- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
MENTAL HEALTH AS A UNIVERSAL HUMAN RIGHT (UHR)
MENTAL HEALTH AS A UNIVERSAL HUMAN RIGHT (UHR)
11-10-2023
-1697198723928.png)
Context
- Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) has requested its members to expedite mental health efforts using a human-rights-based approach on World Mental Health Day (Oct 10).
- World Mental Health Day, celebrated annually on October 10th, aims to raise global awareness of mental health issues and mobilize support for mental health.
Key recommendation of WHO
- The WHO has urged for the establishment of Mental Health as a Universal Human Right (UHR).
- The transformation of societal attitudes and government policies is being pursued.
- The focus is on raising awareness and providing education to effectively address and address mental health issues.
- The goal is to ensure that all individuals have access to accessible mental health services.
- The focus is shifting from psychiatric hospitals to community-based mental health treatment.
What is Mental Health?
- WHO Definition: Mental health is a positive state of emotional and mental well-being, enabling individuals to cope with life's stresses, realize their abilities, learn, work, and contribute to their community.
- Mental Healthcare Act (MHA), 2017: The Act defines mental illness as a significant disorder affecting thinking, mood, perception, orientation, and memory, often linked to alcohol and drug abuse.
What is the Status of Mental Health?
- Global Status: Mental disorders have become a significant global health burden, with no global reduction since 1990.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that mental illness accounts for approximately 15% of global disease conditions.
- India’s Status: The National Mental Health Survey 2015-16 in India indicates that 150 million individuals require mental health care interventions.

What is the significance of Mental Health?
- Mental and physical health are interconnected, with depression increasing the risk of long-term conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and stroke, and chronic conditions increasing the risk of mental illness.
- Since it has a significant impact on overall quality of life, mental health should be acknowledged as a fundamental human right.
- Mental well-being significantly influences an individual's capacity to exercise other rights, including the right to education and the right to work.
What are the harmful effects of poor Mental Health?
- Impact on Physical Health: Positive psychological well-being reduces heart attack and stroke risks, while poor mental status can lead to physical health issues and harmful behavior, including chronic illnesses like diabetes, asthma, cancer, and arthritis.
- Impact on Relationships: Adolescence and young adulthood can be significantly impacted by mental-health conditions, which can negatively affect the development of safe and healthy relationships with various individuals.
- Impact on Productivity: The individual's concentration and productivity are significantly impacted by this.
- Risks of a cyclical relationship: The WHO Report on Mental Health and Development (2010) highlighted the cyclical relationship between vulnerability and poor mental health, highlighting the risks of stigma, discrimination, violence, marginalization, and human rights violations.
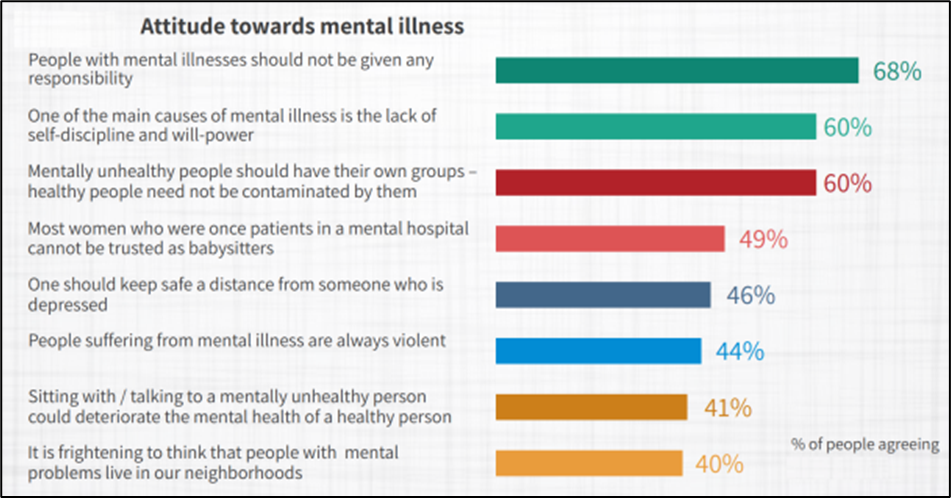
What are the Reasons/ Issues/ Concerns? Challenges related to Mental Health
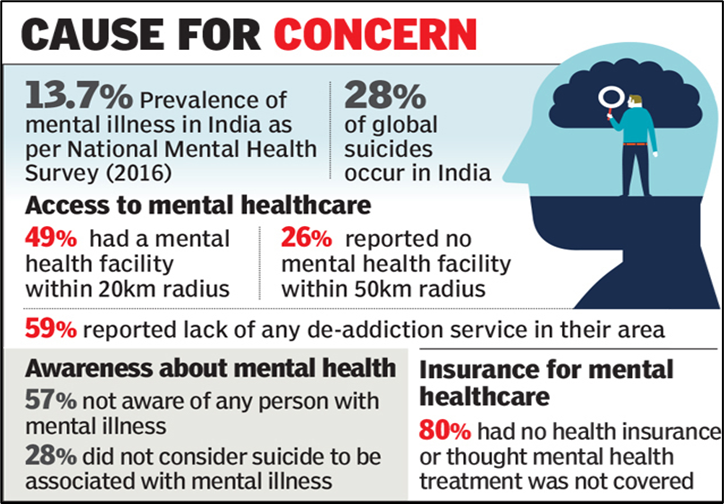
- Public Health Burden: India's National Mental Health Survey 2015-16 indicates that approximately 150 million people in the country require mental health care interventions.
- Human Resources crunch: India's mental health workforce, including psychiatrists, nurses, psychologists, and social workers, has a low proportion per 100,000 population.
- Lack of financial resource allocation: The low financial resource allocation of just over a percent of GDP on healthcare has hindered public access to affordable mental healthcare.
- Lack of awareness: Poor mental illness awareness, social stigma, and abandonment of mentally ill individuals, particularly the elderly and destitute, create social isolation and reluctance to seek treatment, worsening mental illness.
- Gap in Post-Treatment: The current lack of proper rehabilitation for mentally ill individuals post-treatment is a significant issue.
- Rise in Severity: Economic downturns often lead to an increase in mental health problems, necessitating the need for special attention during these challenging times.
- Changed Lifestyle: The rise in social media usage is causing stress and mental health issues, particularly among young people, by reducing face-to-face relationships, reducing meaningful activities, and reducing self-esteem due to negative social comparisons.
- Income Inequalities: Mental health conditions are linked to poverty, with those living in poverty at higher risk of experiencing severe conditions, leading to increased health expenditure and employment loss.
Steps Taken by the Government:
- Constitutional Provision: The Supreme Court has deemed healthcare a fundamental right under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Article 21 stipulates that no person can be deprived of their life or personal liberty unless a legal procedure is established.
- National Mental Health Program (NMHP): The National Mental Health Program (NMHP) was implemented in 1982 to address mental disorders and shortage of professionals, modernizing state mental hospitals and upgrading psychiatric wings.
- The National Mental Health Program (NMHP) utilizes Information, Education and Communication (IEC) activities to raise public awareness about mental illnesses.
- Mental HealthCare Act 2017: The Mental Healthcare Act 2017 aims to decriminalize suicide attempts by providing government rehabilitation opportunities rather than punishment or trial for those who attempt suicide…

- Kiran Helpline: In 2020, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment launched a 24/7 toll-free helpline, 'Kiran', to assist individuals with mental health issues like anxiety, stress, depression, and suicidal thoughts.
- National Tele Mental Health Programme: The government has introduced a National Tele Mental Health Programme in the 2022-23 Budget to enhance access to quality mental health counseling and care services.
- Manodarpan: The Ministry of Education of the Government of India is implementing an initiative to offer psychosocial support to students during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Swachh Mansikta Abhiyan: To encourage people to learn about mental health.
- Issuance of Guidelines/Advisories: The Government has issued guidelines and advisories on managing mental illness, which can be accessed on the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare's 'Behavioural Health - Psychosocial Helpline' website.

What steps need to be can be taken?
- Need to address stigma: The stigma surrounding such issues is deeply ingrained, hindering patients from seeking timely treatment and causing feelings of shame, isolation, and weakness.
- Inclusivity: Mental health should be a key part of public health programs, focusing on stress reduction, healthy lifestyle promotion, high-risk groups, and targeted interventions, especially schools and vulnerable groups like victims of violence.
- Investment on Infrastructure: Improved infrastructure and innovative models are needed for mental health care and treatment, including training Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA) to educate and sensitize women and children about mental diseases.
- Finance allocation: The proposed interventions necessitate substantial budget allocation for mental healthcare, addressing the significant treatment gap in health infrastructure and human resources.
- Comprehensive approach: To effectively address the problem, thorough mapping and research are necessary, backed by political commitment, scientific understanding, and a citizen-driven movement.
- Three Paths to transformation: The World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended three pathways for enhancing mental health:
- Enhance the recognition and investment in mental health by individuals, communities, and governments across all sectors.
- Enhance the physical, social, and economic aspects of environments, including homes, schools, workplaces, and the community, to enhance mental health protection and prevent mental health conditions.
- Strengthen mental health care by providing a community-based network of accessible, affordable, and quality services and supports to meet the full spectrum of mental health needs.
Conclusion
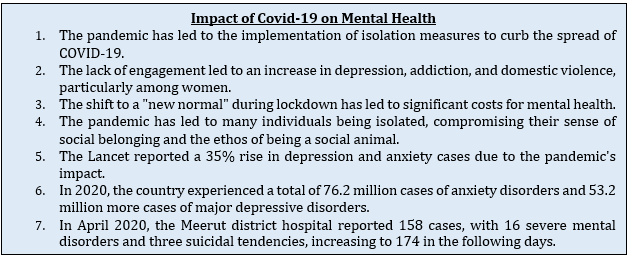
- The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated mental health issues, highlighting the under-equipped mental healthcare system in India to effectively manage the crisis. To tackle the issue, urgent interventions such as increased budget, workforce growth, and enhanced awareness are required.



