- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Euclid Discovers 1st Einstein Ring
Euclid Discovers 1st Einstein Ring
18-02-2025

- On February 10 2025, There was an announcement that Euclid, a space mission by the European Space Agency (ESA), has made a discovery: the detection of a rare Einstein Ring around the galaxy NGC 6505.
- Euclid is a space mission that aims to study the dark Universe.
- Its goal is to learn about mysterious forces in space, like dark energy and dark matter, by observing galaxies and their effects.
- Euclid’s instruments are designed to observe gravitational lensing.
- It will also map 1/3rd of the sky and study billions of galaxies up to 10 billion light-years away.
- The discovery was made during early testing of the mission, started in July 2023. But it was announced this year after confirmation of Einstein ring.
- In September 2023, Euclid sent some test images to Earth.
- The images were blurry at first, but there was a hint of an Einstein Ring. After more observations, the ring was confirmed.
What is an Einstein Ring?
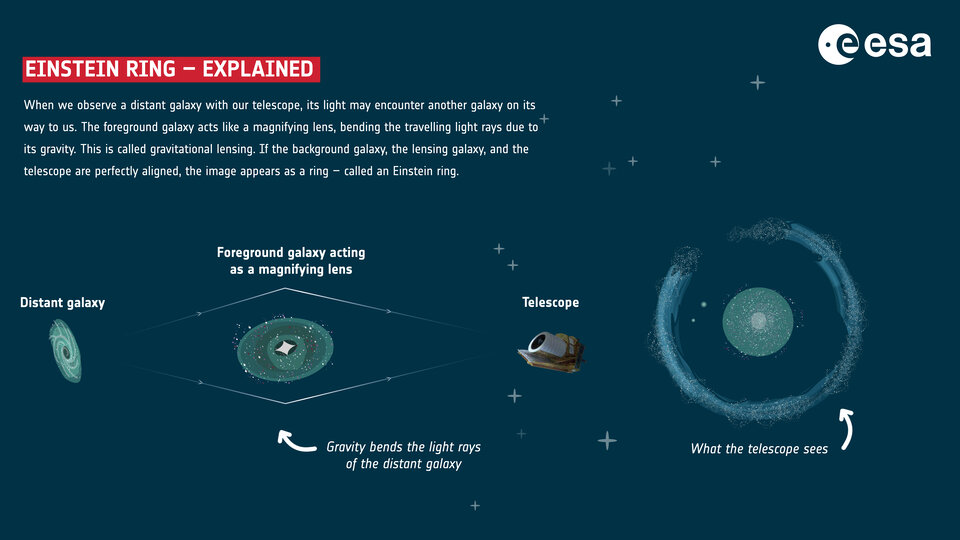
- An Einstein Ring is a theory proposed by Albert Einstein.
- An Einstein Ring is a ring of light.
- An Einstein ring is a specific example of gravitational lensing where light from a distant galaxy or other light source is bent around a closer galaxy or dark matter, forming a ring-like structure.
- This occurs when the light source, the massive lensing object, and the observer are precisely aligned.
What is Gravitational Lensing?
- Gravitational lensing happens when a massive object creates a gravitational field strong enough to warp and magnify the light from objects behind it.
- NGC 6505 acts as the gravitational lens in this scenario, distorting and amplifying the light from a distant galaxy located about 4.42 billion light-years away.
Why is this Discovery Important?
- This is the 1st time an Einstein Ring has been seen around NGC 6505.
- These rings are rare and important for understanding the Universe, as well as dark matter and dark energy.
- Dark matter is a type of matter that doesn’t emit light or energy, so we can’t see it directly. But scientists know it exists because of how its gravity affects galaxies. It makes up most of the matter in the Universe but remains invisible to telescopes.
- Dark energy is a mysterious force that is causing the Universe to expand faster and faster. Scientists don’t know much about it, but they think it makes up about 68% of the Universe.
- It's "dark" because we can’t directly see it or measure it, but its effects are visible through the speeding up of the expansion of the Universe.
- The discovery helped scientists to learn about the effects of gravity in space.
- Studying the bending light will also help understand the hidden forces, like dark matter and dark energy, that affect the Universe.
- Close to Earth: The close distance of the Einstein Ring makes it easier to study in detail compared to more distant objects.
Future Impact of the Mission
- More Discoveries Expected: The Einstein Ring is just the start. Euclid is expected to find over 100,000 strong lens effects, giving scientists lots of data to study.
- Strong lensing is a type of gravitational lensing that happens when the light bending is so strong that it forms clear and noticeable shapes, like an Einstein Ring..
- Weak lensing is a milder form of gravitational lensing where the light from distant galaxies looks slightly stretched or shifted. It’s harder to see compared to strong lensing but is useful for studying large-scale structures in the Universe.
|
Einstein's General Theory of Relativity is a scientific theory that explains how gravity works. It says that objects with mass (like planets and stars) bend space and time around them, and this bending is what we feel as gravity. It also explains how light gets bent around massive objects, like how gravitational lensing works. |
Key Facts: European Space Agency (ESA)1. Creation of ESA:
2. Origins of ESA:
3. Mission and Purpose:
4. ESA Member States:
5. Key Locations:
|
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |




