- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
China's 4th-Generation Gas-Cooled Nuclear Reactor
China's 4th-Generation Gas-Cooled Nuclear Reactor
08-12-2023
Context
- China has inaugurated the first commercial operations of a fourth-generation gas-cooled nuclear reactor at the Shidao Bay plant in Shandong province in December 2023.
Key Features of Shidaowan Plant
- Utilizes 200 MW high-temperature small modular reactors (SMRs), distinct for their gas-cooling (helium) mechanism compared to conventional pressurized water-cooled reactors.
- SMRs are recognized for being more efficient, cost-effective, and applicable for diverse uses like heating, desalination, and industrial steam production.
China's Nuclear Power overview
- China aims to generate 10% of electricity from nuclear power by 2035 and increase to 18% by 2060.
- As of September 2023, China fell short of its 2020 target to install 58 gigawatts of nuclear capacity.
- China did not sign the COP28 climate conference pledge to triple nuclear power capacity by 2050.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)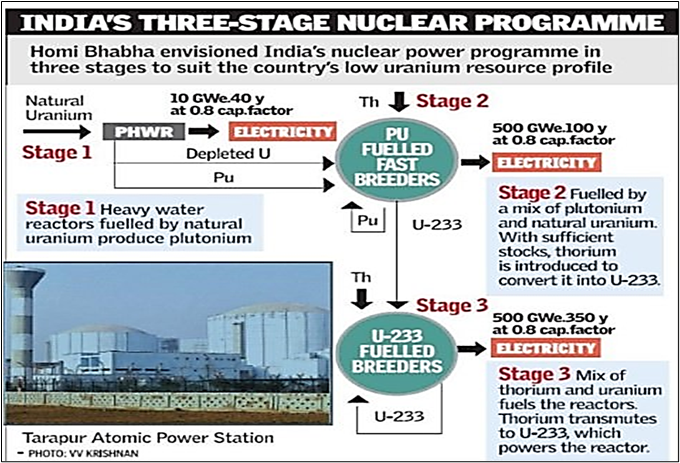
- These are Advanced nuclear reactors with a capacity of up to 300 MW(e) per unit.
- Characteristics: Physically smaller, modular design for factory assembly and transport, and harnessing nuclear fission for energy production.
- Advantages: Lower cost and construction time due to factory-built SMRs, enhanced safety with reduced fuel requirements, and incremental deployment to match increasing energy demands.
Nuclear Power in India
- Current Status: India operates 22 reactors with a total capacity of 7480 MWe.
- Program Stage: India is in the 2nd stage of its 3-stage nuclear program.
Evolution of Nuclear Reactors
- Generation I: Prototypes and early industrial reactors developed in the 1950s and 1960s, commissioned in the 1970s.
- Generation II: Reactors commissioned from the 1970s onwards, emphasizing competitiveness and energy independence.
- Generation III: Focus on safety and security, integrating operational experience from second-generation reactors.
- Generation IV: Ongoing research on technologically advanced systems, considering sustainability, safety, economic competitiveness, and nuclear proliferation resistance.


