- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Europe’s Jupiter Probe to Stage Daring Lunar-Earth Fly-By
Europe’s Jupiter Probe to Stage Daring Lunar-Earth Fly-By
26-08-2024
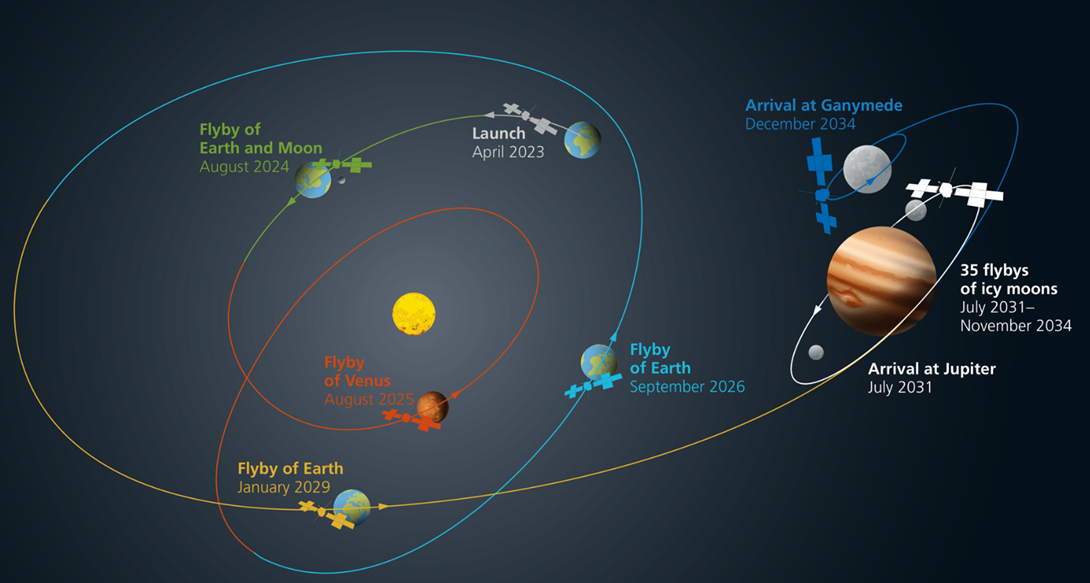
On August 19-20, 2024, European scientists conducted a groundbreaking maneuver with the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE).
- This maneuver involved a double slingshot technique, leveraging both the Moon’s and Earth’s gravity to propel the probe towards Jupiter.
- This intricate operation represents a significant advancement in orbital dynamics and space navigation.
Key Details of the Mission
JUICE Probe’s Trajectory and Maneuver:
- Launch and Approach: Launched just over a year ago, JUICE is executing a complex gravity assist maneuver. The probe is returning to Earth to utilize its gravity in a dual slingshot maneuver—a pioneering approach not previously attempted.
- Double Slingshot:
- First Phase: The probe will use the Moon’s gravity to alter its trajectory towards Earth.
- Second Phase: Earth’s gravity will then be utilized to slow down the probe, a delicate operation requiring precise execution to avoid jeopardizing the mission.
- Mission Risks and Challenges:
- Accuracy: Any miscalculation during the initial lunar assist could amplify errors, potentially derailing the entire mission.
- Propellant Needs: Adjustments and corrections will require additional propellant, making precision crucial.
Historical Context and Innovations:
- Gravity Assist Method: For decades, space missions have employed gravity assists to optimize fuel usage. This method involves using the gravity of celestial bodies to adjust speed and trajectory.
- Novel Approach: The current mission involves an unprecedented attempt to perform two consecutive gravity assists, a first in space exploration history.
Mission Goals and Objectives:
- Target Destination: JUICE aims to reach Jupiter and its three major ocean-bearing moons—Callisto, Europa, and Ganymede—by 2031.
- Further Assists: The mission plan includes additional gravity assists from Venus in 2025, and Earth in 2026 and 2029, to fine-tune the probe’s trajectory.
- Scientific Goals: Following the Galileo mission, JUICE will orbit Jupiter, conduct fly-bys of its icy moons, and finally orbit Ganymede to assess its potential for supporting life.
Scientific and Strategic Importance
Mission Planning and Strategy:
- Optimized Trajectory: Utilizing the Moon’s gravity to adjust JUICE’s path allowed ESA to optimize its trajectory to Venus, maximizing the slingshot effect and minimizing the need for large rockets.
- Configuration Advantage: The mission capitalizes on the Moon’s position relative to Earth to slow down the probe effectively, facilitating a more efficient path to its final destination.
Exploration Goals:
- Understanding Habitability: JUICE will study the conditions on Jupiter’s moons to evaluate their potential to support life, enhancing our understanding of extraterrestrial habitats.
Conclusion
The double slingshot maneuver executed by ESA’s JUICE probe is a landmark in space navigation and mission design. If successful, this maneuver will not only demonstrate advanced orbital gymnastics but also pave the way for future missions exploring the outer reaches of our solar system. The mission will build on the legacy of NASA’s Galileo, contributing valuable insights into the potential habitability of Jupiter’s moons.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus




