- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
LIONS 19 TIMES SAFER IN GUJARAT THAN IN AFRICA: IUCN
LIONS 19 TIMES SAFER IN GUJARAT THAN IN AFRICA: IUCN
11-03-2024
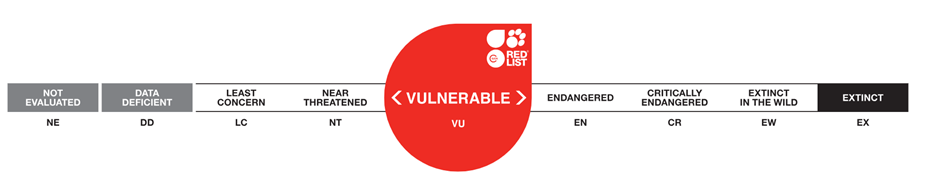
- Gujarat celebrates as the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) reclassifies Asiatic lions from endangered to vulnerable.
- Positive shift reflects Gujarat's successful conservation efforts.
- Status
Listed in Schedule I of Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972, in Appendix I of CITES and as vulnerable on IUCN Red List
- HABITAT TYPE: Forest, Savanna, Shrubland, Grassland, Desert
Comparison with African Lions:
- IUCN's latest global report highlights significant differences between African and Indian lions.
- African lions are 19 times more likely to be at risk of population decline than Indian lions (a 33% decline in lion populations in Africa).
- Widespread poaching in Africa contributes to the high risk.

Safety in Gujarat:
- Gujarat is the only habitat of Asiatic lions in the world.
- The Saurashtra region in Gujarat provides a safe haven for lions.
- The risk of decline in lion numbers in Saurashtra is estimated at only 2%.
Binomial Reclassification:
- Previously, Asiatic lions were classified separately as Panthera leo persica.
- Due to genetic similarity with African lions it is now grouped under Panthera leo leo.
- The IUCN estimates the wild lion population at 23,000, including 674 in Gujarat.
Threats to Lion Population:
- The main threats include habitat loss, conversion of protected areas and degradation of the prey base.
- Targeted poaching for body parts is emerging as a significant threat.
Economic Impact and Conservation:
- Lions cause huge economic losses in East Africa.
- Coexistence with humans helps preserve the lion population in Gujarat.
Historical Significance and Habitat Preservation:
- Lions found in Eastern Europe about 700 years ago, distributed from Africa to central India.
- India signed an agreement in the late 1960s to exchange lions for cheetahs with Iran.
- The presence of lions helps control the population of wild boar and nilgai, which benefits farmers.
Future Conservation Efforts:
- Proposal to expand the Greater Gir Sanctuary in Gujarat, tripling its size to 30,000 sq km.
- The goal of providing large protected areas for apex predators.
Conclusion:
Asiatic lions have been reclassified as vulnerable due to Gujarat's successful conservation efforts. Continued efforts are important to ensure the survival of this iconic species.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



