- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
HUMAN-ANIMAL CONFLICT IN INDIA
HUMAN-ANIMAL CONFLICT IN INDIA
02-03-2024

Key Issues:
- India's wildlife heritage is endangered by escalating human-animal conflict driven by habitat loss and encroachment.
Key Animals:
-
Elephants:


- India has ~30,000 wild Asian elephants.
- Over 500 humans and 100 elephants die annually in conflicts.
- Causes of death: poaching, poisoning, electrocution, train collisions.
-
Tigers:
-

- India holds 75% of the world's wild tiger population.
- 125 humans killed in reserves between 2019-2021.
- Maharashtra accounts for nearly half of these deaths (61).
Causes
-
Habitat loss and fragmentation: mining, quarrying, development, encroachment.
-
Retaliatory killings by humans.
-
Noise and light disturbances from human activities.
Focus: Assam
-
Highest elephant population density in India.
-
48 of India's 150 elephant corridors (a 40% increase since 2010).
-
Human-tiger conflict is less common in this region.
Conflict Mitigation Efforts
-
Community-based guarding and warning systems.
-
Solar-powered fences.
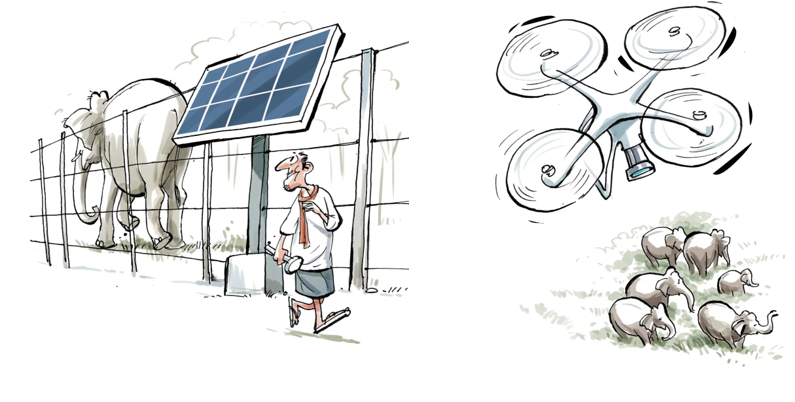
-
Lemon tree cultivation (natural deterrent).
-
Beehive fencing.
-
Haati Mitra initiative (elephant movement monitoring).




