- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
MISSION DIVYASTRA: THE FIRST FLIGHT TEST OF AGNI-5 MISSILE
MISSION DIVYASTRA: THE FIRST FLIGHT TEST OF AGNI-5 MISSILE
12-03-2024
- India conducted a first successful flight test of Indigenously Developed ‘Agni-5’ missile equipped with MIRV (Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle) technology.
- India joined the elite club of 5 nations (US, Russia, China, France and the UK) to be equipped with MIRV capabilities capable of deploying MIRV-equipped missiles, significantly enhancing its strategic deterrent capabilities.
- India has already carried out several tests of Agni-5 but it was for the first time that the flight test was carried out with MIRV.
What are Agni Missiles?
|
Understanding MIRV Technology:
- MIRV technology enables a single missile to carry multiple independently targetable warheads.
- Each warhead can be programmed to strike different targets, providing flexibility and precision in targeting.
- Developed initially by the US and the Soviet Union during the Cold War era, MIRV technology has since been adopted by other nuclear powers.
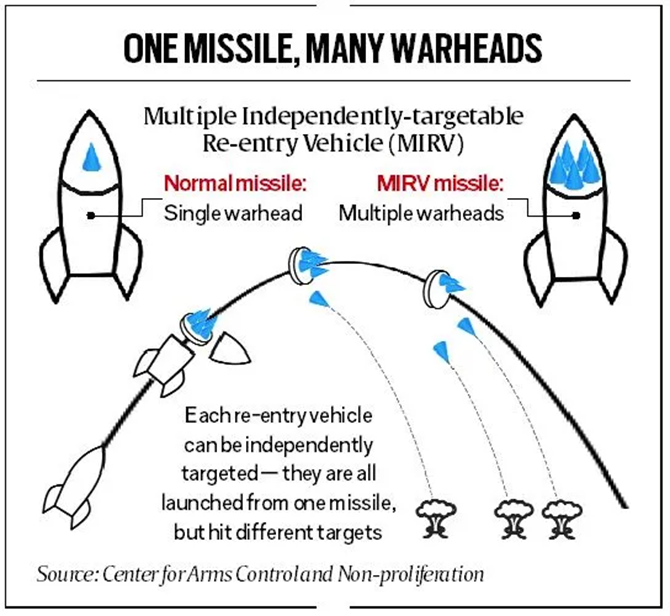
Operational Advantages of MIRV Technology:
- Missiles equipped with MIRVs can attack multiple targets simultaneously, maximizing the potential damage they can cause to adversaries.
- The complexity of tracking and intercepting multiple weapons challenges existing missile defence systems, increasing the probability of successful penetration.
- The ability to deliver a destructive response act as a powerful deterrent against adversaries, thereby strengthening national security.
Integration with Agni Missile System:

Agni upgrade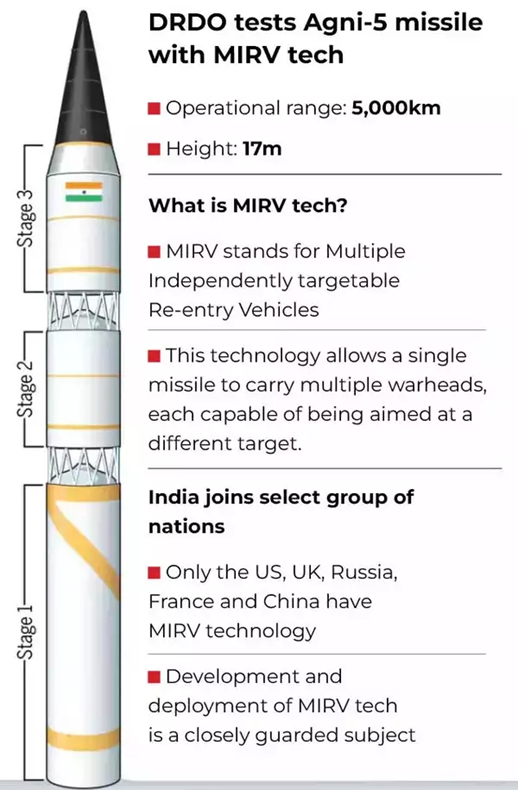
- The integration of MIRV technology is a long-awaited upgrade for the Agni family of short, medium and intercontinental range ballistic missiles indigenously developed by the DRDO. Agni missiles are the main land-based delivery systems for India’s nuclear weapons.
- Developed in the 1990s, the first-generation Agni missiles were deployed in the armed forces in the mid-2000s. Agni-1 to Agni-4 missiles have ranges between 700 to 3,500 km and can carry single payloads weighing between 12 and 40 kilotons.
- Agni-5, the version that has been equipped with MIRV technology, can travel more than 5,000 km, and can potentially enter the intercontinental range as well, considered to be 5,500 km and above.
- Agni-5 has been tested several times since 2012, with new features and capabilities. Its previous flight happened in December 2022, when its night-time capabilities were tested, among other things.
- Meanwhile, DRDO has also been developing Agni-P missiles, which are modernised versions of the short-range Agni-1 and Agni-2 variety. This missile was tested twice in 2021, and on both occasions there was the expectation that it would be integrated with MIRV technology.
- A recent test was carried out from Dr APJ Abdul Kalam Island, off the coast of Odisha, which hosts India’s integrated missile test range. “Various telemetry and radar stations tracked and monitored multiple re-entry vehicles. The mission accomplished the designed parameters,”
Strategic Implications:
- India's acquisition of MIRV technology strengthens its position in the context of regional and global security dynamics.
- The successful test demonstrates India's indigenous technological prowess and self-reliance in defense capabilities.
Conclusion: The successful test of Agni-5 with MIRV technology represents an important milestone in India's strategic deterrent capability. This development highlights India's ability to adapt and innovate in response to emerging security challenges. As India enhances its defense capabilities, it is committed to ensuring peace and stability in the region while protecting its national interests
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
Watch Detailed Video Of This Topic



