- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
CPS of Asian Development Bank
CPS of Asian Development Bank
22-08-2023
Latest Context:
Recently, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) launched a new “Country Partnership Strategy 2023-27” for India.
Key highlights of the CPS 2023-27 are:
- The CPS 2023-2027 will give a boost to ADB’s “Strategy 2030”.
- ADB under Strategy 2030 aims to achieve the goal of prosperous, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable Asia and the Pacific region.
- In the overall loan portfolio during the CPS period, ADB and domestic cost-sharing will be in the ratio of 70:30.
- 3 key pillars of CPS 2023-27 strategy are:
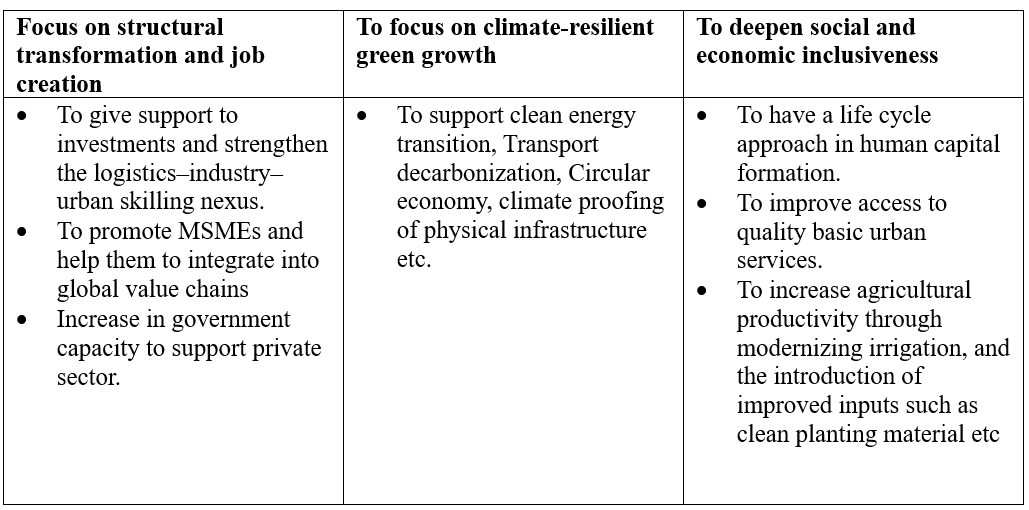
About the Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- It’s a regional development bank that was established in the year 1966.
- It is headquartered in Manila (Philippines) and comprises 68 member countries, both from within and outside the Asia-Pacific region.
- ADB's mission is to promote economic and social progress in Asia and the Pacific region by reducing poverty and improving living conditions.
- India became a member of the ADB in 1966 only and has since maintained a close relationship with it.
- The partnership between India and the ADB encompasses a wide range of development activities, including infrastructure development, energy projects, urban development, agriculture, rural development, education, health and capacity building.
Some key aspects of the India-ADB partnership include:
- Financial Assistance: The ADB provides financial assistance to India in the form of loans, grants, and technical assistance to support various development projects. These funds are used to address critical infrastructure gaps, promote inclusive and sustainable growth, and enhance the quality of life for the people of India.
- Infrastructure Development: The ADB plays a significant role in supporting India's infrastructure development. It finances projects in sectors such as roads, railways, ports, power transmission, and water supply. These investments contribute to improving connectivity, enhancing economic competitiveness, and fostering regional integration.
- Sustainable Development: The partnership between India and the ADB also focuses on promoting sustainable development. The ADB supports initiatives that address climate change, promote renewable energy, improve water resource management, and enhance environmental sustainability. These efforts align with India's own goals of achieving sustainable development while addressing climate challenges.
- Capacity Building and Knowledge Sharing: The ADB provides technical assistance and knowledge sharing platforms to enhance India's institutional capacity and expertise. It supports initiatives that promote policy reforms, governance improvements, and project management skills. This collaboration facilitates the exchange of best practices and enables India to benefit from the ADB's expertise in various sectors.
- Regional Cooperation: The India-ADB partnership extends to regional cooperation initiatives. India actively participates in regional programs supported by the ADB, such as the South Asia Subregional Economic Cooperation (SASEC) program. These initiatives aim to enhance regional connectivity, trade, and economic cooperation among South Asian countries.
- Social and Inclusive Development: The partnership emphasizes social and inclusive development in India. The ADB supports programs that aim to reduce poverty, improve access to education and healthcare, promote gender equality and empower marginalized communities. These efforts contribute to achieving more equitable and inclusive development outcomes.
- Policy Dialogue and Reforms: The ADB engages in policy dialogue with the Indian government to support policy reforms and institutional strengthening. It provides technical expertise and advice on policy formulation, implementation, and monitoring to enhance governance, improve regulatory frameworks, and create an enabling environment for sustainable development.
Challenges in India-ADB partnership are:
- Project Implementation Delays: The implementation of development projects supported by the ADB in India can sometimes face delays due to bureaucratic procedures, land acquisition issues, and coordination challenges. These delays can hinder the timely delivery of project outcomes and impact the overall effectiveness of the partnership.
- Financing Constraints: Despite the financial assistance provided by the ADB, there may still be financing constraints in implementing large-scale infrastructure projects in India. The cost of such projects can be substantial, and securing additional funding from other sources may be required. Ensuring a sustainable financing model and attracting private investment can be challenging.
- Capacity Constraints: Building and enhancing the capacity of Indian institutions to effectively utilize ADB funds and manage projects can be a challenge. It requires strong project management skills, technical expertise, and effective coordination among various stakeholders. Strengthening institutional capacity at all levels is essential to ensure the efficient implementation and sustainability of projects.
- Socio-Cultural and Environmental Factors: Development projects supported by the ADB in India need to consider socio-cultural sensitivities and environmental impacts. Projects may face opposition from local communities due to concerns about displacement, cultural heritage, or environmental degradation. Balancing development objectives with social and environmental considerations can be a complex task.
- Policy Reforms and Institutional Challenges: Implementing policy reforms and institutional changes to create an enabling environment for development can be challenging. It may require overcoming bureaucratic hurdles, addressing governance issues, and ensuring the effective implementation of policy changes. This process can take time and effort, impacting the pace of project implementation.
- Regional Cooperation: While the India-ADB partnership encourages regional cooperation, geopolitical factors and bilateral relationships among countries in the region can present challenges. Differences in priorities, political tensions, and coordination complexities may affect the implementation of regional initiatives and projects.
Conclusion
CPS 2023-27 for India is in harmony with India’s national development priorities to be achieved by the year 2047. Also, it will leverage India’s unique position to deepen regional cooperation and integration in South Asia.



