- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
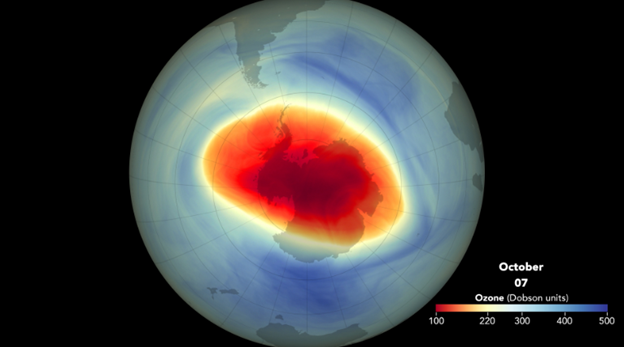
Antarctic Ozone Hole
Antarctic Ozone Hole
25-11-2023
Why in News?
A recent study published in Nature Communications revealed that the Antarctic Ozone Hole has experienced massive growth over the past four years.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study?
- Ozone Depletion:
- The Antarctic ozone hole has consistently been large and thinning in recent years, contradicting the expected recovery trend since the 2000s.
- The hole's ozone concentration has significantly decreased, indicating a significant thinning of the ozone layer.
- Despite the Montreal Protocol's efforts to reduce human-generated chemicals, the concentration of ozone at the core of the ozone hole has decreased by 26% between 2004 and 2022.
- Polar Vortex Influence:
- The Antarctic ozone hole is located within the polar vortex, a circular wind pattern that forms during winter and remains until late spring.
- Antarctic mesosphere air enters stratosphere vortex, introducing natural chemicals like nitrogen dioxide, impacting ozone chemistry in October.
- Factors Affecting Ozone Depletion:
- The size and behavior of the Antarctic ozone hole are influenced by meteorological conditions like temperature, wind patterns, wildfire aerosols, volcanic eruptions, and solar cycle changes.
- Recommendations:
- Further research is needed to comprehend the impact of air descent from the mesosphere on ozone chemistry.
- The study of these mechanisms is expected to provide insights into the potential future behavior of the Antarctic ozone hole.
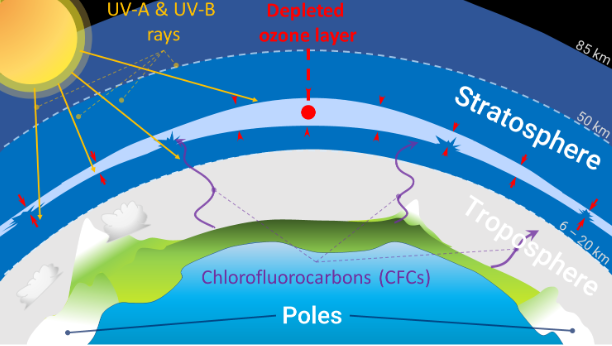
What is an Ozone Hole?
- About:
- An Ozone Hole is a severe depletion of the Earth's stratosphere's ozone layer, a region with a higher concentration of ozone molecules.
- Ozone molecules (O3) in this layer are crucial in protecting Earth from harmful UV radiation from the sun.
- The depletion of the ozone layer results in a region with significantly reduced ozone concentrations, which is frequently observed in Antarctica.
- This phenomenon primarily occurs in the Southern Hemisphere's spring months (August to October) and can be influenced by global factors.
- Reasons for Ozone Hole:
- Ozone-depleting substances (ODS), such as Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), halons, carbon tetrachloride, and methyl chloroform, are human-generated chemicals responsible for depleting the atmosphere.
- Substances released into the atmosphere rise to the stratosphere, breaking down due to ultraviolet radiation, releasing chlorine and bromine atoms, which destroy ozone molecules.
- The Antarctic ozone hole is a severe example of this phenomenon, resulting in a drastic decrease in ozone levels, allowing harmful UV radiation to reach Earth's surface.
- Impact:
- The rise in UV radiation poses significant health risks to humans, including increased rates of skin cancers, cataracts, and compromised immune systems.
- UV radiation harms ecosystems, while ozone depletion indirectly influences climate change by altering stratosphere patterns, potentially affecting weather and climate in specific regions.

Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
PLFS 2025: Monthly Jobs Data, Bigger Survey
PLFS 2025: Monthly Jobs Data, Bigger Survey

