- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Heat Wave Conditions
Heat Wave Conditions

Latest Context
Currently, Since April 2023, Odisha is facing an intense heatwave, with the rising temperatures crossing 40°C in most monitoring centres across the state. This heat wave is the result of a delayed monsoon. On June 8, the monsoon arrived over the Kerala coast which is delayed in comparison to its normal onset date of June 1.
Conceptual Framework of Heat Waves: Heatwaves are referred to as prolonged durations of excessively hot weather which severely affect human health, the economy, and the environment, in India. Being a tropical country, especially India is highly vulnerable to heatwaves that have become more frequent and intense in recent years.
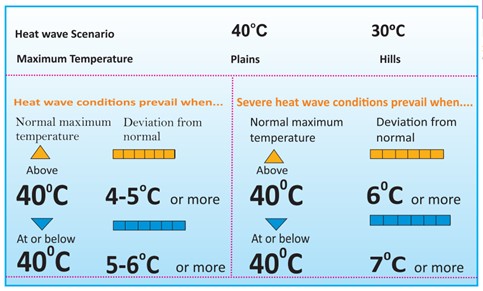
IMD Criteria for Declaring Heat Wave in India:
- Heat Waves are determined on the basis of temperature. When the maximum temperature of a station reaches at least 40°C for Plains and at least 30°C for Hilly regions.
- If a station’s normal temperature is less than or equal to 40°C, then a 5°C to 6°C increase in it from the normal temperature is called a heat wave condition.
- Further, a severe heat wave condition is characterized by an increase of 7°C or more from the normal temperature.
- Additionally, if irrespective of normal maximum temperature, the actual maximum temperature remains 45°C or more, then a heat wave is declared.
Reasons for Heat Waves
- Sparse Pre-Monsoon Season Showers: Large parts of India remain arid and dry due to less moisture. An uncommon trend in India is the sudden end of pre-monsoon rain showers that contributed to the heat waves.
- Global Warming: Global warming is one of the major factors of heat waves in India. Human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial activities cause the long-term increase in Earth's average temperature which is known as Global warming. It may cause higher temperatures and changes in weather patterns resulting in heat waves.
- Urbanization: "Urban heat island effect" is the result of rapid urbanization and the growth of concrete jungles in cities. Due to having high population density, buildings, and concrete surfaces Urban areas absorb and retain more heat which leads to high temperatures, particularly during heat waves.
- El Nino: Increased temperature due to El-Nino and combining it with the weather pattern in Asia create record-high temperatures. During the Southwest Monsoon, trade winds coming from South America normally blow westward towards Asia and the warming of the Pacific Ocean results in the weakening of these winds. Hence, heat content and moisture get limited and result in reduction and uneven distribution of rainfall across the Indian subcontinent.
Effects of Heat Waves:
- Water Resources: They can increase water scarcity, reduce water availability for agriculture and domestic use, dry up water bodies, and increase competition for water resources. As a result, it may lead to conflict over water, and impact water-dependent industries, negatively impacting irrigation practices.
- Health: Heat Waves may lower the human body’s ability to control temperature and can result in many diseases like heat cramps, heatstroke, heat exhaustion, and hyperthermia. Severe heat waves may lead to hospitalizations extremely rapidly or have a lagged effect.
- Energy: Heatwaves may enhance the electricity demand from a cooling point of view which may cause high strain on power grids and potential blackouts. It can destabilize the whole economy, negatively affecting productivity and vulnerable populations who are not having access to reliable electricity for cooling during heatwaves.
Way Forward
- A Heat Waves Action Plan: Deaths due to heat waves can be controllable. It is the need of the hour on the part of the government to prioritize a long-term action plan to protect human lives, wildlife, and livestock. Attention must be paid to Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-30. The state must play a very critical role and share responsibility with other stakeholders.
- Implementing Climate Action Plans: In true spirit, National Action Plan for Climate Change (NAPCC) must be implemented for inclusive growth and ecological sustainability. Nature-based solutions must be taken into consideration in order to handle climate change caused by heat waves in such a way that is ethical and promotes intergenerational justice.
- Sustainable Cooling: A widely-used strategy known as Passive cooling technology to build naturally ventilated buildings can be a vital alternative to address the urban heat problems for residential and commercial buildings. In the third part of its AR6, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) stated that ancient Indian building designs that have used this technology can be moulded to modern facilities in the context of global warming.

Prelims
Q. What are the possible limitations of India in mitigating global warming at present and in the immediate future? (2010)
1. Appropriate alternate technologies are not sufficiently available.
2. India cannot invest huge funds in research and development.
3. Many developed countries have already set up their polluting industries in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Bring out the causes for the formation of heat islands in the urban habitat of the world. (2013)



