You will learn very important aspects based on following important questions for UPSC Prelims/ Mains/ Interview:
|
Linking NATGRID with NPR (Completely Explained)
Context
The government had many databases like Aadhaar, CCTNS, NRC, NPR, still NATGRID was set up in 2008. This is because these databases operated separately, which NATGRID – and its present linkage with NPR – aims to overcome.
Why was NATGRID set up under the Ministry of Home Affairs after the 2008 Mumbai attacks?
- After the 2008 Mumbai Terror Attacks, the government decided to review what went wrong.
- It found that India already had many databases like Aadhaar, CCTNS, NRC and NPR. But these databases worked separately, not as one system.
- Police and intelligence agencies could not easily link information from different databases and important clues remained scattered causing delays, intelligence blind spots and missing links before the attacks.
- This lack of real-time information sharing was seen as a major weakness.
- To fix this, the government decided to create one common platform and therefore, NATGRID was set up in 2009 as India’s Master Intelligence Database.
- NATGRID was placed under the Ministry of Home Affairs because counter-terrorism, internal security, policing, and intelligence coordination fall within the Ministry’s mandate.
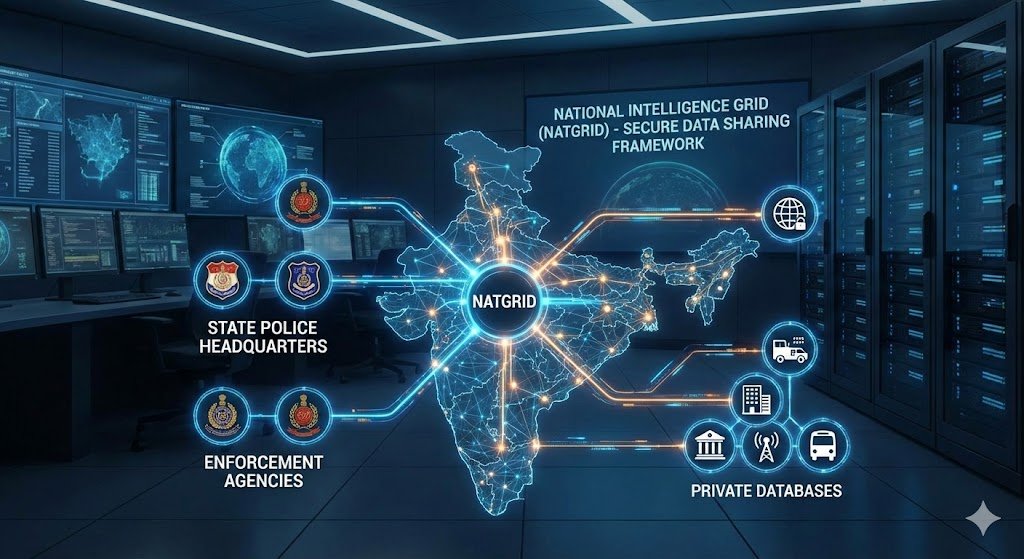
What is the National Intelligence Grid (NATGRID)?
- It is a secure and centralized technology platform.
- It is not a database. It means that it does not store data permanently or generate original data.
- It helps intelligence and law enforcement agencies connect different pieces of information (like Identity records, Travel details, Financial transactions and Communication metadata) from different sources (government and private databases).
- It supports counter-terrorism, internal security, and serious crime investigation.
- This improves intelligence-led policing and strengthens India’s internal security framework.
How is it different from previous databases?
| Basis | Other Databases (Aadhaar, CCTNS, NRC, NPR) | NATGRID |
| Nature | Stand-alone databases that store data | Not a database; a secure technology platform |
| Purpose | Created for a single function such as identity, policing records, or population data | Created for intelligence sharing and security analysis |
| Data creation | Generate and store original data | Does not create or store data permanently |
| Scope of use | Limited to one department or sector | Used across multiple agencies and sectors (Helps agencies connect the dots) |
| Data access | Data is accessed within that single database (No cross-database analysis) | Data is accessed from many databases together (Cross-database intelligence analysis) |
| Speed | Information sharing is slow or manual | Provides real-time, digital access |
From which government and private databases does NATGRID collect data?
- NATGRID integrates data from a wide range of government and private databases, enabling multi-dimensional intelligence analysis.
- Government Databases: NATGRID collects information from many government databases related to identity, travel, crime, and finance, such as:
| 1. Aadhaar – for identity details | 5. Railway passenger data – for train travel information |
| 2. National Population Register (NPR) – for resident and family details | 6. Driving licence and vehicle registration records – for transport details |
| 3. Passport and visa records – for travel and nationality information | 7. Airline travel data – for flight booking and travel history |
| 4. Immigration and foreigner registration data – for entry and exit details | 8. CCTNS (Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems) – for FIRs and crime records |
- For financial intelligence, NATGRID also uses:
- Tax records
- Export–import data
- Suspicious transaction reports from the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU)
- Private Databases: From private companies, NATGRID accesses only basic data (metadata) and not personal content. These include:
- Telecom companies – call detail records (who called whom, time and duration, not call content)
- Banks – transaction logs and account-related details
- Insurance companies – policy-related records
- Transport and toll systems – FASTag records and booking details
- The system does not allow blanket access to personal communications such as call recordings or message content.
To which intelligence and law-enforcement agencies is this data made available by NATGRID, and in what manner?
- The initial access to NATGRID was limited to the following 10 central intelligence and law-enforcement agencies:
| 1. Intelligence Bureau (IB) | 6. Research and Analysis Wing (RAW) |
| 2. National Investigation Agency (NIA) | 7. Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) |
| 3. Enforcement Directorate (ED) | 8. Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) |
| 4. National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) | 9. Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU-IND) |
| 5. Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) | 10. Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC – through its enforcement arms) |
- Recently, access has been expanded to Superintendent of Police (SP)-rank officers in State police forces to speed up investigations.
- Manner in which data is accessed
- Data is accessed only for a specific case.
- Each search must clearly mention the purpose of investigation.
- All queries are digitally logged in the system.
- Queries can be audited and checked later.
- Officers cannot freely browse data; access is controlled and monitored.
- NATGRID currently handles around 45,000 queries per month, showing its regular use in criminal investigations.
What are the key technological components of NATGRID (Hub, data integration, analytics, AI tool Gandiva, etc.)?
- Hub-and-Spoke Architecture
- NATGRID works on a secure hub and spoke model where it acts as a central hub and the original data remains with the respective departments.
- When an authorised officer makes a request, relevant data is temporarily fetched. Data is not copied or stored permanently in NATGRID to ensure data security.
- Data Integration Layer
- Different databases store data in different formats.
- NATGRID has a data integration layer that standardises data and converts it into a common format. This allows cross–database analysis.
- Advanced Analytics Tools
- NATGRID uses data analytics tools to analyse large volumes of data.
- These tools help in:
- Pattern recognition (finding suspicious behaviour)
- Link analysis (connecting people, accounts, and locations)
- Network mapping (tracking crime or terror networks)
- This supports intelligence-led investigation instead of manual checking.
- AI Tool – Gandiva
- It is an indigenous AI-based analytical tool, named after Arjuna’s bow.
- It supports multi-source data collection, entity resolution (checking if records belong to the same person) and Facial recognition.
- If a suspect’s photo is available, it can be matched with telecom KYC, driving licence, vehicle registration, and other photo IDs.
- After linking with NPR, Gandiva can also access family-wise demographic details of a suspect.
- This saves time, manpower, and investigation effort.
- Organised Crime Network Database
- NATGRID’s IT platform is also used to build an Organised Crime Network Database.
- This database helps in secure data–sharing between National Investigation Agency (NIA) and State Anti-Terror Squads (ATS).
- It improves coordination against Terrorism and Organised crime networks.
Why is NATGRID being linked to the National Population Register (NPR) in 2025? What are the security benefits and the concerns (right to privacy, data protection, misuse, etc.) associated with this integration?
Reason for Linking:
- The NPR contains family-wise demographic and residential details of about 119 crore residents. This data was first collected during the 2011 Census and last updated in 2015.
- By linking NPR with NATGRID, investigators can quickly verify a person’s identity and background.
- This helps the government to strengthen internal security and investigations.
Security Benefits of Linking NATGRID with NPR
- It helps in faster identity verification.
- It makes it easier to detect fake or duplicate identities.
- It allows agencies to trace family and residential links of suspects.
- It helps in identifying Illegal migrants, Terror sleeper cells and Organised crime networks.
- It strengthens Fraud prevention, Counter-terrorism efforts and Organised crime detection.
- It speeds up criminal investigations, which is why the Ministry of Home Affairs has encouraged States to use NATGRID more actively.
Concerns Related to This Integration
- Right to Privacy: Critics fear that linking population-wide data with intelligence systems may lead to excessive surveillance. There are also concerns about profiling of citizens (collecting and combining a person’s data to create a detailed profile about them, often without their knowledge or consent).
- Data Protection: India does not yet have a fully tested data protection framework. Large-scale data integration raises the risk of data leaks or misuse.
- Function Creep: There is concern that data collected for one purpose may be used for other purposes later. This is known as function creep.
- Link with NRC: NPR is widely seen as the first step towards a National Register of Citizens (NRC). This has increased public sensitivity and political concerns around the linkage.
The government has responded by emphasising that access is restricted, queries are logged, and oversight exists, but the debate highlights the need for stronger statutory safeguards and transparency.
What safeguards and oversight mechanisms exist to prevent misuse of NATGRID by agencies or individuals, and what role does NATGRID play in combating terrorism, organised crime, financial crimes, and cybercrime in practice?
Safeguards and Oversight Mechanisms to Prevent Misuse of NATGRID
- Controlled and Purpose-Based Access: NATGRID can be accessed only by authorised officers. Every data request must be made for a specific case. The officer must clearly mention the purpose of the query.
- Logging and Audit Trail: Every search made on NATGRID is digitally recorded. These records can be checked later. This creates accountability and discourages misuse.
- Classification of Data: Data is classified into Non-sensitive, Sensitive and Highly sensitive. Highly sensitive data (bank statements, tax records, financial transactions) is given extra scrutiny.
- Senior-Level Supervision: Senior officers monitor how NATGRID is used. Junior officers cannot access the system freely. This ensures institutional oversight.
Role of NATGRID in Combating Terrorism, Organised Crimes, Financial Crimes, and Cybercrimes
- Role in Counter Terrorism: It helps agencies to correlate travel history, financial flows, telecom metadata, and identity records to detect terror networks and sleeper cells.
- Combating Organised Crime: It helps map crime syndicates working across States. It connects people, money, and movement.
- For Financial Crimes: It supports agencies like the Enforcement Directorate by tracing money laundering trails and shell companies.
- For Cybercrimes: It assists in identifying mule accounts, SIM misuse, and coordinated fraud networks.
- NATGRID represents a shift from reactive (after crime) policing to intelligence-led investigation, allowing agencies to act faster and more accurately, while remaining bound by oversight mechanisms.
Conclusion
NATGRID was created to integrate and analyse data in real time for internal security. Its linkage with NPR and use of AI tools like Gandiva have strengthened investigations, but its effectiveness depends on strong oversight, controlled access, and data-protection safeguards to protect citizens’ rights.