1. Argentina
Why in the News?
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has landed in Buenos Aires, Argentina, marking a historic bilateral visit, the first such trip by an Indian prime minister in 57 years, since Indira Gandhi’s 1968 visit.
- This two day mission is the third stop on his five-nation tour, following visits to Ghana and Trinidad & Tobago.
What are the Key Highlights?
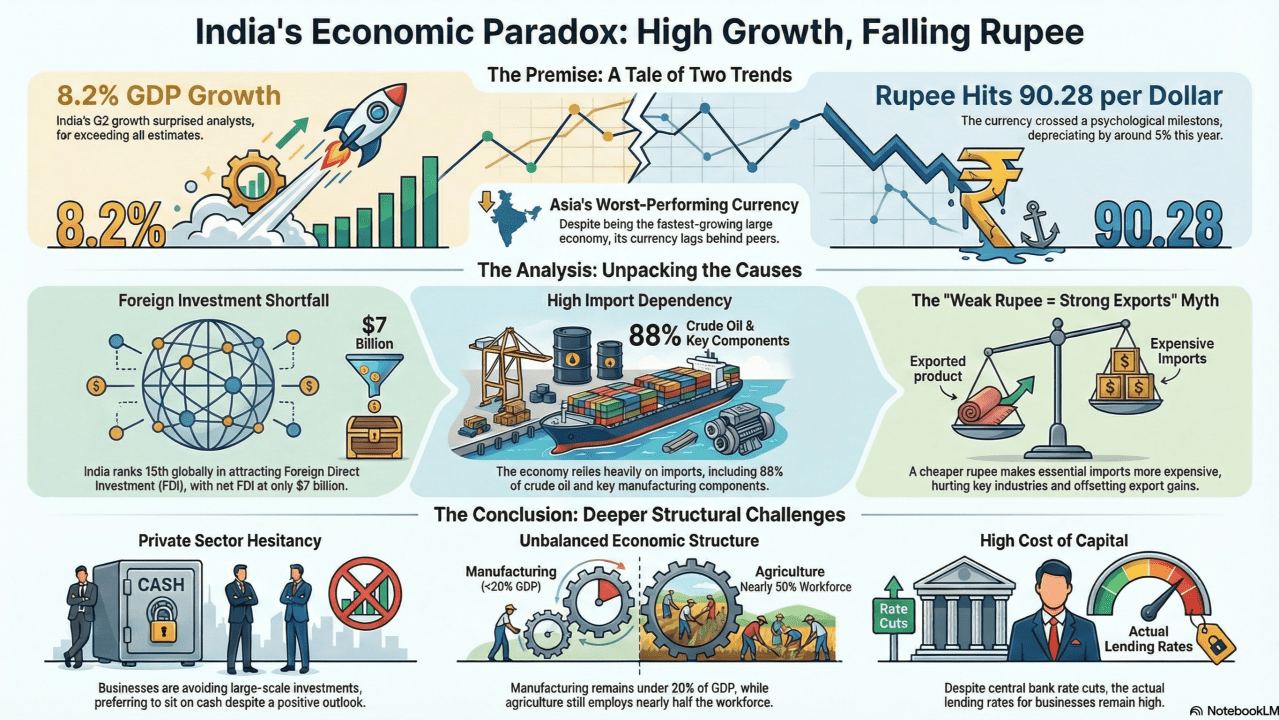
- Geographical Overview:
|
Feature |
Description |
| Continent | South America |
| Latitude/Longitude | Approximately 23°S to 55°S latitude |
| Borders | Chile (west), Bolivia & Paraguay (north), Brazil & Uruguay (northeast), Atlantic Ocean (east) |
| Length (N-S) | Approximate 3,650 km, one of the longest north-south countries in the world |
| Capital | Buenos Aires (on the eastern coast, on the Río de la Plata estuary) |
- Physical Geography:
- Andes Mountains (Western Argentina):
- Forms the natural boundary with Chile.
- Includes Aconcagua (6,961 m), highest mountain in the Americas.
- Significant for glacial water sources, tourism, and minerals.
- Patagonia (South Argentina):
- Cold desert and steppe region, includes plains and plateaus.
- Sparsely populated.
- Important for oil, gas, and sheep rearing.
- Home to Perito Moreno Glacier (a UNESCO World Heritage Site).
- Pampas (Central Argentina):
- Fertile plains known for extensive agriculture and cattle ranching.
- Argentina is one of the world’s leading exporters of beef, soybeans, and wheat.
- Gran Chaco (North Argentina):
- Semi-arid lowland region.
- Rich in biodiversity but threatened by deforestation.
- Home to indigenous communities.
- Mesopotamia Region (Northeast):
- Between Paraná and Uruguay Rivers.
- Rich in forests and wetlands.
- Includes Iguazú Falls (UNESCO site, shared with Brazil).
- Andes Mountains (Western Argentina):
- Hydrology and Rivers:
|
River |
Significance |
| Parana River | Second-longest in South America, major for navigation and hydroelectric power (Itaipu Dam nearby) |
| Uruguay River | Eastern border with Uruguay |
| Rio de la Plata | Estuary formed by confluence of Paraná and Uruguay rivers, Buenos Aires lies on its banks |
| Colorado & Negro Rivers | Important in southern irrigation and hydroelectricity |
- Important Places:
|
Place |
Why Important |
| Buenos Aires | Capital, port city, political & economic hub |
| Mendoza | Near Andes, wine production & Aconcagua mountain base |
| Cordoba | Industrial & educational center |
| Rosario | Major port on Parana River, agriculture hub |
| Ushuaia | Southernmost city in the world, gateway to Antarctica |
| Iguazu Falls | World-famous waterfall, UNESCO heritage site |
| Falkland Islands (UK territory, claimed by Argentina) | Geopolitical hotspot |
| Tierra del Fuego | Archipelago shared with Chile; end of the mainland |
- Other Important Information
- South-South Cooperation:
- Argentina is a part of the Global South, and India-Argentina ties are increasing in space tech, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and lithium.
- Lithium Triangle:
- Argentina, Bolivia, Chile form the Lithium Triangle — key for EV batteries.
- Climate & Biodiversity:
- Large latitudinal extent = varied ecosystems.
- Important examples for biogeography, climate zones, and conservation issues.
- Antarctica Connection:
- Ushuaia was used as a base for Antarctica expeditions.
- South-South Cooperation:
2. Siang Upper Multipurpose Project
Why in the News?
- The Siang Upper Multipurpose Storage Project, located in Arunachal Pradesh, has gained attention due to:
- Geopolitical concerns over China’s dam-building upstream on the Yarlung Tsangpo (Brahmaputra).
- Potential for hydropower generation, flood control, and water storage.
- Concerns about ecological impacts and displacement of tribal populations.
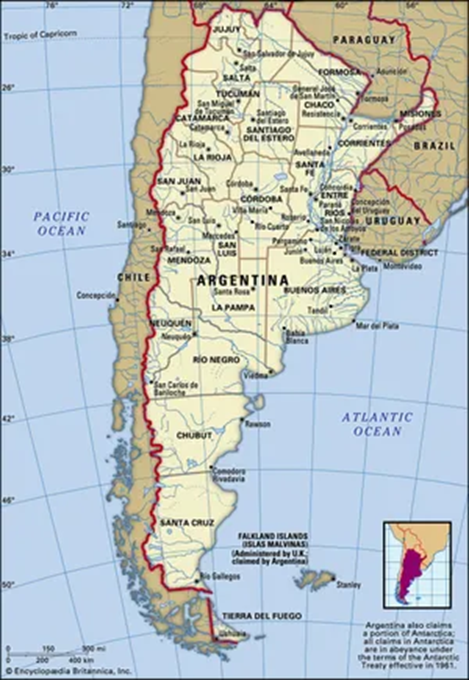
Geographical Location:
|
Aspect |
Details |
| River | Siang River (main stem of the Brahmaputra in Arunachal Pradesh) |
| State | Arunachal Pradesh |
| Districts Covered | Upper Siang District |
| Upstream Origin | Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibet, enters India as Siang |
| Downstream Confluence | Merges with Dibang and Lohit rivers to form Brahmaputra in Assam |
| Nearby Important Towns | Yingkiong, Tuting
|
| Coordinates (Approx.) | Latitude: ~28.5° N, Longitude: ~95.0° E |
| Topography | Located in Eastern Himalayas, rugged terrain, deep gorges, and forested valleys
|
Project Features:
|
Parameter |
Details |
| Type | Multipurpose Storage Project |
| Components | Hydropower, irrigation, flood moderation, water storage |
| Proposed Dam Height | Over 280 metres (One of the tallest in India) |
| Capacity | Estimated hydropower generation of 11,000 MW+ |
| Authority | NHPC Ltd. (or relevant Central PSU) |
| Status | Under appraisal / planning stage |
Objectives:
- Hydropower generation for the North-East and national grid.
- Flood control downstream in Assam.
- Strategic water storage against China’s upstream dams.
- Irrigation and drinking water for downstream regions.
Environmental and Social Concerns:
|
Issue |
Details |
| Displacement | Large-scale displacement of Adi and other tribal communities. |
| Biodiversity | Located in the Eastern Himalayas—a biodiversity hotspot with rare flora & fauna. |
| Seismic Zone | High seismic activity—Earthquake-prone area (Zone V). |
| Cultural Sites | Close to indigenous sacred sites and tribal heritage zones. |
| Deforestation | Risk of submergence of large forest areas. |
Strategic & Geopolitical Relevance
- Counters Chinese hydropower projects on upstream Yarlung Tsangpo.
- Acts as India’s strategic water buffer.
- Ensures river flow regulation for downstream Assam and Bangladesh.
- Tied to India’s “Act East” Policy and Northeast infrastructure development.