- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
INDIA-NEPAL COOPERATION
INDIA-NEPAL COOPERATION
05-06-2023

Latest Context
During the four-day visit of Nepal's prime minister to India, India and Nepal recently launched a number of initiatives and agreements designed to further their bilateral cooperation in the areas of energy and transport development, intending to deepen ties and promote regional connectivity.
Major Highlights of Recent Agreement
Power Sector Cooperation:
- Long-Term Power Trade Agreement: A long-term power trade agreement between India and Nepal aims to buy 10,000 MW of electricity from Nepal over the next years.
Hydropower Projects:
- For the development of the Lower Arun Hydroelectric Project and the Phukot Karnali Hydroelectric Project, Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) were signed by Vidyut Utpadan Company Ltd. in Nepal and National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC) in India.
- The Pancheshwar multipurpose project, which aims to improve collaboration in using the shared water resources of the Mahakali River, was also discussed by the two prime ministers. They both underlined their intention to making real, time-bound progress on the project.
- With an average annual yield of around 2448 GWh, the Phukot Karnali Hydroelectric Project seeks to produce 480 MW of power using the flow from the Karnali River. It has an underground power plant as well as a tall RCC (Reinforced Concrete Cement) dam.
Transport Development:
- Transmission Line and Rail Link: Focus on improving connectivity between the two nations was underlined by the groundbreaking ceremony for the Gorakhpur-Bhutwal Transmission Line and the launch of the Indian Railway freight train from Bathnaha to Nepal Customs Yard.
- Integrated Checkposts (ICPs): ICPs were launched in Rupaidiha (India) and Nepalgunj (Nepal), fostering easier cross-border trade and easing the flow of people and goods.
Other Initiatives:
- A plan to add 69 km to the first petroleum pipeline that crosses borders in South Asia, running from Motihari in India to Amlekhgunj in Nepal, all the way up to Chitwan.
- A second cross-border petroleum pipeline from Siliguri in India to Jhapa in eastern Nepal.
- Nepal will have access to India's inland waterways thanks to a revised Treaty of Transit signed on June 1st, 2023.
- As a result, Nepal would be able to do trade with other countries using Indian ports including Haldia, Kolkata, Paradip, and Visakhapatnam.
- Additionally, it will reduce Nepalese exporters and importers costs and time on transit.
- India and Nepal are working together to establish a fertiliser plant, highlighting the value of cooperation in the agriculture industry.
Other Areas of Cooperation Between India and Nepal
- India and Nepal are close neighbours and enjoy special bonds of friendship and collaboration that are distinguished by an open border and deep-rooted people-to-people contacts of kinship and culture.
- The foundation of the unique ties that exist between India and Nepal is the India-Nepal Treaty of Peace and Friendship of 1950.
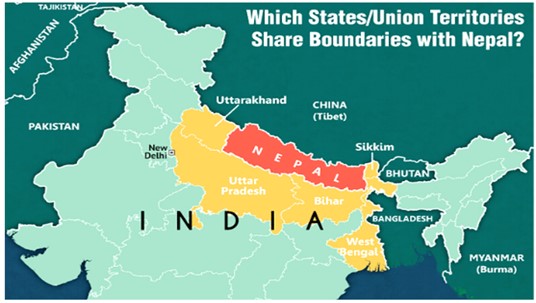
- Over 1850 kilometres of border separates Nepal from Sikkim, West Bengal, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Uttarakhand in India.
- People have been able to cross the border freely for a very long time.
Defence Cooperation:
- India has been giving training and equipment to aid the Nepal Army (NA) in modernising.
- 'Indo-Nepal Battalion-level Joint Military Exercise Surya Kiran' is alternately held in India and Nepal.
- Additionally, the Indian Army now employs roughly 32,000 Gorkha soldiers from Nepal.
Economic Cooperation:
- India is the largest trading partner of Nepal.India's 11th-largest export market is Nepal.
- India exported items worth USD 8 billion to Nepal in 2022–2023 while importing USD 840 million.
- With more than 30% of all permitted foreign direct investments in Nepal coming from Indian companies, they are among the biggest investors in that country.
Cultural Cooperation:
- Given that Buddha was born in Lumbini, which is today's Nepal, India and Nepal have close links to Hinduism and Buddhism.
- In August 2007, the Swami Vivekananda Centre for Indian Culture was established in Kathmandu to highlight the greatest aspects of Indian culture.
- In 1951, Kathmandu saw the founding of the Nepal-Bharat Library. It is thought to be the country of Nepal's first foreign library.
Humanitarian Assistance:
- As part of its commitment towards assistance and rehabilitation after the 2015 earthquake, India has given Nepal 1.54 billion Nepalese Rupees (about 96 crore INR).
Major Challenges Related to India-Nepal Relations
Boundary Dispute:
- One of the controversial issues that has strained India-Nepal ties in recent years is the border dispute. The Kalapani-Limpiyadhura-Lipulekh trijunction area in western Nepal and the Susta area in southern Nepal are the two primary areas of disputes.
- Based on several historical maps and treaties, both nations claim that these lands belong to their respective countries.
- When India opened a road connecting Dharchula in Uttarakhand with Lipulekh pass close to the China border, which Nepal opposed to as an invasion of its sovereignty, the controversy erupted.
- A new political map of Nepal was then published, showing Kalapani-Limpiyadhura-Lipulekh as a part of its territory. As an "artificial enlargement" of Nepalese claims, India rejected this map.
China’s Rising Footprints:
- India is concerned about the region's strategic interests in light of China's growing influence in Nepal. Through projects under its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), such as railways, highways, hydropower plants, etc., China has extended its economic relationship with Nepal.
- Nepal's status as a buffer state between China and India may be weakened by growing collaboration between the two countries.
Way Forward
- Increasing Digital Connectivity: Promoting projects to increase digital connectivity might be a creative approach to interact with Nepal.
- India can encourage e-governance projects, assist Nepal in building its digital infrastructure, and promote international digital cooperation. This might improve connection, open up new economic opportunities, and improve bilateral relationships.
- Strategic Partnerships: On national and international levels, India should actively seek out strategic alliances with Nepal. Both nations may show their dedication to shared values and interests by coordinating their efforts and addressing issues like climate change, disaster preparedness, and regional security.
- In addition to balancing China's influence, this will increase regional stability. In order to promote India's rich legacy, collaborative cultural events, film festivals, and health retreats might have an impact on public opinion.

Q. Consider the following pairs: (2016)
Community sometimes in the affairs of mentioned in the news
1.Kurd — Bangladesh
2.Madhesi — Nepal
3.Rohingya — Myanmar
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
Ans: (c)



