Srisailam Reservoir
Why in the News?
- Telangana Deputy CM urged Andhra Pradesh to stop diversion of 11 tmcft (Thousand Million Cubic Feet) of water/day from the upper part of the Srisailam reservoir via the Pothireddypadu lift system.
- Telangana fears the diversion will empty the reservoir in 25 days, harming farmers in Nalgonda and Khammam districts.
- Telangana also opposed the Banakacherla project and raised concerns about Polavaram dam’s submergence impact.
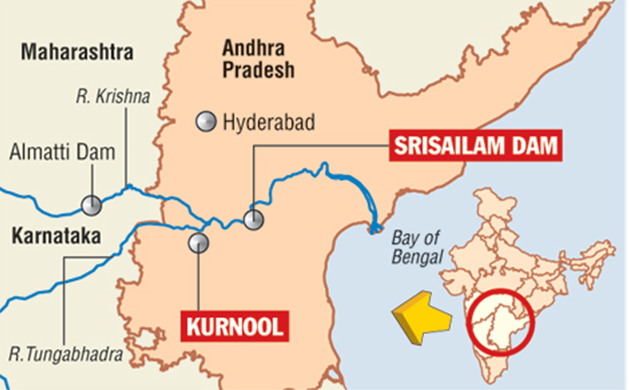
About Srisailam Reservoir
- Location – Built across the Krishna River, it lies in the border region of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, surrounded by the Nallamala Hills.
- Construction – The dam is officially called the Srisailam Dam, a multipurpose project completed in 1981 for irrigation, hydropower, and flood control.
- Capacity – It is the second-largest working hydroelectric station in India with a storage capacity of around 215 tmcft.
- Purpose – Serves irrigation for lakhs of acres in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, provides drinking water to cities like Hyderabad, and supports hydropower generation.
- Hydropower Plant – Equipped with underground powerhouses on both left and right banks with a combined capacity of 1,670 MW.
- Religious Significance – Near the famous Srisailam temple dedicated to Lord Mallikarjuna (one of the twelve Jyotirlingas) and Goddess Bhramaramba.
- Geography – The reservoir is surrounded by dense forests of the Nallamala Hills, making it an important ecological zone.
- Interstate Water Disputes – Regularly at the centre of Krishna River water-sharing disputes between Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, and Maharashtra.
Godavari River
Why in the News?
- The Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP), built on the Godavari River in Telangana, is under scrutiny for alleged construction flaws, site changes, and cost escalations.
- A judicial commission has submitted its inquiry report into KLIP’s lapses, prompting discussions in the Telangana legislature.
- Concerns have been raised over damaged barrages like Medigadda, Sundilla, and Annaram, with charges of faulty foundations and ignoring technical advice.
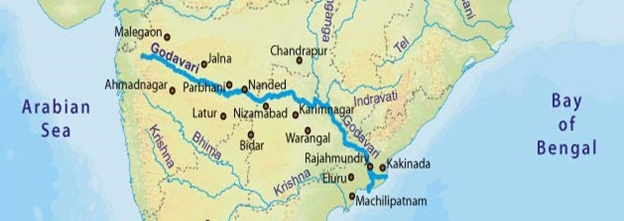
About the Godavari River
- Second-longest river in India – After the Ganga, the Godavari is the longest river in peninsular India, with a length of about 1,465 km.
- Origin – Rises from Trimbakeshwar in the Nashik district of Maharashtra at an elevation of about 1,067 m.
- Drainage Basin – Covers an area of about 3,12,812 sq. km, spanning Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, and smaller portions of Madhya Pradesh and Karnataka.
- Tributaries – Major ones include Pranahita, Indravati, Sabari, Manjira, Purna, and Penganga.
- Religious Importance – Often called Dakshina Ganga (Ganga of the South); the Pushkaram festival is celebrated every 12 years on its banks.
- Dams & Projects – Hosts major irrigation and hydro projects like Polavaram, Jayakwadi, Sriram Sagar, Dowleswaram Barrage, and Kaleshwaram.
- Mouth – Empties into the Bay of Bengal through a wide delta in Andhra Pradesh, which is one of India’s most fertile regions.
- Ecology – Supports rich biodiversity, fertile agricultural plains, and extensive mangrove forests near its delta.