- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 16th June 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 16th June 2025
16-06-2025

1. Republic of Cyprus
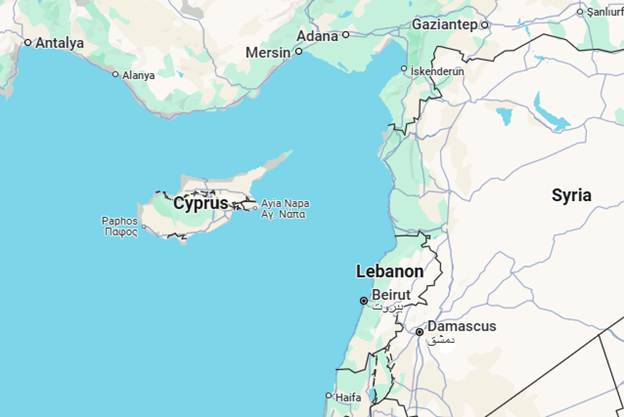
- Cyprus, an island nation in the Eastern Mediterranean, holds significant geographical importance due to the following reasons:
- Strategic Location:
- Junction of Three Continents: Situated at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- Proximity to Hotspots: Located near the Middle East (Syria, Lebanon, Israel), North Africa, and Southern Europe (Greece, Turkey).
- Military Significance: Used historically and currently for military bases and surveillance, especially by the United Kingdom and NATO.
- Access to Maritime Trade Routes:
- Eastern Mediterranean Sea: Acts as a gateway to the Suez Canal and Red Sea, crucial for Europe-Asia trade.
- Hub for Shipping: Cyprus has one of the largest merchant fleets in the EU and serves as a key maritime hub.
- Energy and Natural Resources:
- Offshore Gas Reserves: Presence of natural gas fields in the Eastern Mediterranean (e.g., Aphrodite field).
- Energy Transit Point: Potential to be a key player in transporting gas from the Eastern Mediterranean to Europe.
- Political and Diplomatic Significance:
- EU Membership: Cyprus is a member of the European Union, giving the EU strategic presence near the Middle East.
- Buffer Zone: The island is divided into Greek Cypriot (South) and Turkish Cypriot (North) regions, with a UN-monitored buffer zone, a critical flashpoint in international diplomacy.
- Tourism and Climate:
- Mediterranean Climate: Attractive for European tourists, especially due to year-round sunshine.
- Cultural Crossroads: Rich historical and cultural heritage from Greek, Roman, Byzantine, Ottoman, and British influences.
- Strategic Location:
Conclusion:
Cyprus's geographical location makes it a strategic asset for trade, security, and energy in the Eastern Mediterranean. Its importance is amplified by regional tensions and energy politics, making it a crucial player in both European and Middle Eastern geopolitics.
2. Kedarnath, Uttarakhand
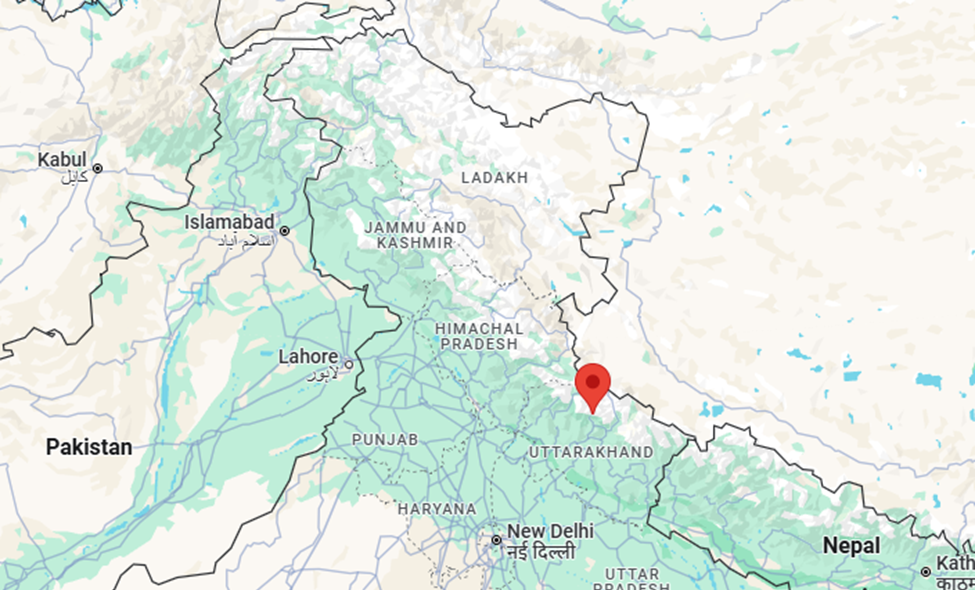
- Kedarnath, located in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, holds immense geographical, spiritual, ecological, and strategic importance in the Indian Himalayan region.
- Location in the Garhwal Himalayas:
- Altitude: Situated at about 3,583 meters (11,755 feet) above sea level in the Rudraprayag district.
- Source of Mandakini River: Lies near the origin of the Mandakini River, a tributary of the Alaknanda, which ultimately contributes to the Ganga.
- Tectonic Activity: Located in the seismically active Himalayan zone, which makes it important for geological and seismic studies.
- Spiritual and Cultural Significance:
- Jyotirlinga Shrine: Home to one of the twelve Jyotirlingas of Lord Shiva, attracting millions of pilgrims annually.
- Char Dham Yatra: One of the four sacred dhams in the Char Dham Yatra, increasing its national spiritual relevance.
- Ecological Importance:
- Alpine Ecosystem: The region is rich in alpine flora and fauna, and serves as a natural habitat for rare Himalayan species.
Glacial Region: Surrounded by glaciers like Chorabari Glacier, which are vital sources of freshwater and crucial for understanding climate change.
- Alpine Ecosystem: The region is rich in alpine flora and fauna, and serves as a natural habitat for rare Himalayan species.
- Disaster and Environmental Management:
- Flash Floods, 2013: The devastating floods of 2013 highlighted the fragility and vulnerability of Himalayan settlements and led to increased focus on disaster-resilient infrastructure and early warning systems.
- Climate Monitoring: Important for observing the impact of global warming on Himalayan glaciers and ecosystems.
- Strategic and Developmental Role:
- Tourism Economy: Kedarnath is a cornerstone of religious tourism in Uttarakhand, supporting local livelihoods and regional development.
- Infrastructure Challenge: Its remote and difficult terrain makes it a testing ground for sustainable development and mountain infrastructure planning.
Conclusion:
Kedarnath's geographical importance stems not only from its religious significance, but also from its strategic Himalayan location, environmental vulnerability, and role in water and climate systems. It serves as a reminder of the delicate balance between spiritual heritage and ecological sustainability in the high Himalayas.




