- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
ELECTRONIC INTERLOCKING SYSTEM IN INDIAN RAILWAYS
ELECTRONIC INTERLOCKING SYSTEM IN INDIAN RAILWAYS
13-06-2023
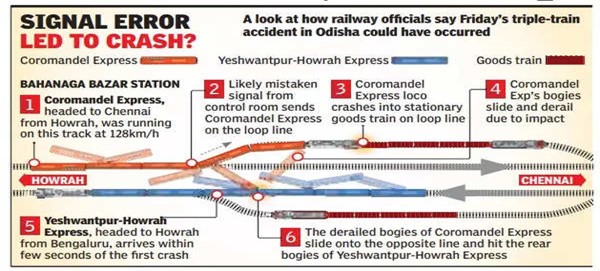

Latest Context
A devastating railway accident occurred in the Balasore district of Odisha, and the reason is being looked into. The incident has sparked questions about the electronic track management system used by the railways.
- The accident was primarily caused by a change in the electronic interlocking, according to the Indian Railway Minister.
Facts about an Interlocking System in Indian Railways
- Interlocking System refers to a crucial safety mechanism used to control train movements and ensure safe operations at railway stations and junctions.
- It is a complex network of signals, points (switches), and track circuits that cooperate to avoid collisions and incompatible motions.
- Electronic Interlocking (EI):
- It uses electrical devices and computer-based systems to manage signals, points, and level-crossing gates.
- EI manages the interlocking logic using software and electonic components, in contrast to conventional relay interlocking systems.
- EI makes sure that everything is synchronised to enable continuous train movement.
- 2,888 stations in India have electronic interlocking systems as of 2022, making up 45.5% of the Indian Railways network.
Components of Electronic Interlocking:
- Signal: Based on the condition of the track ahead, signals utilise light indications to tell trains to stop (red), go (green), or advance (yellow).
- Point: By directing the wheels in the direction of a straight or diverging path, points which are movable portions of tracks, allow trains to change lanes. Electric point switches can be locked or unlocked at the desired location.
- Track Circuit: In order to assess the safety of train operation, electrical circuits installed on tracks identify the presence of a train between two sites.
- Additional Components: Electronic control systems, communication tools, and other apparatus are kept in relay rooms with dual-lock access controls. Similar to an aircraft's black box, a data logger keeps a record of all system activity.
Functionality of the System:
- Command Reception and Route Setting:
- The automated control systems or operators provide orders to the electronic interlocking system, which then gathers data from the yard and processes it to create a safe path for trains to go.
- Alignment and Interlocking:
- The system establishes the intended route by positioning the interlocks signalling devices and essential track switches (points) at the proper locations once the route has been decided.
- Signal for Train Proceeding:
- Depending on the direction of the track and the lack of obstacles on diverging lines, trains are signalled to move forward.
- This guarantees that trains may travel the network in a secure and efficient manner.
- Collision Prevention:
- To find trains, the system makes use of track circuits.
- By keeping an eye on these circuits, the system reduces the likelihood of crashes by preventing numerous trains from operating on the same block or competing pathways.
- Point Locking:
- Until precise circumstances are satisfied, such as when the train crosses a particular piece of track or the signal to proceed is withdrawn, points (switches) are locked in place.
- This guarantees that the points are securely in place and properly aligned for train movements.
- Failure Indication:
- The system notifies operators or maintenance staff in the event of a breakdown or malfunction.
- The usage of a red-light indication, which signifies that the system has discovered a problem and the path ahead is not clear or safe, is one popular technique.
- This forces the proper steps to be done to fix the issue and guarantee safe functioning.




