- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
How Lightning Rods Prevent Lightning Strikes from Reaching People
How Lightning Rods Prevent Lightning Strikes from Reaching People
- With climate change, the frequency and intensity of lightning strikes around the world have been increasing.
- Every year, about 24,000 people are killed by lightning strikes globally, and in India, 2,887 people were killed in 2022 alone.
- Due to this growing danger, there have been calls to treat lightning as a natural disaster in India to help survivors access better protection and rehabilitation.
- In this context, lightning rods have become a critical tool to protect people from lightning strikes by guiding the energy safely into the ground.
What is Lightning?
- Lightning is a high-energy electrical discharge between charged particles in a cloud and the ground.
- Typically, the air around us is an electrical insulator, meaning it does not conduct electricity. However, when electrical energy builds up in the air to 3 million volts per meter, the air can break down and allow electricity to flow.
- Lightning strikes happen when electrical charges in clouds grow so strong that the air can no longer stop them from discharging to the ground.
What is a Lightning Rod?
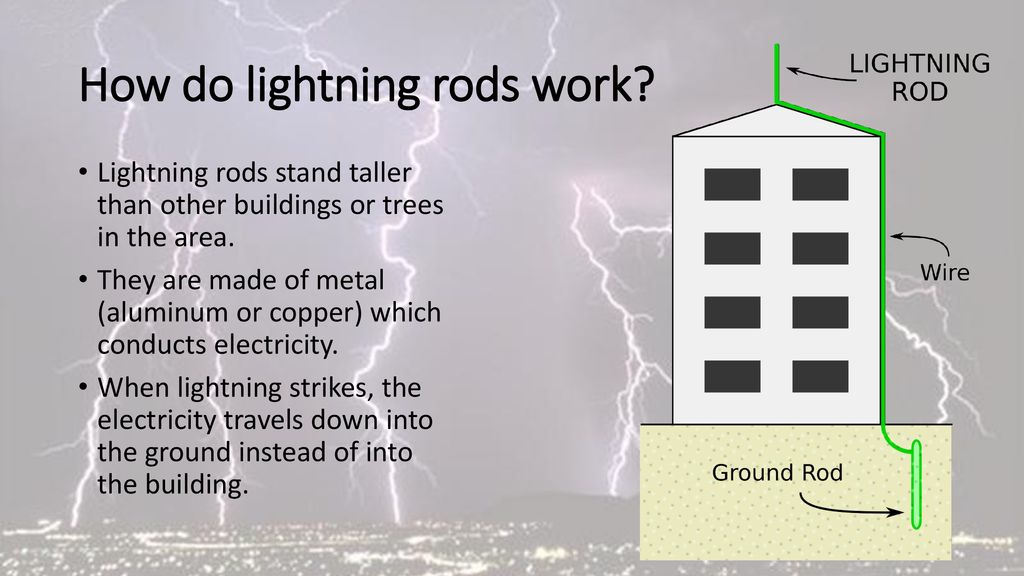
A lightning rod is a metal conductor designed to protect buildings and structures from lightning strikes.
- Lightning always follows the path of least resistance, meaning it will strike the object that provides the easiest route for electrical current.
- Lightning rods are designed to be pointed (sharp tips), which creates a stronger electric field around them.
- This makes it easier for the lightning to "choose" the rod over other objects nearby.
- How the Rod Works:
- Think of the lightning rod as a guide for lightning. When lightning strikes, it is as if the lightning is looking for the strongest point to make contact. The sharp tip of the lightning rod is the first object it will encounter.
- A professor at IIT Kanpur, explains that pointed objects, like lightning rods, create stronger electric fields, which ionize (or charge) the air near them. This ionized air acts as a pathway for the lightning to travel down safely.
Where Does the Current Go After the Lightning Strikes the Rod?
When lightning strikes a rod, it carries the electric charge safely into the ground. Here’s how:
- Flow of Current:
- Just like heat moves from a hot object to a cooler one, electricity flows from a place with higher electric potential (where the charge builds up) to a place with lower electric potential (the ground).
- The earth is a natural, infinite source of low electrical potential, so it can easily absorb the lightning’s charge.
- How the Current is Dissipated:
- The lightning rod is connected to a wire that runs down the building into the earth, where the charge is safely spread out.
- Lightning arresters are special devices that prevent lightning from damaging electrical systems by diverting the current away from sensitive equipment.
Can Lightning Evade a Lightning Rod?
Yes, a lightning strike can avoid a lightning rod if certain conditions are not met:
- Improper Installation: If the rod is too short, too far from the structure, or not properly grounded, lightning may not strike it.
- Environmental Factors: If multiple thunderstorms are happening nearby, the lightning may prefer other objects or structures to the rod.
- If the rod is damaged, corroded, or misshapen over time due to lack of maintenance, it may not be able to attract lightning effectively.
- In some cases, the ground might send out an upward discharge that meets the lightning before it reaches the rod. This can bypass the rod.
- Attraction to Taller Structures: If a tall building or nearby tree is more attractive to lightning, it might strike them instead of the rod.
Engineers have developed new techniques to improve the effectiveness of lightning rods, such as ensuring that the rod is positioned at the best possible height and angle to attract lightning first.
Dangers Posed by Lightning Rods:
While lightning rods protect buildings from lightning strikes, they need to be carefully designed and installed to avoid causing additional hazards:
- Arcing: If the wire connected to the rod bends into a U-shape, the current can arc between the two arms, causing short circuits or fire risks.
- Electrical Safety: The wire must be installed in a way that it doesn’t cause the current to arc to other nearby objects or people.
- Grounding:
- To safely dissipate the electric charge, engineers bury the grounding wire in materials with good electrical conductivity.
- Herbert Ufer, a U.S. engineer, developed the concrete-encased electrode system, which improves the efficiency of grounding by using concrete to enhance the conductivity.
- Standards and Regulations:
- The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) provides global standards for designing and installing lightning rods to ensure safety and effectiveness.
- These standards guide engineers on where to place lightning rods, how to design them, and how to estimate the risk of lightning strikes in different areas.
Conclusion
Lightning rods are essential tools for protecting buildings and people from lightning strikes. They safely guide the dangerous electrical energy of a lightning strike into the ground, preventing damage and harm. However, they must be designed and maintained properly to be effective. With the increasing frequency of lightning strikes due to climate change, understanding how lightning rods work and ensuring their proper installation can help save lives and reduce damage from this natural hazard.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus




