- The Annual Nationwide Mass Drug Administration (MDA) Campaign for eliminating lymphatic filariasis was launched by the Union Health Minister.
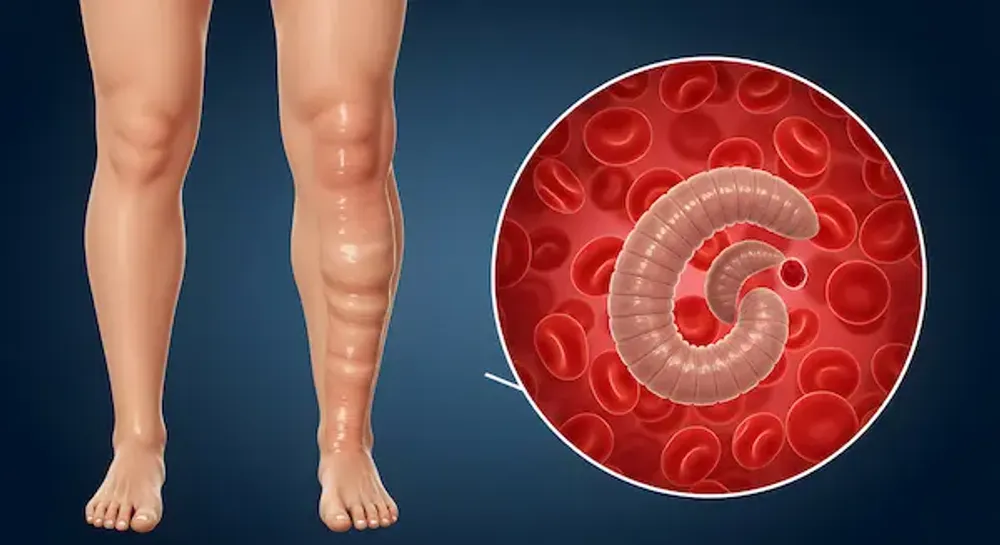
- Lymphatic Filariasis also called elephantiasis (Haatipaon) is a neglected vector borne tropical disease which is transmitted mainly by the female Culex mosquito.
- The disease is caused by parasitic roundworms (nematodes) belonging to the family Filariodidea. Three filarial species are responsible:
- Wuchereria bancrofti — accounts for about 90% of global cases
- Brugia malayi — causes most of the remaining infections
- Brugia timori — also contributes to disease burden
- Transmission cycle: Adult worms settle in the lymphatic vessels, impair lymphatic function, and release millions of microfilariae (immature larvae) into the bloodstream. Humans become infected when mosquitoes transmit these parasites during blood meals.
- Most infections remain asymptomatic, but chronic disease leads to lymphoedema (tissue swelling), elephantiasis (thickening of skin and tissues of limbs), and hydrocele (scrotal swelling).
- Elimination strategy: The spread of infection can be stopped through preventive chemotherapy. As per World Health Organization guidelines, elimination relies on Mass Drug Administration (MDA).
- MDA involves giving annual doses of antifilarial medicines to the entire at-risk population, regardless of individual infection status, to break transmission and progressively eliminate the disease.
You Can Also Read |
|
| UPSC Foundation Course | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |
| Free MCQs for UPSC Prelims | UPSC Test Series |
| Best IAS Coaching in Delhi | Our Booklist |