1. Subansiri River
Why in the News?
- The Union Environment Ministry’s Expert Appraisal Committee (EAC) has recommended environmental clearance for the 2,200 MW Oju hydroelectric project on the Subansiri River in Taksing, Arunachal Pradesh, near the China border.
- The project will be the largest in the Subansiri basin with an approved capacity of 2,200 MW.
- Concerns have been raised over the outdated cumulative impact assessment (2014) for multiple hydel projects in the basin, amid ecological and seismic sensitivities of the region.
About the Place
- Geography & Origin:
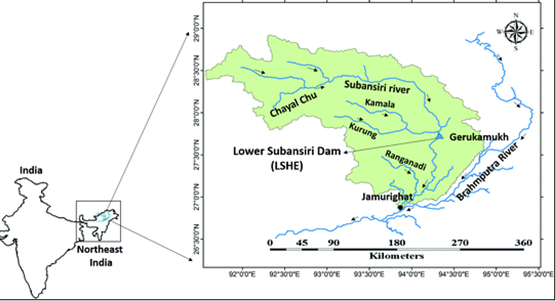
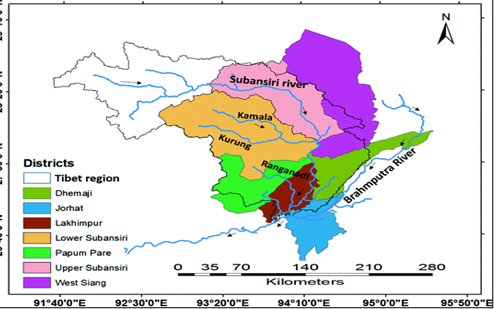
- Subansiri is the largest tributary of the Brahmaputra River.
- Originates in the Tibet Autonomous Region (China), flows through Arunachal Pradesh and Assam, before joining the Brahmaputra.
- Length & Basin:
- Approximately 442 km long (192 km in China, 250 km in India).
- Drains an area of around 37,000 sq. km.
- Hydropower Significance:
- Hosts several planned and under-construction hydel projects, including Upper Subansiri, Lower Subansiri, Oju, Niare, Naba, Nalo, and Dengser.
- The Lower Subansiri Project (2,000 MW) is India’s largest under-construction hydropower project.
- Ecological Importance:
- Rich in aquatic biodiversity, supports the golden mahseer and other endemic fish species.
- Subansiri basin is also prone to glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs), landslides, and seismic risks.
- Cultural and Historical Significance:
- Subansiri valley is home to several indigenous tribes of Arunachal Pradesh, including Tagin, Nyishi, and Galo communities.
- River is central to their livelihoods, culture, and rituals.
- Strategic Relevance:
- Flows close to the India–China border (Taksing sector in Upper Subansiri district), making it strategically sensitive.
- Development projects here are also linked to border infrastructure and national security concerns.
- Environmental Concerns:
- Hydel projects raise issues of deforestation, submergence of forest land, displacement of local communities, and seismic vulnerability.
- Public hearings and environmental clearances often witness resistance from local communities and environmentalists.
2. Morocco
Why in the News?
- India inaugurated its first overseas defence manufacturing facility in Berrechid, Morocco, by Tata Advanced Systems (TASL) in collaboration with DRDO, to produce the Wheeled Armoured Platform (WhAP 8×8) for the Royal Moroccan Army.
- The facility strengthens India-Morocco defence cooperation, leverages Morocco’s strategic location for exports to Africa and Europe, and contributes to regional security.
- The project reflects India’s Aatmanirbhar Bharat vision, promoting international collaboration and local employment.
About Morocco
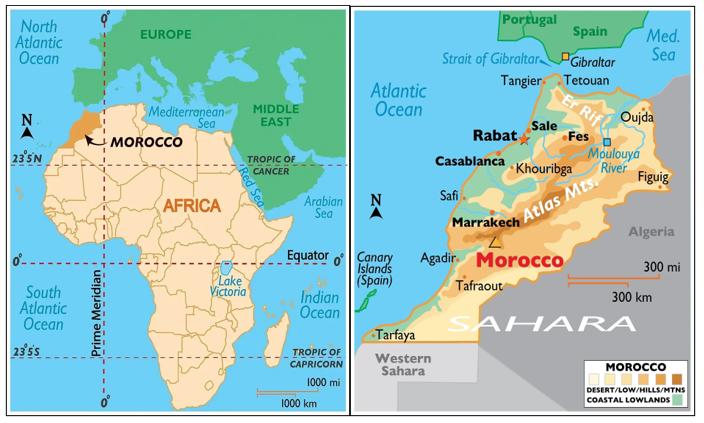
- Location: Morocco is located in the Maghreb region of North-West Africa.
- Borders:
- South: It is bordered by Western Sahara.
- East: It is bordered by Algeria
- West: Atlantic Ocean
- North: Mediterranean Sea
- It has coastlines on both the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, the only African country with this feature.
- Major Cities and Features:
- The largest city is Casablanca, a key industrial and commercial port.
- Two Spanish enclaves, Ceuta and Melilla, lie on the northern coast.
- The highest point is Jebel Toubkal in the Atlas Mountains.
- Climate and Rivers:
- Northern Morocco has a Mediterranean climate—mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. The
- Mououya River, originating in the Atlas Mountains, is an important water source flowing into the Mediterranean.
- Political System: Morocco is a constitutional monarchy with a bicameral legislature.
- Economy: The economy is heavily dependent on raw material exports.
- Language: Official languages are Arabic and Tamazight (Berber).
- Capital: The capital city is Rabat.
|
Also Read |
|
| UPSC Foundation Course | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |
| Free MCQs for UPSC Prelims | UPSC Test Series |
| ENSURE IAS NOTES | Our Booklist |