- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Delay in Protecting Dhanauri Wetland Near Jewar Airport
Delay in Protecting Dhanauri Wetland Near Jewar Airport

- On January 22, 2025, The National Green Tribunal (NGT) asked the Uttar Pradesh government to give an update within four weeks about why the Dhanauri wetland hasn’t been officially declared a protected wetland yet.
- This order came after a petition by bird-watcher Activist, who wants the site to be declared a Ramsar site (a wetland of international importance) and a bird sanctuary.
What is the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands?
Wetlands Definition (Ramsar Convention):Areas where water is present at or near the soil surface, either year-round or seasonally (especially during the growing season). Includes wetlands like coral reefs and mangroves. Recognized internationally for biodiversity conservation and sustainable use. Types of Wetlands (Ramsar Classification)
Ecological Significance Of Ramsar sites:
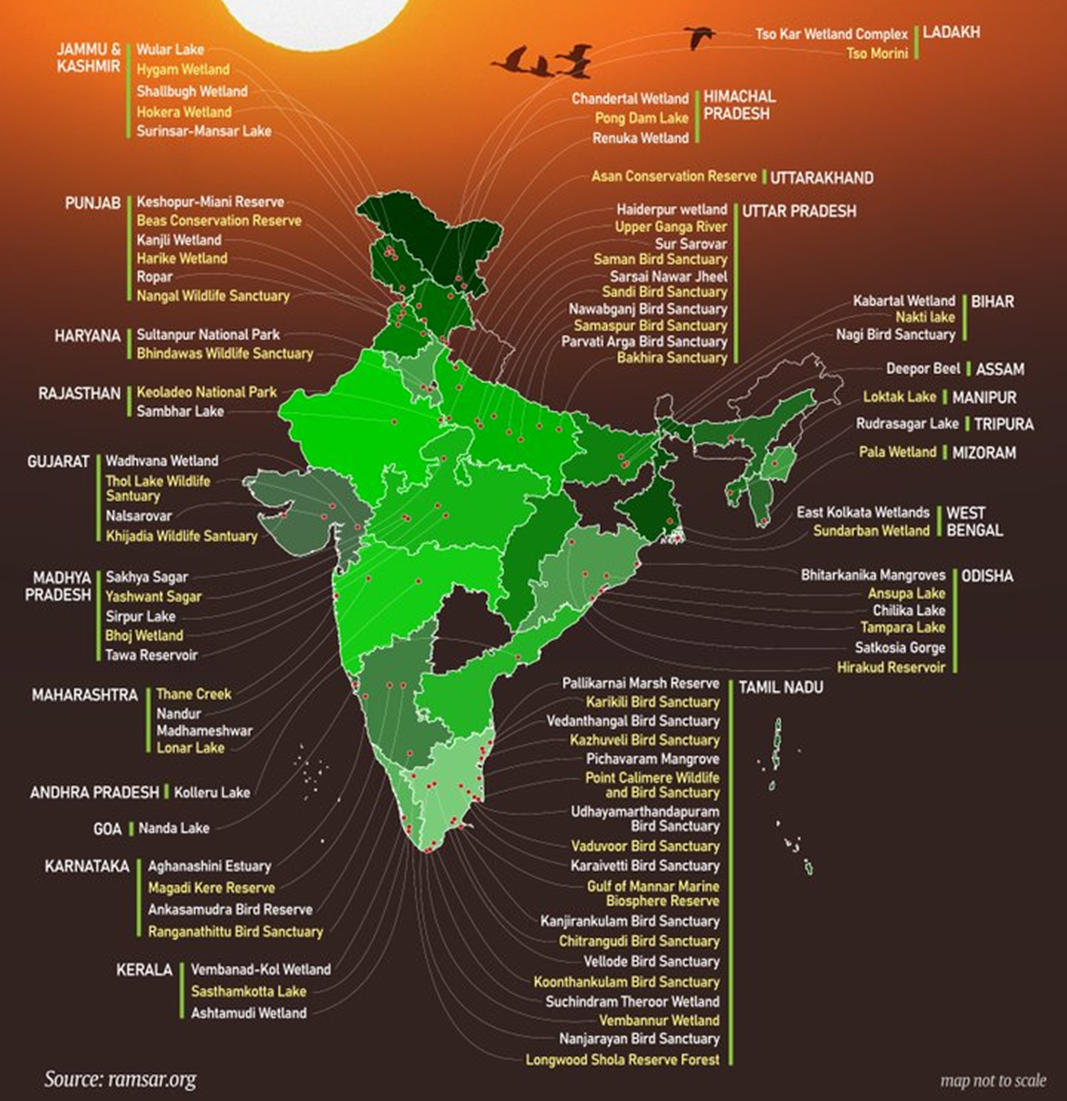
India’s Ramsar Sites (As of December 2024): Total Ramsar Sites in India: 85 (following the addition of 3 new sites). Tamil Nadu has the highest number of Ramsar sites in India, with 18 sites.1. Nanjarayan Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu)
2. Kazhuveli Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu)
3. Tawa Reservoir (Madhya Pradesh)
|
Key Points of Case:
-
Background of the Petition:
- Petitioner wants Dhanauri to be officially recognized as a Ramsar site and a bird sanctuary because of its importance for birdlife, especially migratory birds.
- If Dhanauri is declared a Ramsar site, it would get special protection.
-
NGT’s Order:
- The NGT’s bench showed concern about the delay in declaring Dhanauri as a wetland.
- The UP government had already decided to declare it a wetland, but the process hasn’t been completed.
- The NGT asked why the Uttar Pradesh Forest Department needed 3 more months to consult with local landowners before moving forward, as the decision to protect the wetland had already been made.
-
Reason for Delay:
- The Divisional Forest Officer (DFO) of Gautam Buddha Nagar stated that Dhanauri wetland covers 112.89 hectares, mostly on private land.
- The authorities need to talk to the landowners in the villages of Dhanauri Kalan, Thasrana, and Amipur Bangar to get their consent before moving forward.
- Because this process involves many landowners, the DFO asked for 3 more months to complete these consultations.
-
Impact of Jewar Airport on the Wetland:
- Dhanauri wetland is located near the site for the new Jewar Airport, a big infrastructure project in Uttar Pradesh.
- The airport was approved with conditions that require protecting the local wildlife, including the birds at Dhanauri.
- There are concerns that the airport could disturb the birds that use Dhanauri as a habitat, especially migratory birds. This could harm the wetland’s environment and biodiversity.
-
Legal Process: Who can declare a wetland?
- Wetland Notification: The state government can declare a wetland, but for a Ramsar site, the proposal must be sent to the Union Ministry of Environment, which will decide whether to grant it international protection.
Who Can Declare A Wetland Site As Ramsar Site?National government of a country that is a party to the Ramsar Convention can declare a wetland as a Ramsar site. The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) in India is responsible for this process. How the process works:
|
About National Green Tribunal (NGT):
|
Establishment |
Established in 2010 under the National Green Tribunal Act. |
|
Purpose |
Specialised body for adjudicating environmental cases and addressing multidisciplinary environmental issues. |
|
Objectives |
- Environmental protection - Conservation of natural resources - Enforcement of environmental rights and providing relief/compensation. |
|
Jurisdiction |
- Binding orders - Authority to grant compensation and damages - Cases involving environmental laws and challenges to related orders. |
|
Zones |
Principal Bench in Delhi (North Zone) Regional Benches: Bhopal (Central), Kolkata (East), Chennai (South), Pune (West). |
|
Composition |
- Chairperson: A retired Supreme Court judge or Chief Justice of a High Court, appointed by the Central Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of India, serving for five years or until age 70 - Judicial Members: 10 to 20 - Expert Members: 10 to 20 |
|
Who can approach? |
Any person seeking relief for environmental damage under laws listed in Schedule I of the National Green Tribunal Act, 2010. |
|
Relevant Laws |
- Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974 - Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980 - Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981 - Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 - Biological Diversity Act, 2002 |
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
UPSC Monthly Mgazine |
CSAT Foundation Course |
Free MCQs for UPSC Prelims |
UPSC Test Series |
ENSURE IAS NOTES |
Our Booklist |