- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Growing burden of Non-Communicable Diseases in India
Growing burden of Non-Communicable Diseases in India
19-06-2023


Latest Context:
As per a recent study conducted by the Madras Diabetes Research Foundation along with the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and Ministry of Health and Family Welfare mentioned the growing burden of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) in India.
So, What are Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)?
- Non-communicable diseases (NCDs), also known as chronic diseases, are medical conditions that are not directly transmitted from person to person.
- These diseases typically develop over a long period of time and are generally of long duration.
- Unlike communicable diseases (such as influenza or tuberculosis), NCDs are not caused by infectious agents like bacteria or viruses.
- Risk factors for non-communicable diseases include unhealthy lifestyle choices (e.g., tobacco and alcohol use, poor diet, physical inactivity), environmental factors, genetic predisposition, aging etc.
- Preventive measures and early detection play a crucial role in managing and reducing the impact of NCDs on individuals and societies.
Some common examples of Non-Communicable Diseases include:
- Cardiovascular diseases: These include conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, such as heart disease, stroke, hypertension (high blood pressure), and coronary artery disease.
- Cancer: This term refers to a broad range of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. Examples include lung cancer, breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and prostate cancer.
- Chronic respiratory diseases: Conditions such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), asthma, and chronic bronchitis fall under this category. These diseases affect the lungs and airways, leading to breathing difficulties.
- Diabetes: A chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels due to inadequate insulin production or ineffective use of insulin. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form.
- Chronic kidney disease: This refers to the progressive loss of kidney function over time. It can lead to complications like kidney failure, requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant.
- Neurological disorders: Diseases affecting the brain and nervous system fall into this category. Examples include Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, and multiple sclerosis.
- Musculoskeletal disorders: Conditions affecting the muscles, bones, and joints, such as arthritis, osteoporosis, and back pain, are classified as musculoskeletal disorders.
- Mental health disorders: While not always considered under the umbrella of NCDs, mental health conditions like depression, anxiety disorders, and schizophrenia contribute significantly to the global burden of disease.
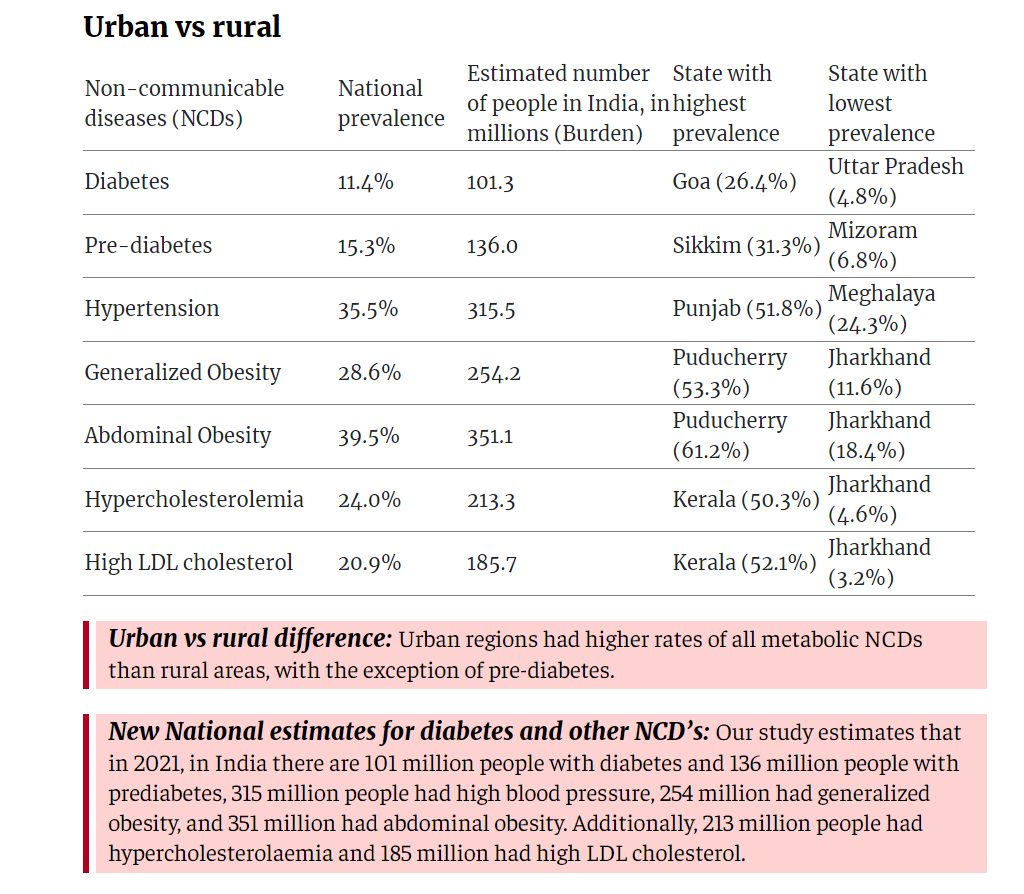
Key Findings of the Study are:
- As per the study, the states like Goa, Puducherry, and Kerala have the highest prevalence of diabetes.
- Diabetes: Presently, India have almost 100 million people suffering from diabetes.
- Prediabetes: Almost 135 million people are in the prediabetes stage in India.
- High blood pressure: Almost 315 million people are suffering from high blood pressure.
- Obesity: Around 255 million people in India were classified as ‘generally obese’, while almost 350 million people are suffering from abdominal obesity.
- Hypercholesterolemia: Almost 215 million individuals have found fat accumulation in their arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- High LDL Cholesterol: Around 185 million individuals had increased levels of Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. LDL is also known as “bad cholesterol” because too much presence of it in blood can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries.
What is the Significance of the Study?
- This study was done with a large sample size of almost 1,13,000 people from diverse regions.
- The study mentioned that diseases like diabetes and other metabolic NCDs are more prevalent in India than previously estimated.
- It has been found that urban areas presently have a higher rate of metabolic NCDs, except for prediabetes.
- Rural areas are expected to experience an increase in diabetes cases in the next almost 5 years, if left unregulated.
- A lot of interstate and inter-regional variations has been found which highlighted the need for state-specific policies and actions.
- This study serves as an early warning for the people regarding the dangers of NCDs and life-altering medical conditions, including strokes.
What are Initiatives taken by India to tackle NCDs?
- National Program for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS): Launched in 2010, this program aims to prevent and control NCDs through health promotion, early diagnosis, treatment, and referral services. It focuses on strengthening infrastructure, capacity building, and creating awareness about risk factors and healthy lifestyles.
- National Tobacco Control Program (NTCP): India has implemented comprehensive tobacco control measures, including the NTCP, to reduce tobacco consumption, promote tobacco cessation, and protect non-smokers from second-hand smoke. The program includes awareness campaigns, enforcement of tobacco control laws, and support for tobacco cessation services.
- Ayushman Bharat - Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY): Launched in 2018, PMJAY is a national health insurance scheme that provides health coverage to economically disadvantaged families. It aims to ensure access to quality healthcare, including NCD prevention, diagnosis, and treatment services.
- National Mental Health Program (NMHP): The NMHP focuses on promoting mental health, preventing mental illnesses, and providing accessible and affordable mental health services. It includes initiatives for early identification and intervention, capacity building of health professionals, and community-based rehabilitation.
- Eat Right India Movement: Launched by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), this initiative aims to promote healthy eating habits and reduce the burden of NCDs related to poor nutrition. It includes various campaigns, such as the "FSSAI Eat Right Challenge," which encourages citizens to make healthier food choices.
- National Salt Reduction Initiative: To address hypertension and related cardiovascular diseases, India has initiated efforts to reduce salt consumption. The "Eat Right India" campaign includes promoting low-sodium diets, creating awareness about the harmful effects of excessive salt intake, and collaborating with food industries to reduce salt content in processed foods.
- National Programme for Health Care of the Elderly (NPHCE): This program focuses on the healthcare needs of the elderly population, including the prevention and management of NCDs prevalent among older adults. It includes screening, early diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation services tailored to their specific health requirements.


