- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 03 DECEMBER 2024
PLACES IN NEWS 03 DECEMBER 2024
03-12-2024
Bhitarkanika National Park
Why in news?
- Migratory and residential bird species have begun arriving at Bhitarkanika National Park with winter's onset.
- Shorebirds like sandpipers, plovers, ducks, geese, herons, cormorants, spoonbills, and egrets are seen in areas like Barunei Muhana and Satabhaya.
- Last winter, 121 bird species totalling 1,51,421 were recorded during the waterfowl survey.
- During winters, Birds migrate from the northern hemisphere and Ladakh to escape harsh winters and leave when water bodies dry up.
About Bhitarkanika National Park:
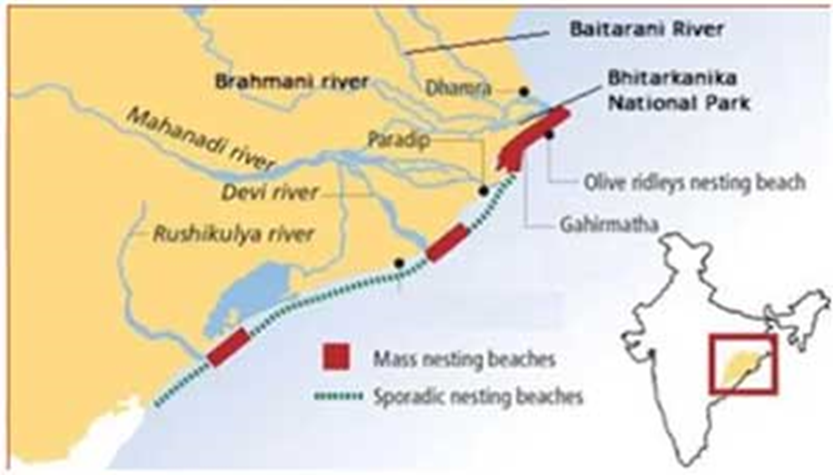
- Bhitarkanika National Park, spanning 145 km², is located in Kendrapara district, Odisha, and was designated a national park in 1998 and a Ramsar site in 2002.
- It is part of the larger Bhitarkanika Wildlife Sanctuary (672 km²), bordered by Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary to the east and intersected by rivers like Brahmani, Baitarani, Dhamra, and Pathsala.
- The park houses India’s second-largest mangrove ecosystem, thriving in tidal estuarine regions and serving as nurseries for aquatic life.
- Mangrove species have adapted to tidal fluctuations, with specialized roots supporting fish habitats and maintaining ecological balance.
- Bhitarkanika hosts diverse ecosystems, including mangrove swamps, rivers, creeks, mudflats, and forested beaches, making it significant for ecological and biological research.
Fauna:
- The park is home to endangered saltwater crocodiles, with 1,671 individuals recorded, including rare specimens exceeding 6 meters in length. It boasts one of the world's largest populations of these crocodiles.
- Other notable fauna includes spotted deer, wild boar, rhesus monkeys, Indian pythons, monitor lizards, and Olive Ridley turtles that nest along Gahirmatha Beach.
- A 2014 mammal survey recorded 1,872 spotted deer, 1,213 wild boars, and smaller populations of otters, jackals, sambar deer, and jungle cats.
Avifauna:
- Bhitarkanika hosts 320 bird species, including eight types of kingfishers, black ibis, darters, and Asian open-bills.
- Annually, approximately 120,000 migratory birds and 80,000 resident birds visit for nesting or wintering.
- In 2023, 179 mangrove pittas were recorded, highlighting the park's rich avian diversity.
Guinea
Why in news?
- Chaos at a soccer game in Guinea's Nzerekore led to a deadly stampede after fans protested a referee's decision.
- At least 56 people died, many crushed near stadium gates as security forces used tear gas to control the crowd.
- Over 20,000 fans attended the match, part of a tournament honouring military leader Mamadi Doumbouya.
- Victims included children, with several injured in critical condition.
About Guinea
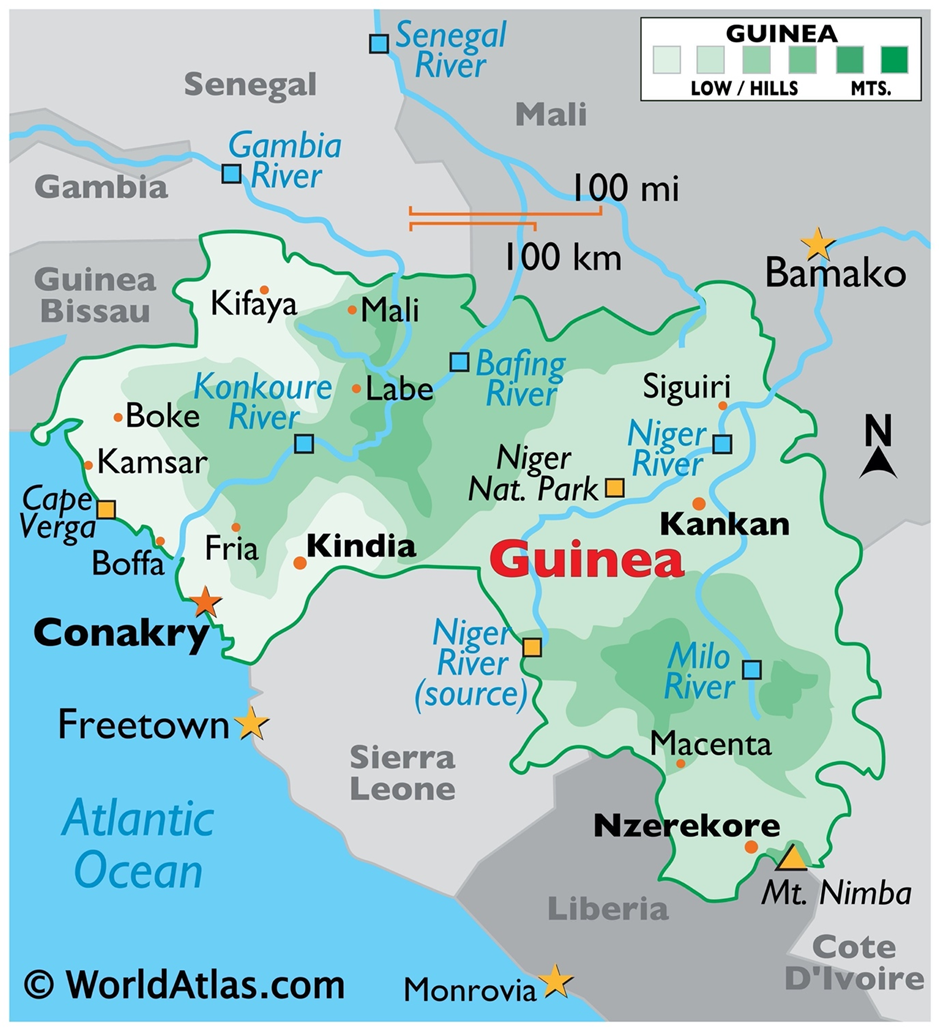
-
Geographical Location:
- Guinea is located on the west coast of Africa, bordered by Guinea-Bissau, Senegal, Mali, Côte d’Ivoire, Liberia, and Sierra Leone.
- It has a coastline along the Atlantic Ocean, stretching approximately 320 kilometres.
- The country's geography includes coastal plains, inland savannas, and mountainous regions, with the Fouta Djallon highlands in the centre.
- Major rivers like the Niger, Senegal, and Gambia originate in Guinea, making it crucial for West African hydrology.
- Guinea’s climate is tropical, characterized by a rainy season (May to October) and a dry season (November to April).
- Conakry, the capital and largest city, is located on the Kaloum Peninsula.
- Guinea covers an area of 245,857 square kilometres and has a population of about 13 million people.
-
Mineral Resources:
- Guinea is one of the world's largest producers of bauxite, holding about 25% of global reserves.
- It is rich in iron ore, including the Simandou deposits, among the world’s largest and highest-quality reserves.
- The country also has significant gold and diamond deposits.
- Other minerals include uranium, graphite, manganese, and limestone.
- Guinea’s mineral wealth remains largely untapped, providing opportunities for economic growth.
- Mining accounts for over 25% of Guinea’s GDP and is the backbone of its economy.
- International companies are heavily involved in resource extraction, but locals often see limited benefits.
-
Military Coup in Guinea:
- Guinea experienced a military coup on September 5, 2021, when Colonel Mamadi Doumbouya ousted President Alpha Condé.
- Doumbouya dissolved the government and suspended the constitution, citing corruption and poor governance as reasons.
- The coup was triggered by discontent over Condé’s third term after controversial constitutional changes allowed his extended rule.
- Doumbouya’s regime promised a democratic transition, but delays in setting an election date have drawn criticism.
- The coup reflects broader instability in West Africa, with governance challenges and economic pressures contributing to military interventions.
- The junta justified its actions as preventing Guinea’s descent into chaos and addressing unmet social expectations.
Other Countries Under Military Coup:
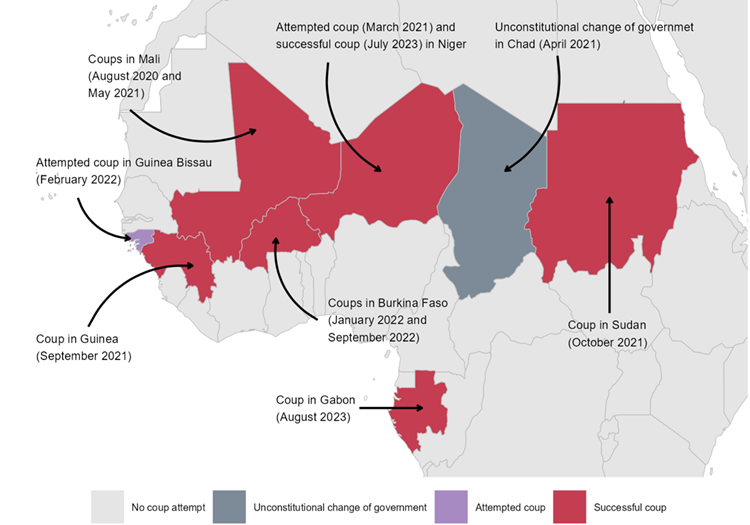
- Mali: Military seized power in 2020 and 2021, delaying civilian rule.
- Burkina Faso: Experienced coups in January and September 2022.
- Niger: Coup in July 2023 toppled President Mohamed Bazoum.
- Chad: Military takeover followed President Idriss Déby’s death in 2021.
Lithuania
Why in news?
- China condemned Lithuania’s expulsion of three Chinese diplomats, calling it a baseless and provocative act that worsens bilateral relations.
- The move follows an investigation into the suspected role of a Chinese ship in damaging undersea data cables between Lithuania and Sweden, for which Sweden has sought China’s cooperation.
- Lithuania cited international law but did not disclose details about the expelled diplomats.
- The incident adds to tensions since 2021, when China downgraded ties with Lithuania over its support for Taiwan, which Beijing claims as its territory.
About Lithuania:
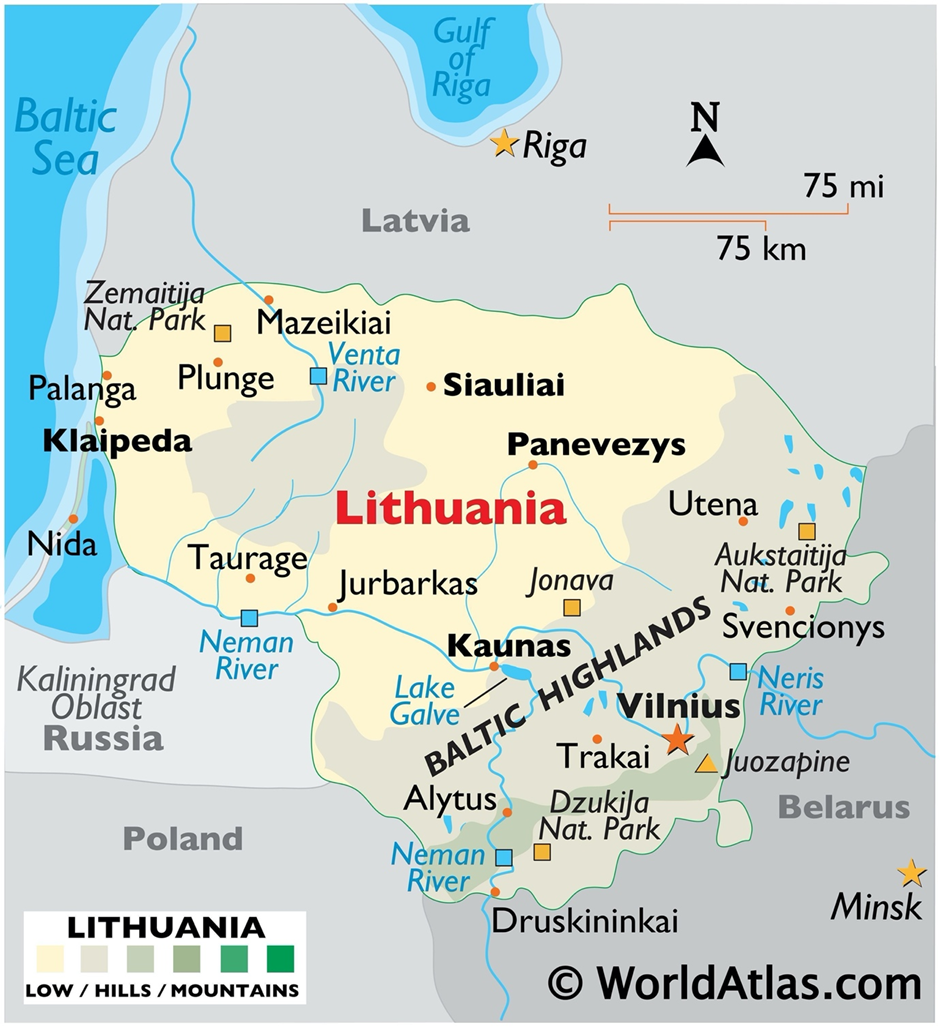
- Lithuania is a Baltic nation in Northern Europe, bordered by Latvia to the north Belarus to the east and south Poland to the south Russia's Kaliningrad Oblast to the southwest and the Baltic Sea to the west.
- Covering an area of approximately 65,300 square kilometres, Lithuania is known for its flat terrain with lowlands and a few hilly regions. Its geographical position makes it a crossroads between Western and Eastern Europe.
- The country's landscape features forests, wetlands, and over 3,000 lakes, offering significant biodiversity.
- The Neman River, the longest river in Lithuania, flows through its territory and drains into the Baltic Sea. Lithuania's climate is a mix of maritime and continental influences, leading to mild summers and cold winters.
- Lithuania’s capital, Vilnius, is located in the south-eastern part of the country and is known for its historic Old Town, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- As a member of the European Union, NATO, and the Eurozone, Lithuania is strategically positioned as a bridge between Europe and neighbouring Eastern nations. Its proximity to major waterways like the Baltic Sea enhances its role in trade and regional connectivity.
Lebanon
Why in news?
- Lebanon has accused Israel of violating a truce agreement by launching an airstrike that killed two people.
- The incident comes amid heightened tensions following cross-border exchanges of fire between Israel and Hezbollah, a powerful militant group based in southern Lebanon.
- These clashes are linked to the broader escalation in the region triggered by the Israel-Hamas conflict in Gaza.
- The truce, aimed at preventing further hostilities along the Israel-Lebanon border, has been fragile, with both sides trading accusations of violations.
- This latest airstrike underscores the risk of the conflict spilling over into neighbouring countries, raising fears of a broader regional war.
About the Israel-Lebanon conflict:
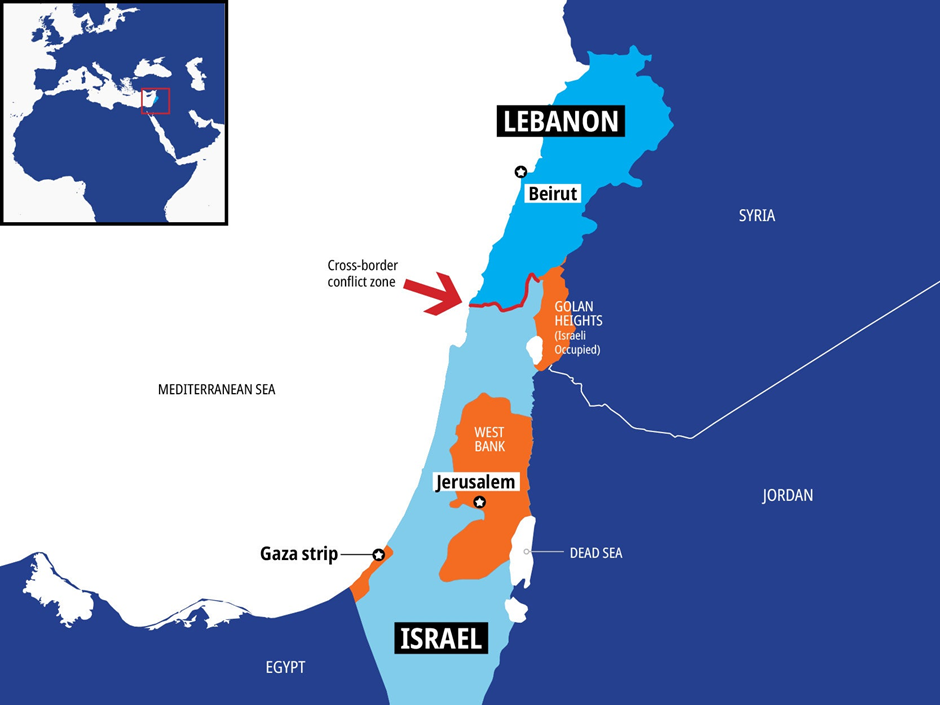
- The Israel-Lebanon conflict stems from longstanding tensions, territorial disputes, and political instability, with roots in the 1948 Arab-Israeli War and Lebanon’s complex religious-political dynamics.
- A key driver of the conflict is the presence of Hezbollah, a powerful Shia militant and political group in southern Lebanon, supported by Iran, which opposes Israel’s existence.
-
Regions often mentioned in news:
- Shebaa Farms, a small strip of land claimed by Lebanon but occupied by Israel since 1967, is often a focal point of disputes.
- The Blue Line, a UN-demarcated border established in 2000 after Israel’s withdrawal from southern Lebanon, remains a site of frequent clashes.
- In 2006, a 34-day war erupted between Israel and Hezbollah, resulting in significant casualties and destruction in Lebanon.
- Recent conflicts have escalated amid regional tensions, particularly due to the Israel-Hamas war in Gaza.
- In October 2023, cross-border exchanges of fire intensified, with Hezbollah targeting Israeli positions and Israel responding with airstrikes in southern Lebanon.
- Beirut, Lebanon’s capital, and Tyre in the south have been highlighted due to civilian casualties and damage from Israeli strikes.
- Northern Israeli regions like Galilee are frequently affected by cross-border rocket fire, leading to evacuations and military responses.
- The ongoing conflict threatens to escalate into a broader regional war, involving multiple actors like Iran, Syria, and other militant groups.
- Efforts by the UN and international mediators to de-escalate have so far yielded limited success, with the region remaining volatile.
|
UPSC CSE PYQS Q1. In the recent years Chad, Guinea, Mali and Sudan caught the international attention for which one of the following reason common to all the them?
Answer: Option D
Q2. Two important rivers- one with its source in Jharkhand (and known by a different name in Odisha), and another, with its source in Odisha merge at a place only a short distance from the coast of bay of Bengal before flowing into the sea. This is an important site of wildlife and biodiversity and a protected area. Which one of the following could be this?
Answer: Option A |




