- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Climate Change Fuels Spread of Dengue Fever in Europe
Climate Change Fuels Spread of Dengue Fever in Europe
24-06-2024
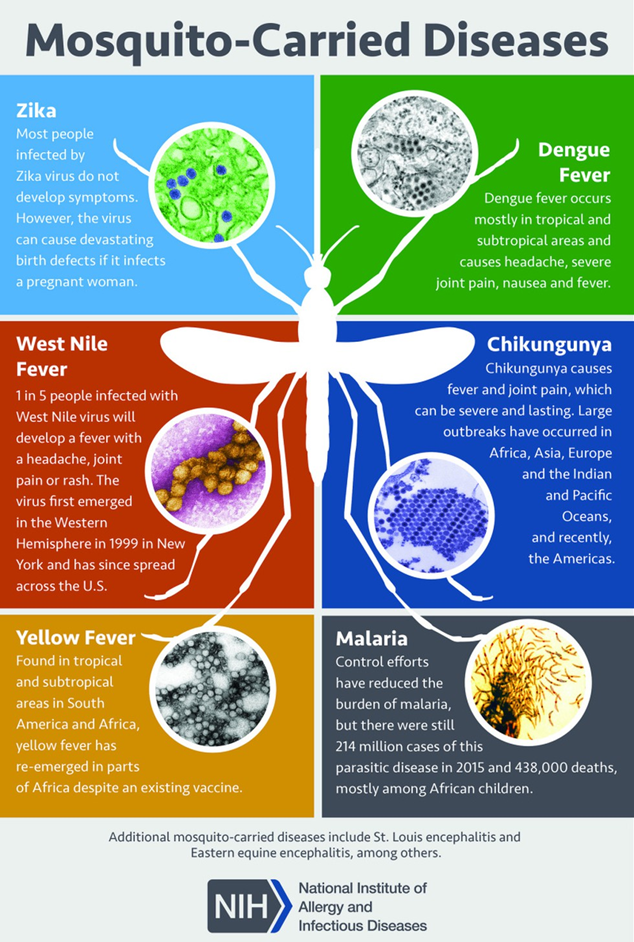
Key Points:
- Climate change is contributing to the spread of dengue fever in Europe, with warmer temperatures helping the Aedes albopictus mosquito thrive.
- The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) reported a significant increase in locally transmitted dengue cases in 2022 and 2023, particularly in France and Italy.
- In 2022, France reported 65 cases of locally transmitted dengue fever, and in 2023, the number of cases rose to 130.
- Dengue fever is not endemic in Europe, but the virus can be introduced into the community through travelers who bring it from abroad.
- The Aedes albopictus mosquito, which transmits dengue, chikungunya, and Zika viruses, has established itself in many parts of Europe, particularly in the Mediterranean and Central Europe.
Background:
- Dengue fever is a viral infection that can cause high fever, headache, and nausea, and can be fatal in severe cases.
- The disease is typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, but climate change is allowing the Aedes mosquito to thrive in new areas.
Causes of the Spread:
- Warmer temperatures:
- Expansion of established mosquito populations: Higher temperatures, especially at night, are allowing the mosquitoes to breed and thrive, leading to an increase in their population.
- Expansion of established mosquito populations: The Aedes albopictus mosquito has spread to many areas around the Mediterranean and Central Europe, and has increased in abundance in areas close to larger population centers.
- Increased international travel: Travelers from dengue-endemic countries are bringing the virus back to Europe, increasing the risk of local outbreaks.
- Vector control: Inadequate vector control measures, such as mosquito eradication and surveillance, are allowing the mosquitoes to spread.
Consequences:
- The increase in locally transmitted dengue cases poses a significant public health risk, particularly in areas with high population densities.
- The disease can have severe consequences, including death, if left untreated.
- The spread of dengue fever in Europe highlights the need for increased awareness, surveillance, and control measures to prevent the spread of the disease.
Expert Insights:
- "Increased international travel from dengue-endemic countries will also increase the risk of imported cases, and inevitably also the risk of local outbreaks." - Andrea Ammon, ECDC Director
- "I believe that what we saw in southern France this past summer [2023] and in other parts of southern Europe is part of a threshold phenomenon. It is true that temperatures have been rising for a long time, but we have more and more [other] factors acting together synergistically." - Thomas Jaenisch, Professor of Global Health at the Colorado School of Public Health
- The WHO's dengue classification of 2009 distinguishes between severe and non-severe dengue, highlighting the importance of accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion:
The spread of dengue fever in Europe highlights the need for urgent action to address climate change and its impact on public health. The disease serves as a warning for the need for increased awareness, surveillance, and control measures to prevent the spread of diseases in non-endemic regions. The situation underscores the importance of international cooperation and collaboration to address the global health implications of climate change.


