- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Common Reporting Standards: OECD
Common Reporting Standards: OECD
01-05-2023


Latest Context
In the meeting of the G20, India is forwarding an agenda to widen the scope of the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) for the inclusion of Non-Financial Assets like real estate properties under the Automatic Exchange of Information (AEOI) among OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) countries.
- Jurisdiction: Currently, India has AEOI with 108 jurisdictions to receive financial information and with 79 jurisdictions for sending information automatically.
- Automatic Exchange of Information: By keeping the fight against tax evasion in consideration, AEOI involves – the systematic and periodical transmission of “bulk” taxpayer information by the source country to the residence country with regard to various categories of income. It helps in providing timely information on non-compliance where tax has been evaded in any way even in the case when tax administrations have had no prior information of non-compliance.
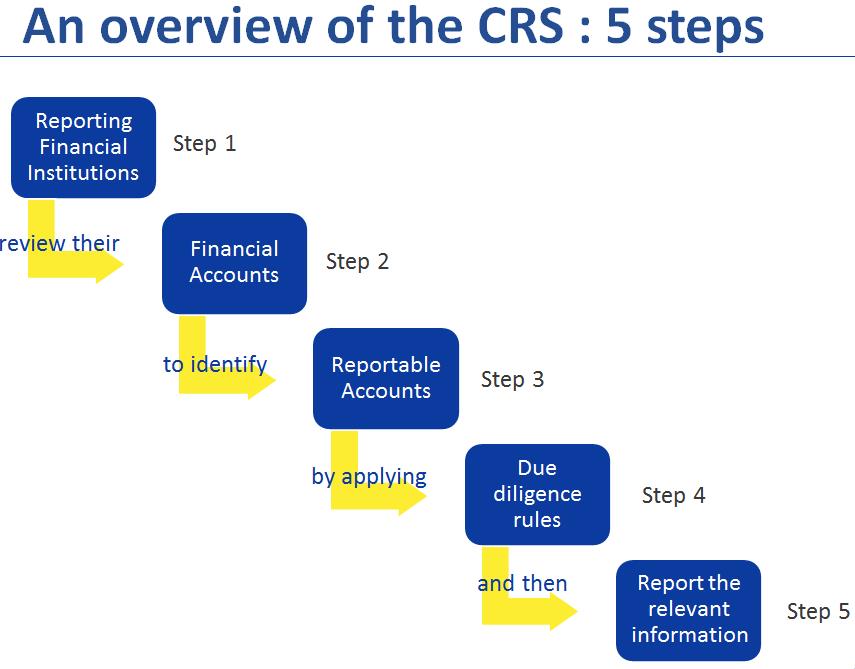
Common Reporting Standard (CRS)
Background
- History of Formation: On May 23, 2014, the G20 Finance Ministers endorsed automatic exchange. On May 6, 2014, the OECD declaration on the automatic exchange of information in tax matters was signed. Consequently, the Standard was approved by the OECD Council on July 15, 2014.
- Objective: Its objective is to exchange financial account information. Financial institutions are required to report different types of accounts and taxpayers covered along with common due-diligence procedures to be followed by financial institutions.
- Jurisdiction: It calls on jurisdictions to obtain information from their financial institutions and automatically exchange that information with other jurisdictions on an annual basis.
Present Framework
- How it works: Presently, the OECD's Automatic Exchange of Information (AEOI) framework provides for sharing of financial account details among signatory countries by keeping check tax evasion in consideration.
- Latest Development: In August 2022, the OECD also approved the Crypto-Asset Reporting Framework (CARF) that provides for the reporting of tax information on transactions in Crypto-Assets in a standardized manner, with a view to automatically exchanging such information.
Necessity for Broadening the Scope of AEIO
- Inclusion of Non-Tax Law Enforcement: There is a need to widen the scope of AEOI so that the information can be used not only to check tax evasion but also for other non-tax law enforcement purposes.
- Inclusion of Non-Financial Assets: In addition to the risks in the Financial Assets there is also a risk of tax evasion in Non-Financial Assets such as real Estate and properties. Therefore, the expansion of CRS is required to include non-financial accounts to check tax evasion.
- To check the Illicit Financial Flows: In accordance with the OECD’s Tax Transparency report, there is a need to check tax evasion and illicit financial flows amid the current geopolitical and debt crisis, especially by Asian nations which are estimated to have lost Euro 25 billion in revenue in 2016. The OECD report said 4 % of Asia’s financial wealth amounting to Euro 1.2 trillion was held offshore which led to a potential annual revenue loss of Euro 25 billion for the region in 2016.
Efforts to Manage Tax Evasion
Global:
- Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS)
- OECD’s Inclusive Framework Statement.
- Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs)
Indian:
- The Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018
- The Black Money (Undisclosed Foreign Income and Assets) and Imposition of Tax Act, 2015
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002.
Way Forward
- Expanding the exchange of financial and non-financial information can have a significant impact on tax collection and non-tax law enforcement efforts.
- The commitment of G20 is to prioritize these initiatives that can lead to increased transparency and accountability in global financial systems, which will in turn benefit everyone.
- To check tax evasion and illicit financial flows, it is highly essential to continue working collaboratively across borders to improve information-sharing mechanisms and ensure their effectiveness while addressing any potential privacy concerns.



