| Important questions for UPSC Pre/ Mains/ Interview:
1. How has India achieved early success in its renewable energy transition? 2. What role do alternative fuels play in India’s clean energy strategy? 3. How is decentralised renewable energy accelerating India’s transition? 4. What is the significance of solar energy initiatives in India’s transition? 5. Why is nuclear energy included in India’s clean energy roadmap? 6. How do global partnerships strengthen India’s renewable transition? 7. What are the key challenges in sustaining India’s renewable energy transition? 8. What should be the way forward for India’s renewable transition? |
Context
At World Economic Forum 2026, India received global endorsement after achieving 50% non-fossil electricity capacity, five years ahead of its 2030 climate commitment.
Q1. How has India achieved early success in its renewable energy transition?
- India’s renewable manufacturing capacity has expanded to 144 GW, strengthening domestic supply chains.
- Solar tariffs declined by nearly 80%, making renewables affordable at scale.
- Renewable energy with storage has become cost-competitive with conventional sources.
- India has achieved globally competitive prices in green hydrogen and green ammonia.
Q2. What role do alternative fuels play in India’s clean energy strategy?
- The ethanol blending programme has reduced 813 lakh metric tonnes of CO₂ emissions.
- Implementation of the National Policy on Biofuels targets 20% ethanol blending by 2025–26.
- Expansion into green hydrogen, sustainable aviation fuel, and other low-carbon fuels is underway.
- The National Green Hydrogen Mission aims for 5 million tonnes production by 2030.
Q3. How is decentralised renewable energy accelerating India’s transition?
- PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana promotes rooftop solar adoption.
- PM-KUSUM enables solar-powered irrigation and agriculture.
- Decentralisation reduces transmission losses and improves energy access in rural areas.
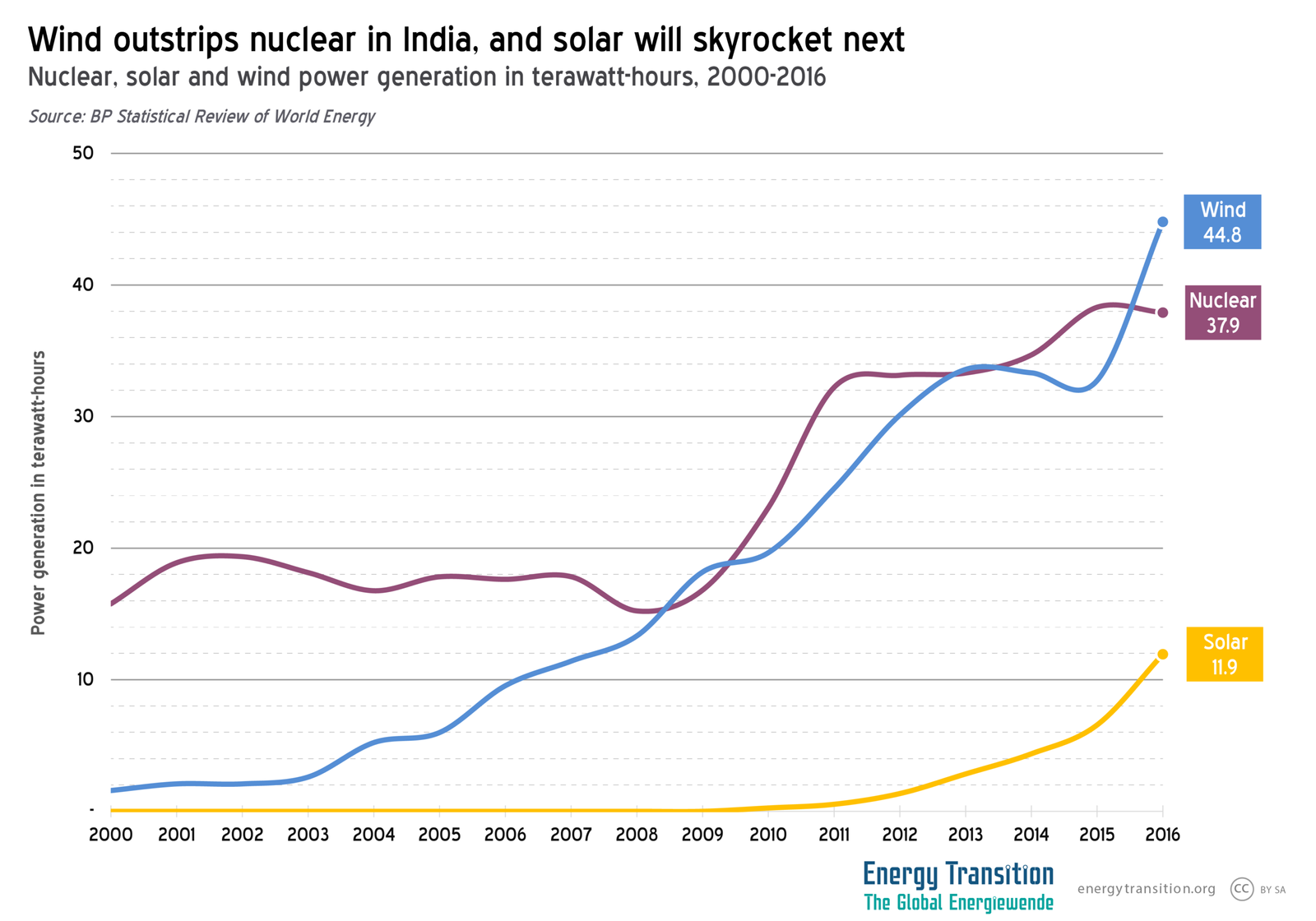
Q4. What is the significance of solar energy initiatives in India’s transition?
- India leads global solar diplomacy through the International Solar Alliance.
- One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG) supports cross-border solar integration.
- The Solar Parks Scheme enables large-scale, cost-efficient solar deployment.
Q5. Why is nuclear energy included in India’s clean energy roadmap?
- Nuclear energy provides firm, non-fossil baseload power.
- India plans to triple nuclear capacity to 22.5 GW by 2032.
- Long-term vision targets 100 GW nuclear capacity by 2047 under the Nuclear Energy Mission.
- It supports grid stability alongside variable renewables.
Q6. How do global partnerships strengthen India’s renewable transition?
- Global Biofuel Alliance enhances fuel security and technology cooperation.
- India steers clean energy dialogue through the G20 Energy Transitions Working Group.
- LeadIT supports industrial decarbonisation globally.
Q7. What are the key challenges in sustaining India’s renewable energy transition?
- Grid integration challenges due to intermittency of renewables.
- High upfront costs for energy storage and green hydrogen infrastructure.
- Dependence on imported critical minerals and advanced technologies.
- Regulatory and land-acquisition bottlenecks at state levels.
Q8. What should be the way forward for India’s renewable transition?
- Accelerate grid modernisation and battery storage deployment.
- Strengthen domestic manufacturing of critical minerals and components.
- Align renewable expansion with industrial decarbonisation and employment generation.
- Enhance policy certainty and centre–state coordination.
Conclusion
India’s early achievement of its renewable energy target demonstrates credible climate leadership. Sustained reforms, grid upgrades, and global partnerships are essential to translate this momentum into long-term energy security and net-zero pathways.
You Can Also Read |
|
| UPSC Foundation Course | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |
| Free MCQs for UPSC Prelims | UPSC Test Series |
| Best IAS Coaching in Delhi | Our Booklist |