- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India’s Trade Gap Reduces
India’s Trade Gap Reduces
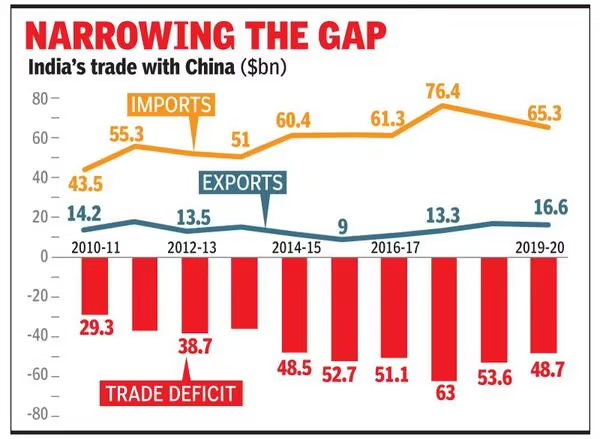
Why in the News?
- India’s total trade deficit fell to $6.6 billion in May 2025, which is 30% less than in May 2024.
- This happened mainly because:
- Oil prices fell, so India had to spend less on oil imports.
- Service exports did well, especially in sectors like IT and business services.
|
TTrade Deficit:
|
Key Highlights
- Export Growth
- Total exports rose 2.8% to $71.1 billion in May 2025 (from $69.2 billion in May 2024).
- Service exports were the major contributor, growing by 9.4% to $32.4 billion.
- Merchandise exports, however, contracted 2.2% to $38.7 billion.
- Non-Petroleum exports grew 5.1% in May 2025.
- Import Trends
- Total imports in May 2025 saw a slight decline.
- Merchandise imports fell by 1.7% in May 2025, affected by lower oil prices.
- Non-petroleum imports grew 10% in May 2025.
- Services imports rose 1.5% in May 2025..
- Trade Balance Overview
- Positive trade balance in services helped offset merchandise trade deficit.
Key Terms:
|
Implications for India:
- Reduced Trade Deficit is a good sign for the Indian Economy:
- India’s services sector is doing well, even when goods exports are not.
- This helps balance the trade.
- The surplus in services helps to cover up merchandise deficit.
- Helps Reduce Current Account Deficit (CAD):
- A current account deficit occurs when the total value of goods and services a country imports exceeds the total value of goods and services it exports.
- A smaller trade deficit means less money is going out of the country.
- This is good for India’s economy.
- India still depends on Global Prices:
- India’s exports still depend a lot on world prices, especially oil.
- If oil prices go up or down, India’s trade gets affected.
Challenges and Way Forward:
|
Challenges |
Way Forward |
|
1. Oil Price Volatility: Global oil prices keep changing, raising India’s import bill, especially for crude oil. |
1. Diversify Export Basket: Boost non-oil exports like electronics, pharma, green tech to reduce dependency on oil. |
|
2. Low Merchandise Export Growth: India’s goods exports are weak and less competitive globally. |
2. Make Exports Competitive: Improve product quality, support MSMEs, and sign trade agreements |
|
3. Overdependence on Services Exports: Too much reliance on IT & service exports is risky in global slowdowns. |
3. Balanced Export Strategy: Strengthen manufacturing exports to reduce risk from service dependency. |
|
4. High Dependence on Imports: India imports many essential items like electronics, fuels, chips. |
4. Import Substitution: Promote domestic production of key goods (like semiconductors, solar modules) under schemes like PLI. |
|
5. Weak Trade Infrastructure: Poor logistics, port delays, and high costs affect trade. |
5. Improve Trade Infrastructure: Build better ports, roads, and digital systems to lower cost and time. |
|
Ensure IAS Mains Question: Q. India’s trade performance in recent months shows contrasting trends in goods and services. Analyse the reasons and suggest steps to strengthen overall export growth.(150 words) |
|
Ensure IAS Prelims Question: Q. With reference to India’s trade trends in May 2025, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer: b Explanation: Statement 1 is correct: In May 2025, service exports grew by 9.4%, while merchandise exports contracted by 2.2%, indicating stronger performance of services over goods. Statement 2 is incorrect: Non-petroleum imports actually increased by 10% in May 2025, showing higher demand for non-oil goods. Statement 3 is correct: The surplus in services trade helped offset the deficit in merchandise trade, leading to an overall narrowing of India’s trade deficit to $6.6 billion. |
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |




