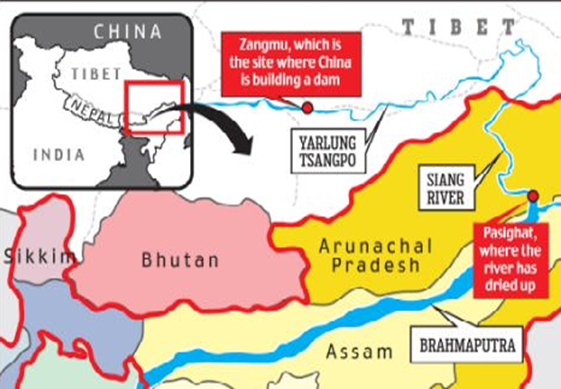
Latest Context:
Recently, India proposed to construct a barrage on Siang River to save it from hazards posed by Chinese dam being built in the Tibet region.
About Siang River
- Also known as the Tsangpo River in Tibet and is one of the major rivers in northeastern India and southern Tibet.
- It is a transboundary river that flows through both India and China before eventually joining the Brahmaputra River in Assam.
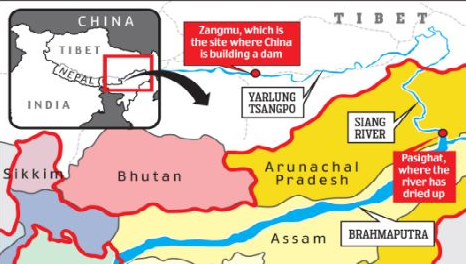
Some details details about the Siang River:
- Origin: The Siang River originates in the vicinity of the Mansarovar Lake in Tibet. It flows eastward through Tibet before entering India’s Arunachal Pradesh.
- Name: In Tibet, the river is known as the Tsangpo River. As it enters India, it becomes the Siang River. Further downstream, after its confluence with the Lohit and Dibang Rivers, it becomes the Brahmaputra River.
- Geography: The Siang River flows through rugged and mountainous terrain in the eastern Himalayas. It passes through deep gorges and canyons, making it a challenging river to navigate.
- Tributaries: Several major tributaries, including the Lohit River and the Dibang River, join the Siang River in Arunachal Pradesh. These tributaries significantly contribute to the flow of the river.
- Ecological Importance: The Siang River and its tributaries are ecologically significant, as they flow through a region rich in biodiversity. The river basin is home to diverse flora and fauna, including various species of fish and other aquatic life.
- Hydroelectric Potential: Due to its swift flow and significant drop in elevation, the Siang River has a considerable hydroelectric potential. There have been proposals to construct hydroelectric dams along its course, which has raised environmental concerns and debates.
- Cultural Significance: The Siang River holds cultural and religious significance for the people living in the region, particularly in Tibet. It is associated with Tibetan Buddhism and is considered sacred by many.
- Navigation: The Siang River is not widely used for navigation due to its challenging terrain and rapids. However, it has the potential for adventure tourism, such as rafting and kayaking, for those seeking challenging water sports.
Impact of China’s mega dam on India
- Water Flow and Disruption: One of the most significant concerns for India is the potential alteration of the natural flow of the Siang River and its downstream continuation as the Brahmaputra River. The construction of dams in Tibet could lead to changes in water flow patterns, which can affect water availability downstream. This can have serious consequences for agriculture, fisheries, and overall water supply in northeastern India and Bangladesh.
- Hydropower Generation: China’s dam projects on the Siang River have the potential to generate a significant amount of hydropower. While this can be a source of clean energy, it can also raise concerns in India if the dam reduce the downstream flow of water. India relies on the Brahmaputra for its own hydropower projects in the northeastern states, and any reduction in water flow can impact these projects.
- Environmental Concerns: Large dam construction can have detrimental environmental impacts. It can lead to habitat destruction, changes in sediment flow, and the potential for landslides. These changes can affect the ecology of the region, particularly in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Geopolitical Tensions: The construction of dams by China in the Tibetan plateau has been a source of geopolitical tensions between the two countries. Disputes over water resources in the region have the potential to worsen India-China relations.
- Water Security: India is concerned about its water security, particularly in the northeastern states. Any significant changes in water flow in the Brahmaputra River system can affect the availability of water for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use in the region.
- Environmental Impact on Downstream Nations: Beyond India, downstream countries like Bangladesh also rely heavily on the Brahmaputra River for water resources. Changes in water flow due to dams in Tibet can affect these nations as well, potentially leading to regional conflicts over water resources.
Conclusion and Way Forward:
To address these concerns, India has been engaged in diplomatic discussions with China on issues related to transboundary rivers, including the Brahmaputra. These discussions aim to promote transparency, data sharing, and cooperative management of shared water resources. However, reaching mutually agreeable solutions can be complex, and the impacts of China’s dam construction projects remain a subject of ongoing concern in the region.







