Ganga River
Why in the News?
- Incessant rainfall in Uttar Pradesh (August 2025) has caused severe flooding in 13 districts, with the Ganga flowing above the danger mark in Varanasi, Mirzapur, Ghazipur, and Ballia.
- In Varanasi, the Ganga crossed the danger level (72.1 m against 71.262 m), submerging ghats, disrupting cremation rituals, and forcing the famed Ganga Aarti to shift to rooftops.
About Ganga River
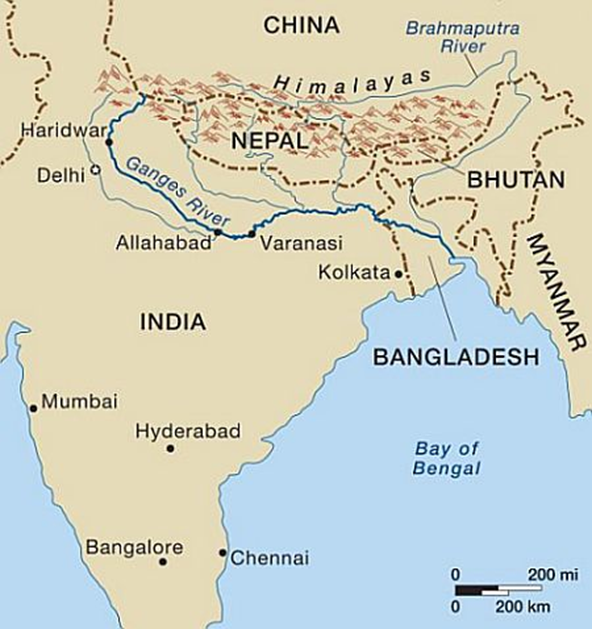
- The Ganga is the longest river of India (approx. 2,510 km), originating from the Gangotri Glacier (Gaumukh, Uttarakhand) as the Bhagirathi.
- It flows through Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, and West Bengal, before draining into the Bay of Bengal.
- Major tributaries: Yamuna, Ghaghara, Gandak, Kosi, Son, Betwa, Chambal.
- The river is sacred in Hinduism, worshipped as Goddess Ganga, and central to rituals, pilgrimages, and festivals like Ganga Dussehra.
- Important cities on its banks: Haridwar, Kanpur, Prayagraj (confluence with Yamuna), Varanasi, Patna, Kolkata.
- The river basin is the largest in India, supporting ~43% of India’s population and providing fertile alluvial soil for agriculture.
- Environmental concern: Ganga is among the most polluted rivers due to untreated sewage, industrial waste, and religious offerings.
- Government initiatives: Namami Gange Programme (2014), National Ganga River Basin Authority, and Ganga Action Plan to rejuvenate and clean the river.
Yamuna River
Why in the News?
- On Thursday (Sept 4, 2025), the Yamuna river level in Delhi reached 207.48 metres at the Old Railway Bridge, causing floods in several low-lying areas.
- Floodwaters reached Delhi Secretariat and nearby regions, while Mayur Vihar Phase I and roads leading to Yamuna Bank Metro Station were submerged, disrupting transport and daily life.
- Incessant rainfall worsened the situation, leading to traffic snarls and alerts from flood control authorities.
About Yamuna River
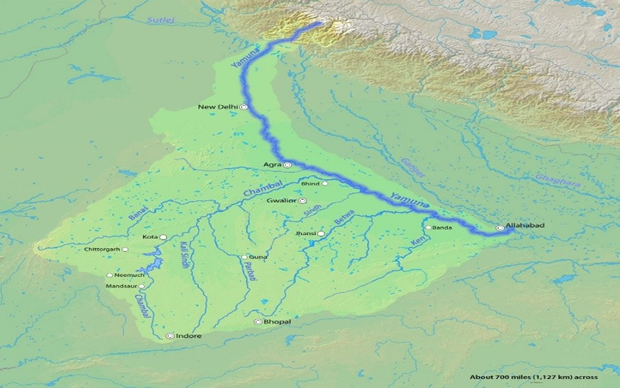
- The Yamuna is the largest tributary of the Ganga, with a total length of about 1,376 km.
- Originates from the Yamunotri Glacier at Bandarpoonch peak in Uttarkashi district, Uttarakhand.
- Flows through Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Delhi, and Uttar Pradesh, before merging with the Ganga at Prayagraj (Triveni Sangam).
- Major tributaries: Tons, Chambal, Betwa, Ken, Sindh.
- Important cities on its banks: Delhi, Mathura, Agra, Etawah, Prayagraj.
- The river holds immense religious significance in Hinduism, associated with Yamuna Devi and connected to the legends of Lord Krishna (Mathura, Vrindavan).
- Yamuna provides water for drinking, irrigation, and industries, sustaining millions of people in North India.
- Environmental concern: The Delhi stretch is one of the most polluted river stretches in India, due to untreated sewage, industrial effluents, and encroachments.
- Conservation measures: Yamuna Action Plan (YAP) launched in 1993 with Japanese assistance, and multiple drives under the Namami Gange Mission.