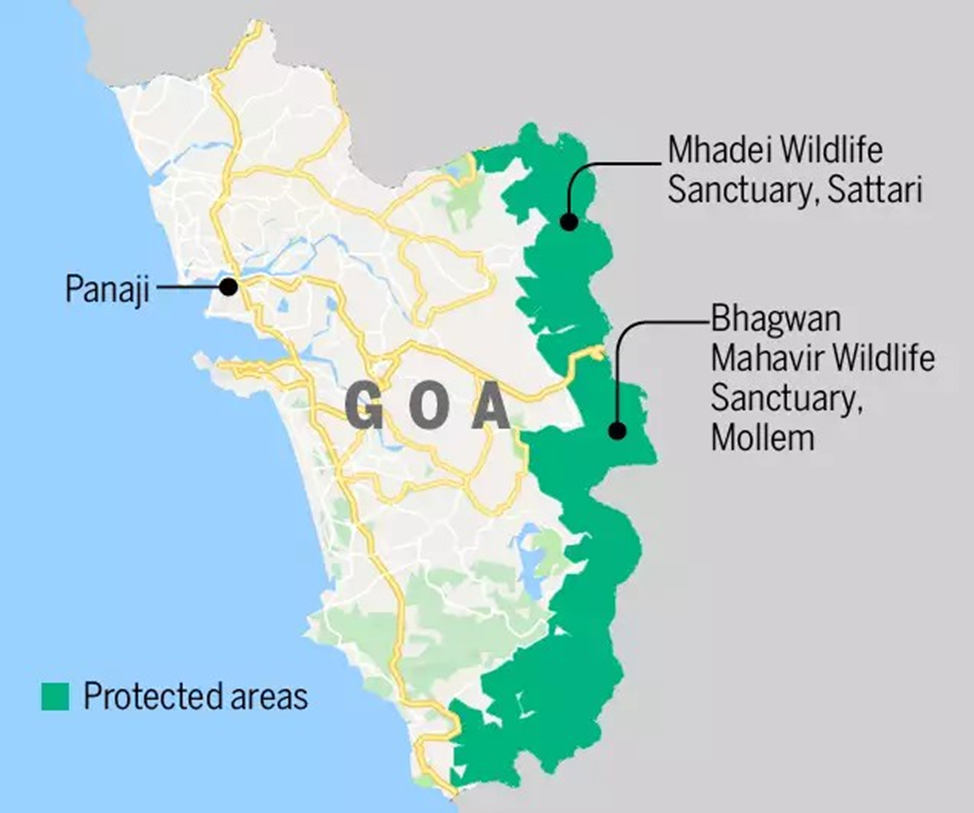
Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
a. Environmentalists oppose eco-tourism in Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary, warning it threatens fragile tiger habitats and disrupts the region’s ecological balance.
About Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Location:
- Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary, located in Sattari taluka of North Goa, spans an area of 208.5 km² within the Western Ghats, a UNESCO-listed Global Biodiversity Hotspot.
- The Mhadei River, also known as the Mandovi, originates in Karnataka and flows through this sanctuary, supporting its lush ecosystems.
- The region is noted for scenic waterfalls like Vazra Sakla and Virdi Falls, making it ecologically and hydrologically vital.
- Goa is the only Indian state to protect its entire stretch of the Western Ghats, with Mhadei forming a critical ecological corridor.
- Ecological Significance:
- Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary is a rich biodiversity reserve, being considered for
Project Tiger status due to the presence of Bengal tigers.
-
- Other mammals include black panthers, gaur, sloth bears, leopards, sambar deer, jungle cats, wild boars, giant squirrels, and bonnet macaques.
- It is recognised as an Important Bird Area (IBA IN177), home to over 255 bird species, including Malabar grey hornbill, Nilgiri wood-pigeon, and crimson-backed sunbird.
- The sanctuary hosts a wide range of reptiles like king cobras, pythons, and all of India’s “Big Four” venomous snakes, along with many endemic amphibians and rare caecilians.
- With 257 butterfly species, including the southern birdwing and blue tiger, Mhadei is a vital haven for invertebrates and a living laboratory for ecological research.
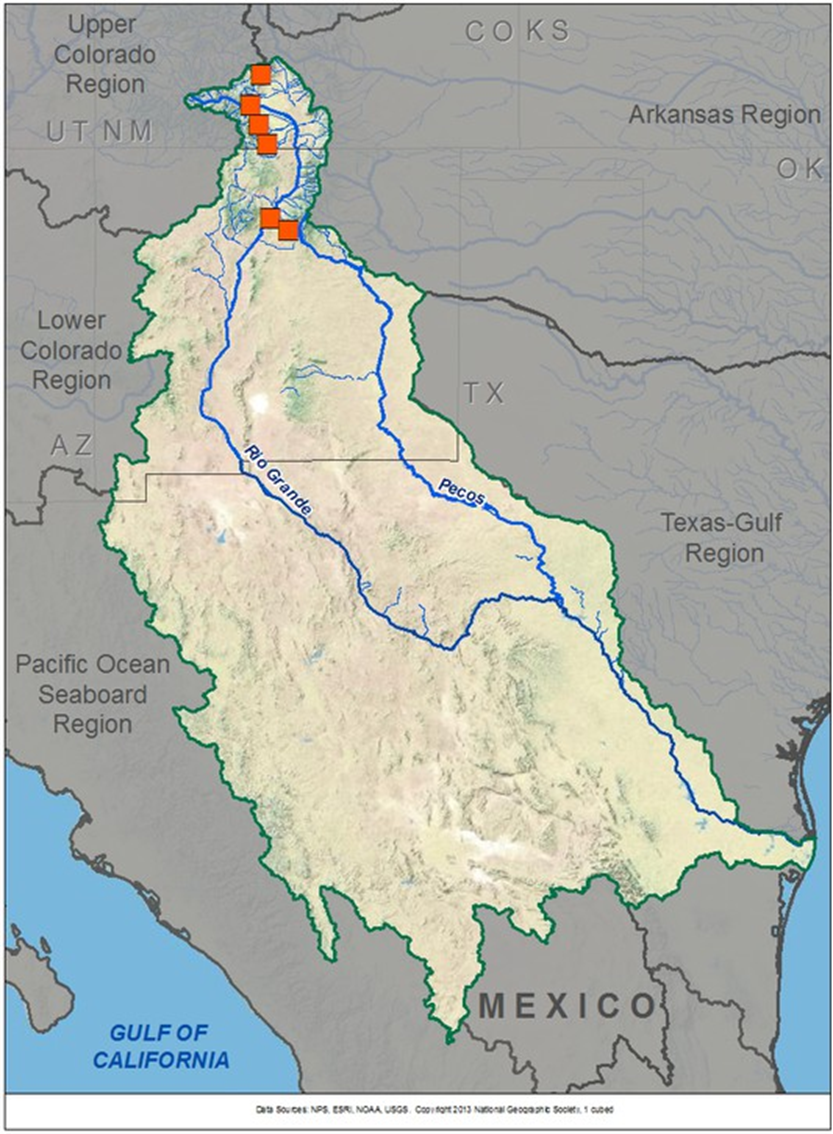
Rio-Grande Basin
Why in news?
a. Mexico and the U.S. signed a water-sharing pact to manage the Rio Grande Basin resources amid growing scarcity and climate-related stress.
About Rio-Grande Basin:
- Location and Course:
- The Rio Grande is the fifth-longest river in North America, stretching approximately 1,900 miles from its origin in the Rocky Mountains of Colorado.
-
- It flows through New Mexico, forms a large part of the Texas–Mexico border, and finally empties into the Gulf of Mexico.
- The Rio Grande basin covers about 336,000 square miles, though only half contributes to the river’s flow due to arid conditions.
- Major reservoirs like Falcon, Amistad, and Elephant Butte play a crucial role in irrigation and hydroelectric power generation.
- Water Agreement and Treaty Context:
- Under the 1944 U.S.–Mexico Water Treaty, Mexico is obligated to deliver 1.75 million acre-feet of Rio Grande water to the U.S. every five years.
- Due to prolonged drought and over-extraction, Mexico had delivered less than 600,000 acre-feet in the current cycle (ending October 2025), prompting U.S. pressure.
- The April 2025 agreement includes an immediate transfer of 56,750 acre-feet from the Falcon and Amistad reservoirs, along with increased U.S. shares from six tributaries to compensate for the deficit.
- Significance:
- This agreement is vital for South Texas farmers, especially amid severe water shortages.
- It averts potential economic losses and eases diplomatic tensions, including
tariff threats from the U.S. administration.
-
- The accord highlights the strategic and economic importance of the Rio Grande for agriculture, energy, and regional stability.
- Environmental Importance:
- The Rio Grande supports over 2.1 million acres of cropland, sustains
biodiversity, and underpins local economies.
-
- However, climate change, reduced flows, and unsustainable usage pose serious risks.
- Bilateral cooperation, like this agreement, is essential for long-term river health and regional resilience.
Iberian Peninsula
Why in news?
a. An unprecedented blackout swept across the Iberian Peninsula, severely impacting Spain and Portugal, disrupting essential services and prompting Spain to declare a national emergency.
About Iberian Peninsula:
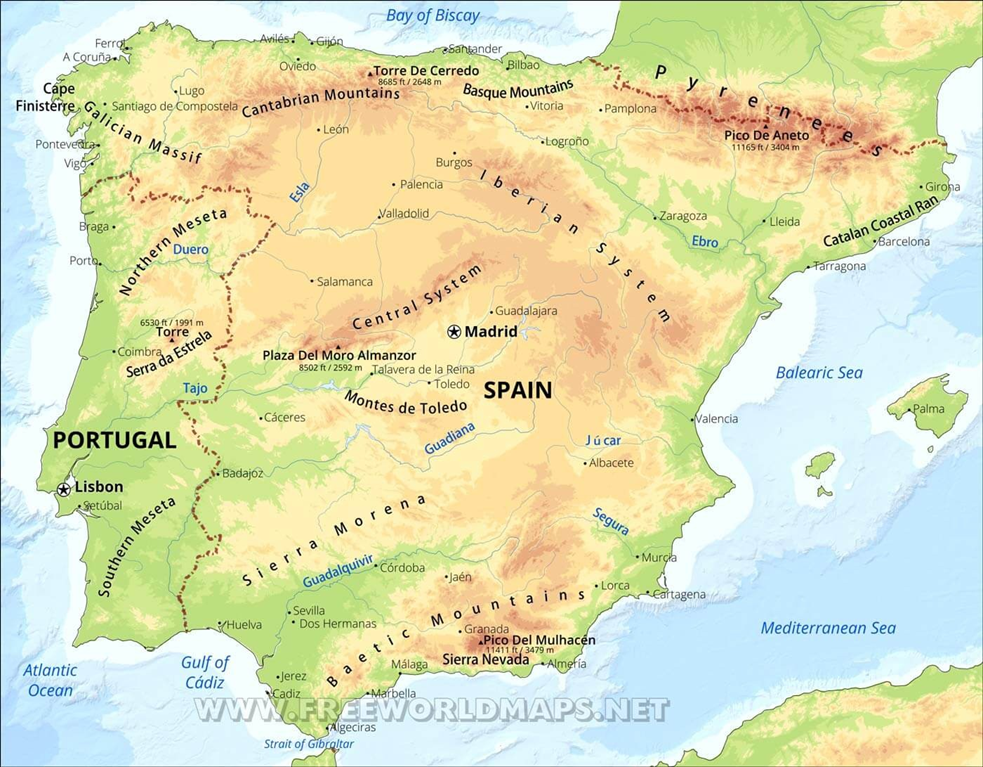
- Location and Geography:
- The Iberian Peninsula is located in southwestern Europe, comprising Spain and
Portugal, along with a small part of France.
-
- It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west and north, and the
Mediterranean Sea to the east.
-
- The Pyrenees mountain range forms the natural border between the peninsula and the rest of Europe.
- The region has a Mediterranean climate, characterised by hot, dry summers and mild winters, which significantly influences the daily lives of its inhabitants.
- Reason Behind the Outage:
- The outage began after a high-voltage connection between Spain and France was interrupted around noon on April 28.
- This disruption led to a cascading effect, causing the entire power grid in the Iberian Peninsula to collapse.
- While the initial interruption was not unusual, the system failure was exacerbated by fluctuations in power demand and possibly a failure in a power plant.
-
- Despite Spain's efforts to transition to renewable energy, this incident highlighted vulnerabilities in the power grid, particularly due to the intermittent nature of renewable sources like wind and solar.
- Experts also pointed out the lack of sufficient grid infrastructure and electricity storage systems.
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |




