- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Black Sea: Russia Withdrew its Large Warships
Black Sea: Russia Withdrew its Large Warships
10-05-2024
The Black Sea has recently attracted attention as Ukraine deployed explosive drone boats to target small, high-speed vessels after Russia withdrew its large warships.
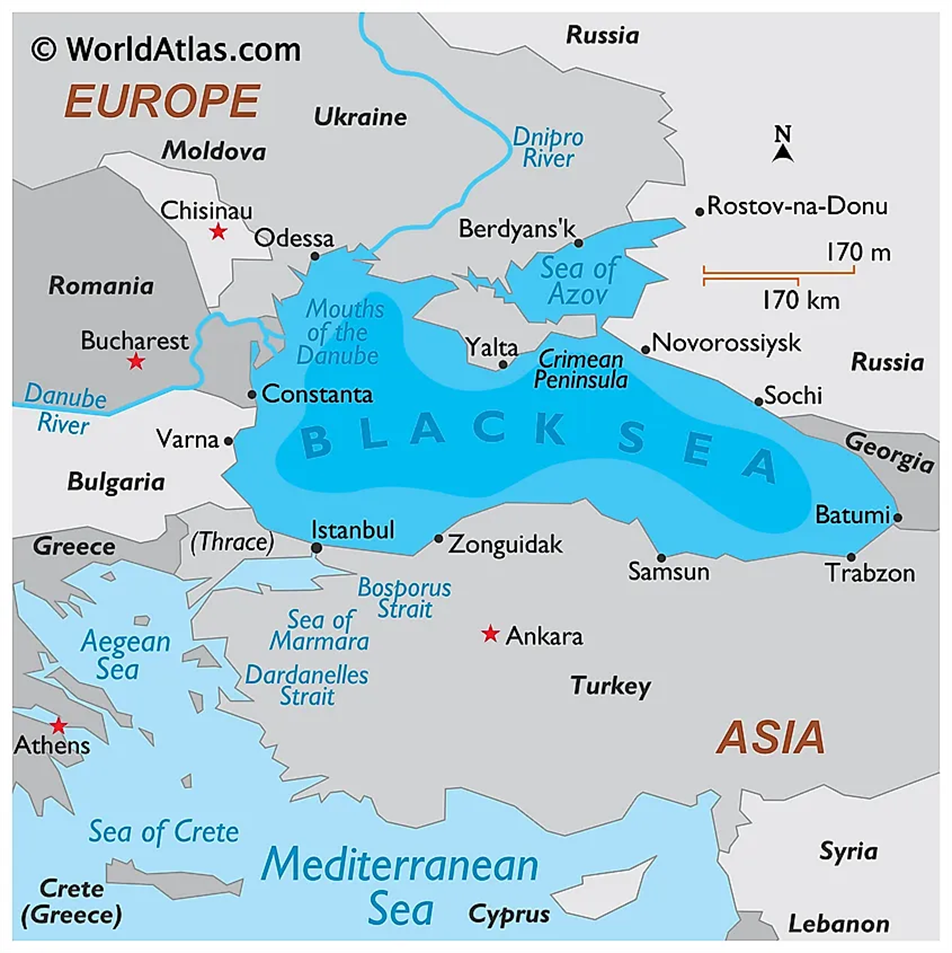
- Location and Area:
- The Black Sea is a large inland sea situated at the southeastern edge of Europe.
- It covers an area of approximately 436,000 square kilometres (168,000 sq mi).
- Bordering Countries:
- The Black Sea is bordered by several countries:
- Ukraine to the north
- Russia to the northeast
- Georgia to the east
- Turkey to the south
- Bulgaria and Romania to the west
- The Black Sea is bordered by several countries:
- Coastline Length:
- Russia has the longest coastline on the Black Sea (2,300 km), followed by Turkey (1,329 km) and Ukraine (1,282 km).
- Crimean Peninsula:
- The Crimean Peninsula extends into the Black Sea from the north.
- Connections to Other Seas:
- The Black Sea is connected to the Aegean Sea (part of the Mediterranean Sea) through the Bosporus Strait, the Sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles Strait.
- It is also connected to the Sea of Azov by the Kerch Strait.
- Geological History:
- The Black Sea was formed when structural upheavals in Asia Minor split off the Caspian basin from the Mediterranean Sea.
- Over time, the Black Sea gradually became isolated, resulting in its lower salinity compared to the world's oceans.
- Freshwater Inflows:
- The Black Sea receives freshwater inflows from numerous rivers, including the Danube, Southern Bug, Dnieper, Rioni, and Dniester.
- Meromictic Basin:
- The Black Sea is the largest meromictic basin, meaning that movement of water between the lower and upper layers of the ocean is rare.
- Anoxic Basin:
- The Black Sea is one of the world's largest anoxic basins, containing areas with very little dissolved oxygen.
- Islands:
- The Black Sea contains several islands, with Snake Island (Ukraine), Giresun Island (Turkey), and St. Ivan Island (Bulgaria) being the largest.
- Definition of a Strait:
- A strait is a naturally formed narrow strip of water between two continents, islands, or two larger bodies of water.
- It is often used for navigational purposes and sometimes referred to as a channel when found between two landmasses.



