26-12-2025 Mains Question Answer
Explain types of Motion which are possible between the plates. What causes plate motion?
The Earth’s lithosphere is divided into several rigid plates floating over the semi-molten asthenosphere. The relative movement of these plates along their boundaries produces distinct geological processes shaping the Earth’s surface.
Three Types of Motion are possible between the plates:
- Separation or Divergent
- Closing together or Convergent
- Shearing or transforming
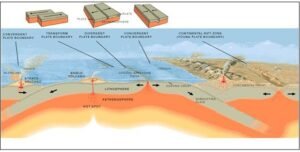
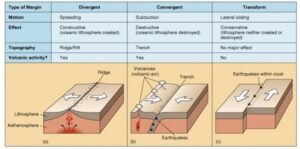
Divergent (Constructive) Plate Motion:
- Plates move away from each other.
- Characteristics:
- Occurs at mid-oceanic ridges and continental rifts.
- Creates new oceanic crust through seafloor spreading.
- Associated with basaltic volcanism, shallow-focus earthquakes, and rift valleys.
- Examples:
- Mid-Atlantic Ridge (Eurasian & North American plates diverging)
- East African Rift System (African plate splitting)
Convergent (Destructive) Plate Motion
- Plates move towards each other; one may subduct.
- Ocean–Continent Convergence
- Denser oceanic plate subducts under lighter continental plate.
- Produces volcanic arcs, fold mountains, deep-sea trenches.
- Example: Andes Mountains (Nazca plate subducting under South America)
- Ocean–Ocean Convergence
- One oceanic plate subducts under another.
- Leads to island arcs and deep trenches.
- Example: Japan, Philippines
- Continent–Continent Convergence
- No subduction due to similar densities.
- Plates crumple to form massive fold mountains, high seismicity.
- Example: Himalayas (Indian plate colliding with Eurasian plate)
- Ocean–Continent Convergence
Transform (Conservative) Plate Motion
- Plates slide horizontally past each other along transform faults.
- Characteristics:
- No creation or destruction of crust.
- Frequent shallow but powerful earthquakes.
- Little to no volcanism.
- Examples:
- San Andreas Fault (Pacific & North American plates)
- North Anatolian Fault (Turkiye)
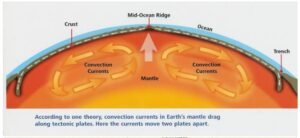
Causes of Plate Motion
Plate movement is driven by internal heat and density variations within the Earth, creating forces that push or pull plates.
- Mantle Convection Currents
- Heat from the core causes convection in the semi-fluid asthenosphere.
- Hot, buoyant material rises → cools → sinks → drags plates along.
- This is considered the primary driver of plate motion.
- Ridge Push (Gravitational Sliding)
- At mid-ocean ridges, newly formed crust is hot and elevated.
- Gravity causes it to slide down and push the plate away from the ridge.
- Slab Pull
- The most powerful force.
- Old, cold, dense oceanic plate sinks into mantle at subduction zones.
- Its weight pulls the rest of the plate with it.
- Slab Suction
- Subducting slabs induce flow in surrounding mantle, drawing nearby plate edges toward subduction zones.
- Gravitational Differentiation / Isostatic Adjustment
- Plate motion also reflects the attempt to maintain equilibrium (isostasy) due to density differences between continental and oceanic crust.
Conclusion
Plate motions—divergent, convergent, and transform—are manifestations of the dynamic Earth driven by deep thermal and gravitational forces. These interactions generate major geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain building, and ocean basin formation, making plate tectonics the fundamental unifying theory of Earth sciences.

