- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 17th June 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 17th June 2025
17-06-2025

1. IRAN
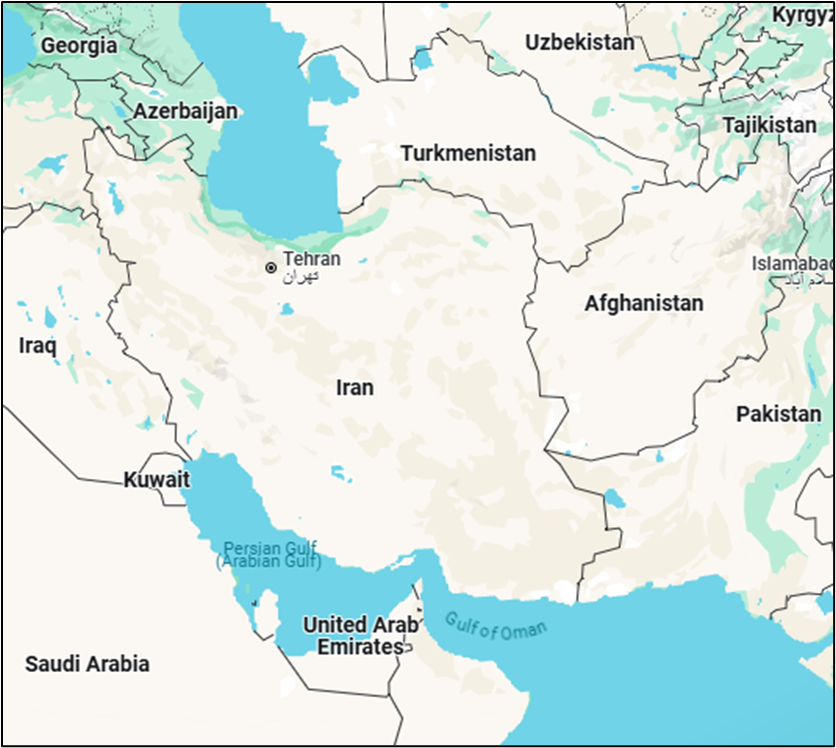
- Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, is a geopolitically and geostrategically significant country in Western Asia, occupying a pivotal location at the crossroads of Central Asia, South Asia, and the Middle East. Here's a detailed breakdown of its geography:
- Location and Extent:
- Continent: Asia
- Coordinates: Approximately between 25°N to 40°N latitude and 44°E to 63°E longitude
- Borders:
- North: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, and the Caspian Sea
- East: Afghanistan and Pakistan
- West: Turkey and Iraq
- South: Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman (with maritime boundaries with UAE, Saudi Arabia, Oman)
- Strategic Significance
- Iran controls the Strait of Hormuz, a crucial choke point through which ~20% of global petroleum passes.
- Acts as a land bridge between the Middle East, Central Asia, and the Indian subcontinent.
- Major Physiographic Regions
- Zagros Mountains: Extend along western Iran, forming a rugged terrain.
- Elburz Mountains: Located in the north, with Mount Damavand (5,610 m), the highest peak in Iran.
- Central Plateau: A large desert basin region including:
- Dasht-e Kavir (Great Salt Desert)
- Dasht-e Lut (one of the hottest places on Earth)
- Khuzestan Plain: Fertile area in the southwest near the Iraq border, rich in oil.
- Coastal Regions:
- Northern: Caspian Sea coast – lush and humid
- Southern: Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman – arid and hot
- Climate: Mostly arid and semi-arid with significant continental variations.
- Caspian Sea region: Subtropical and humid
- Desert interiors: Extreme heat and dryness
- Mountain regions: Cold and snowy in winters
- Rivers and Water Bodies
- Karun River: Iran's only navigable river; vital for irrigation and transport.
-
-
- Lake Urmia: A large salt lake in the northwest, shrinking due to overuse and climate change.
- Caspian Sea: Largest enclosed inland water body in the world; shared with other Caspian littoral states.
- Persian Gulf & Gulf of Oman: Provide maritime access and strategic depth.
- Natural Resources:
- Rich in oil and natural gas – among the world’s top holders.
-
-
-
- Also has deposits of copper, iron ore, zinc, coal, and uranium.
- Human Geography:
- Major cities: Tehran (capital), Mashhad, Isfahan, Shiraz, Tabriz
-
-
-
- Ethnic diversity: Persians (majority), Azeris, Kurds, Lurs, Balochs, Arabs, and Turkmens
- Population concentrated around foothills, rivers, and coastal plains, avoiding desert interiors.
- Geopolitical Relevance:
- Iran's geography gives it influence over:
- Energy trade routes
- Land access to Central Asia
- Maritime access to Indian Ocean Region (IOR)
- Iran's geography gives it influence over:
-
2. Israel
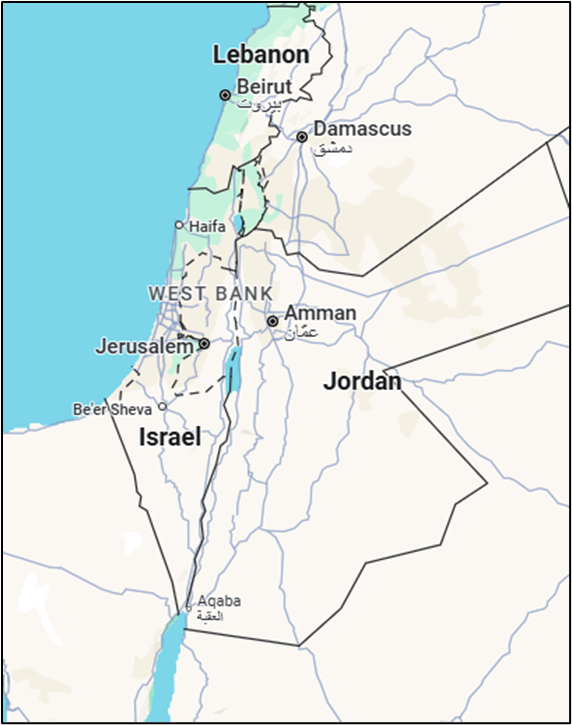
- Location and Extent
- Located in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea.
- Bordered by:
- Lebanon (north)
- Syria (northeast)
- Jordan (east)
- Egypt (southwest)
- Palestinian Territories (West Bank & Gaza Strip)
- Coordinates: 31°N, 35°E
- Total Area: Approx. 22,000 sq km (small country, about the size of Meghalaya)
- Physical Features
- Coastal Plain:
- i. Along the Mediterranean Sea.
- ii. Fertile land, urbanized (Tel Aviv, Haifa).
- iii. Major economic and population zone.
- Central Highlands:
- i. Includes Judean and Samarian Hills.
- ii. Jerusalem is located here (~750m above sea level).
- iii. Rugged terrain, moderate rainfall.
- Jordan Rift Valley:
- i. A part of the Great African Rift System.
- ii. Includes the Jordan River, Sea of Galilee, and Dead Sea.
- iii. Dead Sea: Earth’s lowest point on land (approx. 430 m below sea level).
- Negev Desert:
- i. Covers more than 50% of Israel’s area (south).
- ii. Arid, rocky desert with sparse population.
- iii. Towns: Beersheba, Eilat.
- Coastal Plain:
- Rivers and Water Bodies:
- Jordan River: Main river (flows from Mount Hermon to the Dead Sea).
- Sea of Galilee (Lake Kinneret): Freshwater source.
- Dead Sea: Highly saline, no aquatic life.
- Yarmouk River: Tributary of Jordan River (shared with Syria and Jordan).
- Climate
- Mediterranean Climate in the north and coastal plain (wet winters, dry summers).
- Semi-arid to arid in the south (Negev Desert).
- Rainfall varies from 700 mm/year in the north to <100 mm/year in the south.
- Frequent droughts and water scarcity.
- Natural Resources
- Scarce water, major constraint.
- Minerals: Potash, bromine, phosphates (from Dead Sea).
- Natural gas: Offshore reserves (Tamar, Leviathan fields).
- Agricultural innovation: Drip irrigation, greenhouse farming.
- Geopolitical Significance
- Controls strategic terrain near Suez Canal and Red Sea (via Eilat).
- Proximity to conflict-prone areas: Golan Heights, West Bank, Gaza Strip.
- Shared water sources: hydro-political tensions (Jordan River Basin).
- Environmental Issues
- Water scarcity and over-extraction of aquifers.
- Land degradation in arid regions.
- Urban sprawl and loss of biodiversity.
- Climate change impacts rainfall and agriculture.
- Strategic Geographic Features
- Golan Heights: Occupied from Syria in 1967; important for defense and water sources.
- Red Sea Access: Eilat Port gives access to Asian and African trade.
- Mediterranean Ports: Haifa, Ashdod, vital for trade and energy.




