- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Discovery of 'Neo' Protein
Discovery of 'Neo' Protein
08-06-2024
- Recent research has brought to light a novel protein named "Neo," which is crucial in bacterial defence against viral infections, notably bacteriophages.
- Research led by Stephen Tang and Samuel Sternberg in 2023 revealed the presence of Neo while working on Klebsiella pneumoniae.
- Klebsiella pneumoniae are a common type of bacteria found in your intestines. They are normally harmless
Neo's Mechanism:
Bacteria have a defence system called DRT-2, which helps them fight off viruses (phages). This system works by creating new DNA in a unique way:
- Regular: The DRT-2 system makes a copy of a specific RNA molecule. This copy is like a single strand of DNA. This happens all the time, even when there is no virus around.
- Virus Alarm: When a virus infects bacteria, the DRT-2 system is activated. It makes a second copy of the DNA, creating a complete double-stranded DNA molecule.
- Defense Mode: This new double-stranded DNA contains instructions to make a special protein called Neo. This protein acts like a "pause button" for bacteria, making them inactive. This prevents the virus from spreading to other bacteria.
- The gist: DRT-2 helps bacteria protect themselves from viruses, as it creates a new DNA molecule that puts the bacteria to sleep, effectively stopping the spread of the virus.
Significance of Neo:
-
Neo: A New Way to Fight Bacterial Infections:
- Scientists have discovered a protein called Neo that can help stop the growth of bacteria.
- This discovery has the potential to be used in biotechnology to create new ways of treating bacterial infections.
- Think of Neo as a potential "off switch" for harmful bacteria.
-
Shared History of Reverse Transcriptases:
- There are special enzymes called reverse transcriptases in both humans and bacteria.
- These enzymes have the ability to make DNA from RNA (the opposite of the usual process).
- Interestingly, these enzymes in humans and bacteria share a common ancestor, suggesting a shared evolutionary history.
- This means that reverse transcriptases in bacteria likely evolved into the ones found in humans today.
-
Similar Functions:
- Not only do these enzymes share a common origin, but they also work in similar ways.
- Understanding how these enzymes work in bacteria could give us insights into how they function in humans.
- This could be particularly helpful in studying certain diseases and developing new treatments.
Reverse Transcription:
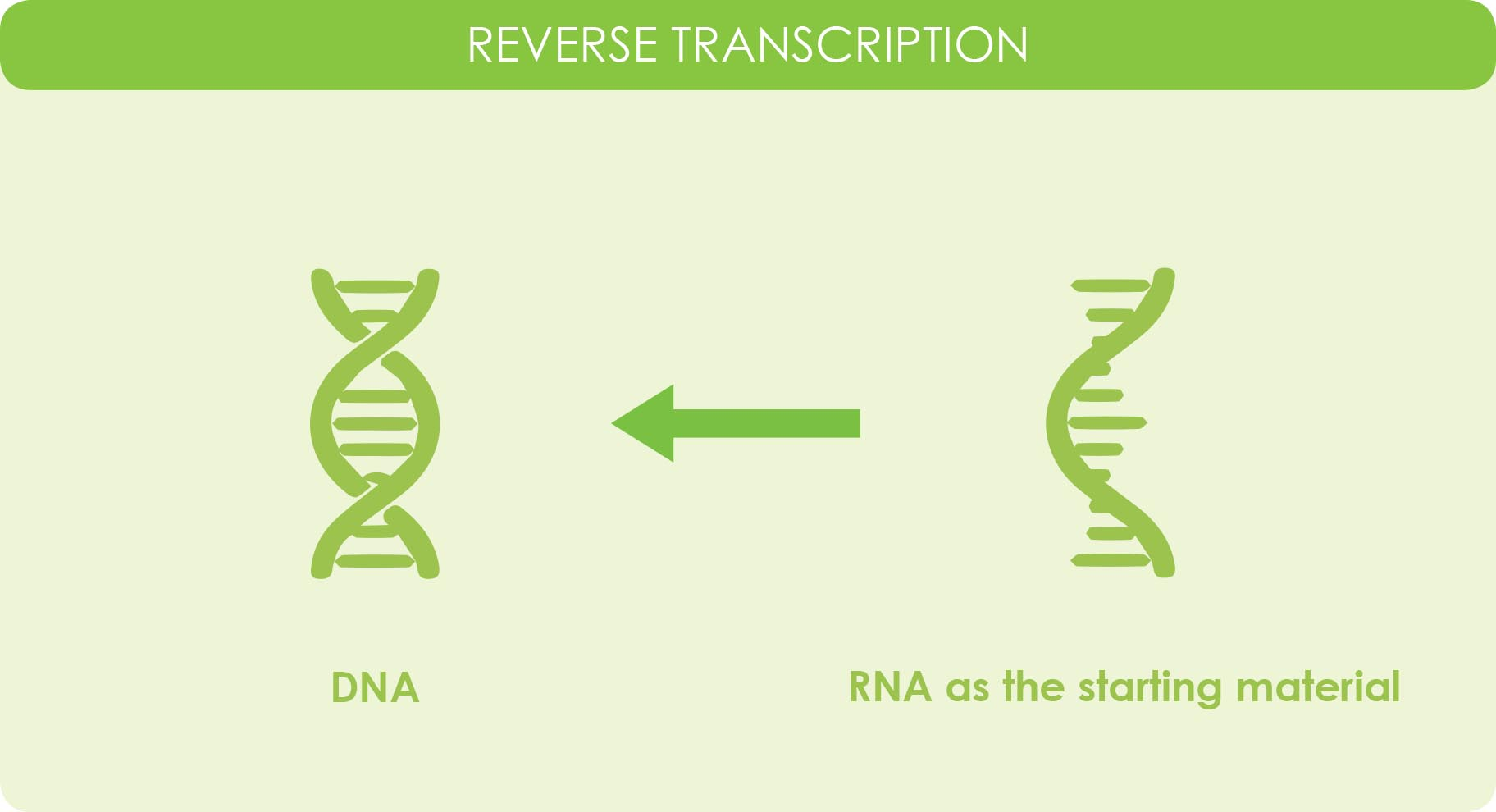
- The process of creating DNA copies from RNA is called reverse transcription, this process is performed by an enzyme called reverse transcriptase.
- Discovered by Howard Temin and David Baltimore in 1970, reverse transcriptase has been instrumental in molecular biology and the study of RNA viruses like HIV.
- It is crucial in gene cloning, PCR, and genome analysis.
- Additionally, reverse transcriptase has played a vital role in diagnostics, enabling the detection and quantification of viral loads, as seen in the case of SARS-CoV-2, and contributing to disease surveillance, public health measures, and vaccine development.
What is DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid):
- DNA is a molecule that carries genetic information, responsible for transmitting hereditary traits from parents to offspring.
- Its double helix structure is composed of nucleotides with four nitrogenous bases:
- adenine
- cytosine
- guanine
- thymine.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi


