- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
INDIA RECORDS HIGHEST NUMBER OF FAILED DOPE TESTS AMONG COUNTRIES
INDIA RECORDS HIGHEST NUMBER OF FAILED DOPE TESTS AMONG COUNTRIES
07-04-2024
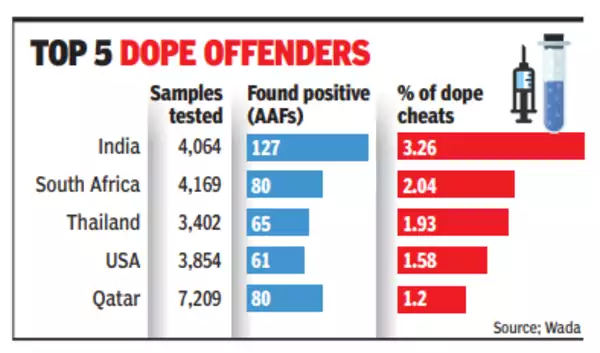
- India has emerged as the country with the highest percentage of doping offenders, according to the 2022 testing figures released by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).
- The report revealed that out of 4,064 samples collected from Indian athletes (including urine, blood, and athlete biological passports), 127 individuals tested positive for banned substances.
- South Africa follows India as countries with the highest number of athletes testing positive for banned substances.
World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA)
- WADA's Role:
- Established: 1999 as an independent international agency to combat doping in sports.
- Primary Objectives: Develop and harmonize anti-doping rules and policies across all sports and countries.
- Key Activities:
- Scientific Research: Conduct and support research to detect and prevent doping.
- Education: Promote anti-doping awareness and education among athletes, coaches, and other stakeholders.
- Capacity Building: Assist in developing anti-doping capacities and infrastructure in different countries.
- Code Monitoring: Monitor the implementation of the World Anti-Doping Code, which harmonizes anti-doping policies globally.
- Formation and History:
- In 1998, the International Olympic Committee (IOC) convened the First World Conference on Doping in Sport in response to the cycling doping scandals.
- The conference concluded with the Lausanne Declaration, which called for the creation of an independent international anti-doping agency.
- WADA's Establishment: WADA was established on November 10, 1999, in Lausanne, Switzerland, to coordinate the global fight against doping in sports.
- Organizational Structure:
- Headquarters: Montreal, Canada
- Legal Status: Swiss private law, not-for-profit foundation
- Governance:
- Foundation Board (Board): Comprises 42 members representing the Olympic Movement and governments from various continents.
- Executive Committee (ExCo): A 16-member committee responsible for managing and running the agency.
FAQs:
Q1: What is the International Olympic Committee (IOC)?
- The International Olympic Committee is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. Founded in 1894 by Pierre de Coubertin and Demetrios Vikelas, it is the authority responsible for organising the modern Olympic Games.
- The IOC also decides the rules and regulations of the Olympic Games, and decides when and where the next Olympics event will be held.
The IOC's mission is to:
- Promote Olympism
- Support ethics and good governance in sport
- Support the education of youth through sport
- Ensure fair play and avoid violence
- Protect clean athletes
- Encourage the development of sport for all
- Promote sustainable development in sport
Q2: What is athlete biological passport ?
An athlete biological passport is an individual electronic record for professional athletes, in which profiles of biological markers of doping and results of doping tests are collated over a period of time.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



